lymphatic system Flashcards
(25 cards)
Primary and secondary organs
Lymphatic system
Primary organs= generate lymphocytes (B and T)
- bone marrow
- thymus
- cloacal bursa (birds only
Secondary organs= sites of lymphocyte activation/ differentiation
- lymph nodes
- spleen
- mucosal associated lymphoid tissue
Function of lymphatic system
lymphatic system protects the body against pathogenic organisms and help in removal and disposal of cells undergoing natural or induced degenrations
lympatic phagocytosis
List mechanisms of action and cells of lymphatic system
Mechanisms of Action
Phagocytosis
- macrophages
Production of immunologically competent cells
- APC’s
- dendritic
- macrophage
- b-cell
- B and T lymphocytes
Mononuclear phagocytic system
Mononuclear phagocytic system
Fixed macrophages
- sinusoids of liver, spleen, lymph node, bone marrow
Free macrophages
- blood, lung, serous cavities
B and T lymphocytes location

Identify and Explain

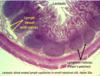
Cloacal Bursa in Birds
=equivilent to bone marrow (produce b cells)
Dark Cortex- densly packed lymphocytes
Lighter Medulla- lymphocytes, macrophages and reticular epithelial cells. Lymphocytes start emigrating through surface epithelium
Identify and expalin

Thymus
- Location: in mediastinum of heart
- Function: maturation of T cells
- Structure
- Cortex- dark stained due to greater # of lymphocytes
- immature T-cells
- positive/good lymphocytes
- macrophages near medulla eliminate dead t cells
- Medulla- contains epithelial reticular cells
- mature T-cells
- negative/bad lymphocytes
- thymic corpuscules and hassalls corpuscles
- Cortex- dark stained due to greater # of lymphocytes

Identify

Thymic/Hassals corpuscle in Medulla of Thymus
Thymic Involution
Thymic involution= inacivation of thymus
- active in immature animals. involution after sexual maturity
- gradual depletion of lymphocytes
- replacement by adipocytes
Lymph Nodes
Lymph Nodes= secondary lymphatic organ
- Function: filters antigens from lymph before returning to blood stream
- Structure
- Capsule
- Cortex
- primary and secondary follicles (b-cells)
- paracortical tissue (t-cells)
- subcapsular sinus
- Medulla
- medullary cords
- medullary sinus
*
Diagram of Lymph Node

Identify


Identify

Medulla
- Sinuses
- Cords
Identify

Lymph node
When stimulated my antigen, primary follicles become secondary

Identify
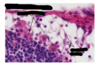

Trace flow of blood and lymph
- blood into node via afferent lymphatic vessel
- through postcappilary venule
- out through efferent lymphatic vessel
- to thoratic duct and heart

Spleen
Spleen= secondary lymphatic organ
- Function: filters blood
- recovers and stores iron
- removes antigens from blood
- mounts immune response against blood pathogens
- stored RBC’s and platelets
- Structure:
- capsule
- trabeculae
- central artery or vein
- trabeculae
- capsule
Identify and explain

Sleen
- outer capsule= dense CT with smooth muscle
- gives rise to…
- trabeculae= collegen, elastic, and smooth muscle
- each trabeculae contains central artery or vein

Identify

Spleen

Identify and Explain

Pulp in Spleen
White pulp
- Germinal center and Follicular area is B-cell ruch
- Central arteriole surrounded by…
- PALS is where T-lymphocytes are
- B-cells too!
Reb pulp
- rbc rich

Mucosal Associated Lumphoid Tissue
Mucosal Associated Lumphoid Tissue
- Gut associated lymphoid tissue
- Broncial associated lymphoid tissue
- Tonsil
- Ocular
- Urogenital
- Mammary
Stomiach


Identify

Small intestine
Peyers patches= aggregated lymphatic nodules in t he lamina propria and submucosa of ileum (B-cells migrate here from bone marrow sometimes)
- M-cells: specialized epithelial cells that take somehting from gi tract and put it on other cells in peyer’s patch
- L-lymphocytes
- Mac-macrophages