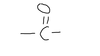Chapter 3.1: Carbon: The Framework of Biological Molecules Flashcards
(56 cards)
Define hydrocarbons
molecules consisting only of carbon and hydrogen
What are molecules consisting only of carbon and hydrogen?
hydrocarbons
Why do hydrocarbons make good fuels?
Make good fuels since C-H bond stores a lot of energy
Define functional group
a molecular group attached to a hydrocarbon that confers chemical properties or reactivities
What is a molecular group attached to a hydrocarbon that confers chemical properties or reactivities?
functional group
What type of biological molecules are hydroxyl groups found in?
carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids
What type of biological molecules are carbonyl groups found in?
carbohydrates and nucleic acids
What type of biological molecules are carboxyl groups found in?
proteins, lipids
What type of biological molecules are amino groups found in?
proteins, nucleic acids
What type of biological molecules are sulfhydryl groups found in?
proteins
What type of biological molecules are nucleic acids groups found in?
phosphate
What type of biological molecules are methyl groups found in?
proteins
Define isomers
one of a group of molecules identical in atomic composition, but differing in structural arrangement
What is one of a group of molecules identical in atomic composition, but differing in structural arrangement?
isomer
Define structural isomers
isomers with differences in the actual structure of their carbon skeleton
What are isomers with differences in the actual structure of their carbon skeleton?
structural isomers
Define stereoisomers
isomers that have the same carbon skeleton, but differ in how the groups attached to this skeleton are arranged in space
What are isomers that have the same carbon skeleton, but differ in how the groups attached to this skeleton are arranged in space?
stereoisomers
Define enantiomer
stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other
What are stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other?
enantiomer
Define chiral molecule
a molecule that has mirror-image versions
What is a molecule that has mirror-image versions?
chiral molecule
Define polymer
a molecule composed of many similar or identical molecular subunits
What is a molecule composed of many similar or identical molecular subunits?
polymer