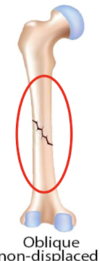
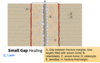
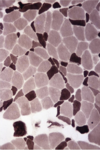
STEEPLECHASE - MUSCULOSKELETAL Flashcards

Brachygnathia

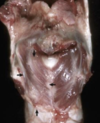
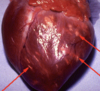
Complete palatoschisis

Prognathia

Pectus excavatum

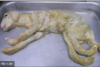
Kyphosis

Scoliosis

Block vertebrae

Butterfly/hemivertebrae

Lordosis

Manatee - confined in small aquarium, developed severe scoliosis (lateral deviation)

Spina bifida in dog

Mircomelia

Peromelia

Notomelia

Hemimelia

Amelia

Polydactyly
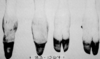
Syndactyly

Ectrodactyly

Dactylomegaly

Adactyly



Osteogenesis impefecta - lateral deviation in joints, collagen I mutation

Osteogenesis imperfecta

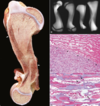


Osteopetrosis
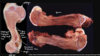


Congenital cortical hyperostosis


Congenital hyperostosis


‘Lion jaw’ craniomandibular osteopathy

Craniomandibular osteopathy ‘Lion jaw’

Chondrodysplasia

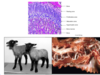


Disproportionate dwarfism - Grey alpine calf w/ Ellis van Creveld syndrome (chondrodysplasia)

Manganese deficiency, not congenital, acquired/nutritional deficiency (chondrodysplasia)

Texel lamb - disproportionate dwarfism, shortened limbs and wide base (chondrodysplasia)

(Chondrodysplasia)
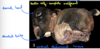

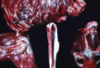
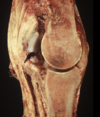
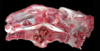
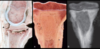
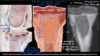
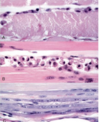
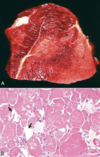
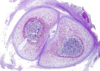
Osteochondrosis

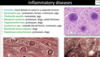
Osteochondrosis latens - well-demarcated area of necrosis of cartilage

Osteochondrosis manifesta - arrows = associated with areas of foci of necrosis - areas of retained cartilage = hypertrophic chondrocytes
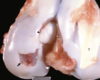
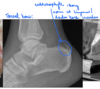
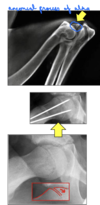
Osteochondrosis dissecans - arrow pointing to ‘joint mice’

Vertebral myelopathy


Dynamic vertebral myelopathy - flexion



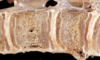
Osteoporosis


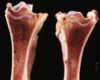
Rickets and osteomalacia
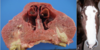


Head brachygnathia superior

Dental dysplasia, with small pink-grey barely erupted teeth in a two-week old Holstein calf with osteogenesis imperfecta (right), left = normal calf
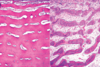


Osteopetrosis

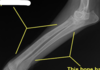
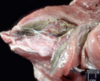
Cervical vertebral myelopathy “Wobbler syndrome”
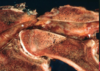
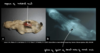
Cervical vertebral malformation-malarticulation in a horse. Flexion of the cervical vertebrae results in stenosis of the spinal canal (asterisk). Flaring of caudal epiphysis (arrowhead), can also contribute to spinal compression

Cervical vertebral malformation-matriculation in a horse, Osteochondrosis of the articular facet joints can contribute to the intervertebral joint instability
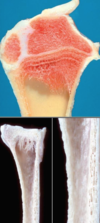
Osteoporosis

Osteoporosis

Osteoporosis

Osteoporosis

Costochondral junction, rickets
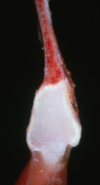
Pig, rib, dysplasia
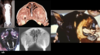
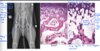
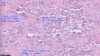
Fibrous osteodystrophy, “Rubber jaw”

Fibrous osteodystrophy
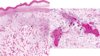
Fibrous osteodystrophy

Fibrous osteodystrophy








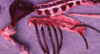
Congenital porphyria

Porphyria

Erythropoietic porphyria
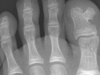
Exostosis

Enostosis
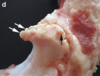
Osteophyte