Connective Tissue Flashcards
List all the types of connective tissues.
- Embryonic
- mesencymal tissue
- Adult
- Proper connective tissue
- loose
- dense
- adipose
- reticular
- Proper connective tissue
- Special
- cartilege
- bone
- blood
Give some functions of connective tissue.
connect
suspend/give form/divide
insulation
storage
defend
provide nutrition
repair and regenration
Name the pluripotent cell giving rise to all connective tissues

Mesenchyme cells
***State the tissue subunits of the following forms of connective tissue: adipose, proper.
adipose= adipocytes
proper=
ground substance
ground substance= a component of the matrix
made of proteoglycans, Glucosaminoglycans, and glycoproteins

**List the cells associated with each of the CT’s we have studied in this section.
Embryonic CT- Mesenchymal cells
Adipose CT- Adipocytes
List resident in connective tissue.
(Only focus on resident cells)
Types of resident cells:
- Fibroblasts, reticular cells, adipocytes, mesnechymal cells, microphages, mast cells.

List forms of matrix fiber seen in connective tissue.
Collagen-Thicker and paler in slide (white)
- strong but do not stretch
- most numerous fibers in CT and bone
- arranged in bundles
- reason for white color of tendons and sclera
Elastic-Thin and dark staining in slide
- weak and elastic
- Pink in HE (naturally yellow)
- stretches 2 1/2 times its legnth
- aorta, elastic arteries, lungs, vocal cords, dermis, pinna of ear, epiglottis
Reticular- form fine network of reticulum
- can only be stained with silver stain (arfentaffin)
- means they are “argyrophilic”
- form reticular CT, which is the scaffolding for cells in lymph node, spleen and bone marrow

Differentiate in section collagen and elastic fibers.

Define parenchyma and stroma. List some organs where these terms apply.
parenchyma: the tissue of an organ that conducts the specific function of the organ. (functional tissue)
stroma: everything else in organ (blood vessels, nerves, ducts…) (structural tissue)
ex. neurons are parenchyma of brain
hepatocytes are parenchyma of liver
List some organs having reticular CT stroma.
EXPANDABLE ORGANS
spleen
lymph node
liver
lymphatics
CV
Give locations where elastic tissue can be found.
elastic tissue- Aorta and elastic arteries, lungs, vocal cords, dermis, pinna of ear, epiglottis
Describe the production and drainage of tissue fluid at the capillary level.
k
Identify

unilocular adpiose tissue= type of proper connective tissue
Identify

fibroblasts
Identify

mesenchymal cells
Identify

multiocular adipocytes
Identify

dense irregular connective tissue (dermis)
**Dense Connective Tissue
- Irregular or regularly arranged
- Densely packed fibers
- Strong tissue
Identify

dense regular connective tissue
Identify

loose connective tissue
Loose Connective Tissue (Areolar CT)
- Ubiquitous tissue
- Loosely arranged fibers
- Cellular constituents vary with location

Identify

mast cells

Fibroblasts
Type of resident cell
Form collagenous, elastic and reticular fibers of the matrix.
Macrophages
Type of resident cell.
• Resident phagocytic cell of CT (fixed or motile)
Mast Cell
Resident cell of connective tissue
• Release granules and powerful chemical mediators, such as histamine, cytokines, granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), leukotrienes, heparin, and many proteases into the environment.
• These chemical mediators cause the symptoms of allergy.
• Involved in wound healing and defense also

Types of Collagen
Type 1- bone and fibrocartilage
Type 2- cartilage
Type 3- reticular fibers
Type 4- basement membrane

List the Glycosaminoglycans
Glycosaminoglycans
- Hyaluronic acid
- Chondroitin sulfate
- Keratan sulfate
- Dermatan sulfate
- Heparan sulfate

Connective Tissue Fluid
important component of connective tissue
- Solution of nutrients, dissolved gases derived from plasma
- Bathes matrix and cells with nutrients, aids in removing waste
- Fluid dynamics maintain proper balance
- Lymphatics important in fluid movement and prevention of edema

Matrix
component of connective tissue
- fibers
- ground substance
- tissue fluid
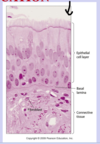
Lable these tissues

*** the deep purple is stratified epithelium

Adpiose Tissue
Adipose tissue= composed of adipocytes (fat cells).
- energy storage
- endocrine function- has regulatory effect on body fat
- unilocular fat cells
- white fat
- energy storage
- insulation
- endocrine (leptin)
- multilocular fat cells
- brown fat
- heat generation


