Parasites of the Cardiovascular System Flashcards
Canine and feline nematodes
Heartworm - Dirofilaria immitis
Size and lifespan of adult heartworm - Dirofilaria immitis (3)
- Females: ~25 cm long
- Males: ~15 cm long
- Live up to 7.5 years in dog
Microfilaria (3)
•Larval stage of Dirofilaria immitis - infectiuous stage, circulate canine blood
•~ 300 µm long
µm long
•Dogs can be patent for 5 years
Wolbachia endosymbiont (5)
- Intracellular bacterium, found in many filarial worms
- Mutualistic or symbiotic relationship
- Harboured by all stages of Dirofilaria immitis
- Required for fertility, survival & development of D. immitis
- Role in pathogenesis unclear - offers potential therapeutic target of ABs
Life cycle of Dirofilaria immitis (8)
- 1). Mosquito bites (vectorborne worm infection) infected dog and ignests larvae (L1).
- 2). Within the mosquito - larvae mature from L1 into L3.
- 3). Infected mosquito bites a healthy dog and transmits larvae (L3) to the dog’s subcutaneous tissues.
- 4). Larvae mature from L3 into L4 and infest the muscles and blood vessels.
- 5). Larvae mature into adult worms and infest the pulmonary artery and right heart.
- 6). Adult worms ate and produce larvae (L1) that are released into the blood (microfilaria)
- Dog = primary definitive host - maturation and reproduction
- Mosquito = intermediate host - where development occurs + vector

Reservoirs of Dirofilaria immitis (2)
- Wild canids - coyotes in USA
- Red foxes in Europe
PPP (pre-patent period) of Dirofilaria immitis
Greater than or equal to 6 months, time dog is infected to seeing microfilaria in bloodstream
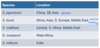
What are the intermediate hosts of Dirofilaria immitis? - Species (3)

Geographical distribution of Dirofilaria immitis

What are the drivers for the spread of Dirofilaria immitis? (4)
- Global warming - climate change - warmer = inc in mosquito vectors (25-27 degrees Celcius), mosquitoes lay eggs in water bodies
- Movement of pets - cats and dogs - bring infection to non-endemic areas
- Biting behaviour of mosquitoes (exophilic to endophilic) - more likely to live indoors rather than outdoors
- Urbanisation of vector - where higher dog density = inc in transmission
What does the pathogenesis of Dirofilaria immitis depend on? (7)

Pathogenesis of Dirofilaria immitis in pulmonary arteries (5)
Pathogensis of Dirofilaria immitis - long-term sequelae (2)

What is the pathogenesis of severe cases with Dirofilaria immitis? (2)

Clinical signs - dogs, lighter infections (2)
- Asymptomatic
- Sustained exercise