Week 2: Esophageal motility Flashcards
(51 cards)
What is the main function of the esophagus?
transit of food to the stomach
Trick is
- dont choke
- dont aspirate food into the trachea
- don’t aspirate air into the gut
Describe esophageal manometry
UES - upper esophageal sphincter
LES - lower esophageal sphincter
At the UES you are above atmospheric pressure
as you go lower the pressure decreases but at the diaphragm above atmo pressure

esophageal manometry during a swallow

initially open and then snap shut
Pressure wave going down but the bottom is open and gravity can take bolus down before even the pressure wave gets there depending on the viscosity of what is being swallowed, this is why liquids can be swallowed faster than solids
stomach relaxes to prepare for the bolus to enter

Functions of the esophagus
4 listed

Reflexes involved in the initiation of swallowing
2 listed

Describe the oral or voluntary phase of swallowing
Moves food into the pharynx
Describe the pharyngeal phase of swallowing
- Larynx moves forward, epiglottis prevents entry into trachea and helps open UES
- soft palate prevents reflux into nasopharynx, provides passage into pharynx
Pharyngeal phase of swallowing
involuntarily and neuronally mediated through Vagal efferents
brain also turns of respiration which picks back up as soon as the UES closes

Describe UES regulation
- tonically contracted between swallows
- relaxes during swallows

Muscle types in the esophagus

Describe the muscles and nerves of the pharynx and upper esophagus

What drives peristalsis
entirely done by neurons contained in the wall of the gut in between the longitudinal and circular muscle fibers
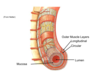
IDentify structure and components


Locations of the principal networks of enteric neurons
- Myenteric plexus
- Submucous plexus

Identify structures and components


Describe peristalsis mechanism
You get a peristaltic contraction behind the bolus and a relaxation in front of the bolus which is in tune with the size, shape and chemistry of the bolus without any input from the brain through the combination of sensory neurons and efferent neurons of the enteric nervous system

Describe the peristaltic reflex
sensory neurons sense the bolus and interneurons to coordinate contraction and relaxation of motor neurons to move the bolus as needed

Regulation of GI smooth muscle peristalsis
bolus hits villi activating sensory neurons and data is transmitted through the interneurons to get a coordinated contraction and relaxation behind and in front of the bolus respectively

Muscles and nerves of the pharynx and upper esophagus

Peristalsis transmissions speeds

M2 receptor second messenger
inhibition of adenylate cyclase
Activation of K+ channels
M2 receptor targets
Heart
M2 receptor effects
Inhibition
M3 receptor second messenger
Stimulation of phospholipase C











