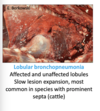
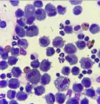
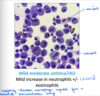
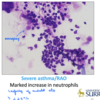
STEEPLECHASE - RESPIRATORY Flashcards

Cow lungs - have distinct lobules (also in pigs and humans)

Horse lungs - have intermediate lobulation (also in small ruminants)

Cat lungs - absent lobules in carnivores

Feline pulmonary aa. - have very thick tunica muscularis

Rodent larger pulmonary veins - have cardiac muscle

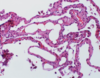
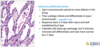
Normal bronchioles
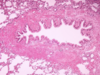
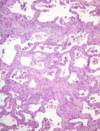
Smooth muscle hypertrophy - inflamed bronchioles

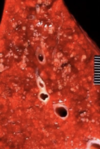
Carbon in alveoli

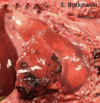
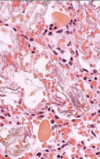
Choanal atresia - camelid

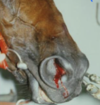
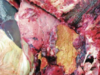
Epistaxis - nosebleed

Waldeyer’s ring - lymphoid tissues circling the oro and nasopharynx

Idiopathic lymphoplasmacytic rhinitis


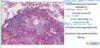
Cow - nasal granuloma (due to chronic allergic (atopic) rhinitis)
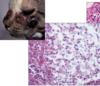
Granulomatous rhinitis - due to cryptococcus - forms thick capsule with narrow-based budding


Granulomatous rhinitis - caused by Rhinosporidium seeberi (forms polyps with huge endosporulating sporangia - endspore w/ capsule)

Sinusitis

Sinusitis
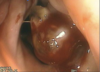
Progressive ethmoid haematoma endoscopy - reddening = haemorrhage

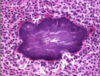
Paranasal sinus cysts in foals and young horses -> face + teeth distortion



Horse - guttural pouch

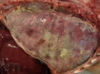
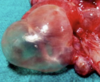
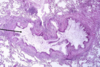
Guttural pouch tympany (air build-up)

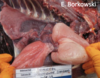
Pig - diverticulum dorsal to oesophagus (pharnyx)
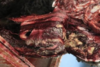
Balling gun injury pharyngeal lesion in ruminants

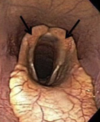
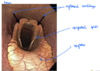
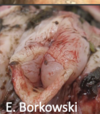
Laryngeal oedema

Laryngitis

Laryngeal paralysis in horses - almost always affects left side

Laryngeal paralysis in horses - denervation atrophy of cricoarytenoid muscles, cartilage sags into larynx
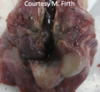
Laryngeal chondritis
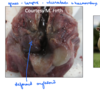

Trachea


Parasites in trachea

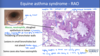
Stenotic nares - Brachycephalic airway syndrome
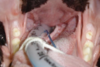
Elongated soft palate - Brachycephalic airway syndrome
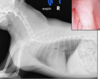
Tracheal hypoplasia - Brachycephalic airway sundrome

Tracheal hypoplasia - Brachycephalic airway syndrome

Tracheal collapse

Tracheal collapse

Tracheal oedema + haemorrhage syndrome (partial obstruction by haemorrhage and oedema or dorsal trachea) AKA ‘Honker syndrome’
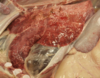
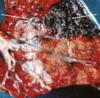
Pneumothorax - lungs very collapsed


Hydrothorax
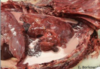
Chylothorax

Fibrinous pleuritis

Pyothorax - pleuritis