Reproductive - Physiology Flashcards
1
Q
Estrogen
- Source
- Functions
A
- Source
- Ovary (17β-estradiol), placenta (estriol), adipose tissue (estrone via aromatization)
- Potency: estradiol > estrone > estriol
- Functions
- Development of genitalia and breast, female fat distribution
- Growth of follicle, endometrial proliferation, increased myometrial excitability
- Upregulation of estrogen, LH, and progesterone receptors
- Feedback inhibition of FSH and LH, then LH surge
- Stimulation of prolactin secretion
- Increased transport proteins, SHBG; increased HDL; decreased LDL
- Pregnancy:
- 50-fold increase in estradiol and estrone
- 1000-fold increase in estriol (indicator of fetal well-being)
- Estrogen receptors expressed in the cytoplasm
- Translocate to the nucleus when bound by ligand

2
Q
Progesterone
- Source
- Functions
- Decreased vs. increased progesterone
A
- Source
- Corpus luteum, placenta, adrenal cortex, testes
- Functions
- Stimulation of endometrial glandular secretions and spiral artery development
- Maintenance of pregnancy
- Decreased myometrial excitability
- Production of thick cervical mucus, which inhibits sperm entry into the uterus
- Increased body temperature
- Inhibition of gonadotropins (LH, FSH)
- Uterine smooth muscle relaxation (preventing contractions)
- Decreased estrogen receptor expressivity
- Prevents endometrial hyperplasia
- Decreased vs. increased progesterone
- Fall in progesterone after delivery disinhibits prolactin –> lactation.
- Progesterone is _pro-gest_ation.
- Prolactin is _pro-lact_ation.
- Increased progesterone is indicative of ovulation.
- Fall in progesterone after delivery disinhibits prolactin –> lactation.
3
Q
Tanner stages of sexual development
- A Tanner stage
- I
- II
- III
- IV
- V
A
- A Tanner stage is assigned independently to genitalia, pubic hair, and breast
- e.g., a person can have Tanner stage 2 genitalia, Tanner stage 3 pubic hair
- I
- Childhood (prepubertal)
- II
- Pubic hair appears (pubarche)
- Breast buds form (thelarche)
- III
- Pubic hair darkens and becomes curly
- Penis size/length increase
- Breasts enlarge
- IV
- Penis width increases, darker scrotal skin, development of glans
- Raised areolae
- V
- Adult
- Areolae are no longer raised
4
Q
Menstrual cycle
- Phases
- Follicular
- Luteal
- Menstruation
- Follicular growth
- Substances
- Estrogen
- Progesterone
A
- Phases
- Follicular phase can vary in length.
- Luteal phase is usually a constant 14 days.
- Ovulation day + 14 days = menstruation.
- Follicular growth is fastest during 2nd week of proliferative phase.
- Substances
- Estrogen stimulates endometrial proliferation.
- Increased estrogen –> LH surge –> ovulation –> progesterone (from corpus luteum) –> progesterone levels fall –> menstruation (via apoptosis of endometrial cells)
- Progesterone maintains endometrium to support implantation.
- Decreased progesterone –> decreased fertility.
- Estrogen stimulates endometrial proliferation.

5
Q
Menstrual cycle
- Oligomenorrhea
- Polymenorrhea
- Metrorrhagia
- Menorrhagia
- Menometrorrhagia
A
- Oligomenorrhea
- > 35-day cycle.
- Polymenorrhea
- < 21-day cycle.
- Metrorrhagia
- Intermenstrual bleeding
- Frequent but irregular menstruation.
- Menorrhagia
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- > 80 mL blood loss or > 7 days of menses.
- Menometrorrhagia
- __Heavy, irregular menstruation at irregular intervals.

6
Q
Oogenesis
- 1° oocytes
- Meiosis I
- Meiosis II
- 2° oocyte
A
- 1° oocytes begin meiosis I during fetal life and complete meiosis I just prior to ovulation.
- Meiosis I is arrested in prOphase I for years until Ovulation (1° oocytes).
- Meiosis II is arrested in metaphase II until fertilization (2° oocytes).
- An egg met a sperm.
- If fertilization does not occur within 1 day, the 2° oocyte degenerates.

7
Q
Ovulation
- Estrogen
- Temperature
- Mittelschmerz
A
- Estrogen
- Increased estrogen, increased GnRH receptors on anterior pituitary.
- Estrogen surge then stimulates LH release –> ovulation (rupture of follicle).
- Temperature
- Increased temperature (progesterone induced).
-
Mittelschmerz
- Refers to transient mid-cycle ovulatory pain
- Classically associated with peritoneal irritation
- e.g., follicular swelling/rupture, fallopian tube contraction
- Can mimic appendicitis.
8
Q
Pregnancy
- Fertilization
- Implantation
- Syncytiotrophoblasts
A
- Fertilization
- Most commonly occurs in upper end of fallopian tube (the ampulla).
- Occurs within 1 day of ovulation.
- Implantation within the wall of the uterus occurs 6 days after fertilization.
- Syncytiotrophoblasts secrete hCG, which is detectable in blood 1 week after conception and on home test in urine 2 weeks after conception.
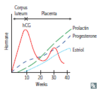
9
Q
Lactation
- After labor
- Progesterone and estrogen
- Suckling
- Prolactin
- Oxytocin
A
- After labor
- The decrease in progesterone and estrogen disinhibits lactation.
- Suckling is required to maintain milk production, since increased nerve stimulation increases oxytocin and prolactin.
- Prolactin
- Induces and maintains lactation
- Decreases reproductive function.
- Oxytocin
- Assists in milk letdown
- Also promotes uterine contractions.
10
Q
Lactation
- Breastmilk
- Breastfeeding
A
- Breastmilk
- The ideal nutrition for infants < 6 months old.
- Contains maternal immunoglobulins (conferring passive immunity; mostly IgA), macrophages, and lymphocytes.
- Reduces infant infections and is associated with decreased risk for the child to develop asthma, allergies, diabetes mellitus, and obesity.
- Exclusively breastfed infants require vitamin D supplementation.
- Breastfeeding
- Decreases maternal risk of breast and ovarian cancer
- Facilitates mother-child bonding.
11
Q
hCG
- Source
- Functions
- Subunits
- Pathology
A
- Source
- Syncytiotrophoblast of placenta.
- Functions
- Maintains the corpus luteum (and thus progesterone) for the 1st trimester by acting like LH (otherwise no luteal cell stimulation, and abortion results).
- In the 2nd and 3rd trimesters, the placenta synthesizes its own estriol and progesterone and the corpus luteum degenerates.
- Used to detect pregnancy because it appears early in the urine.
- Maintains the corpus luteum (and thus progesterone) for the 1st trimester by acting like LH (otherwise no luteal cell stimulation, and abortion results).
- Subunits
- α subunit structurally identical to α subunits of LH, FSH, and TSH.
- β subunit is unique (pregnancy tests detect β subunit).
- Pathology
- hCG is increased in multiple gestations and pathologic states (e.g., hydatidiform mole, choriocarcinoma).
12
Q
Menopause
- Definition
- Age
- Menopause causes…
A
- Definition
- Decreased estrogen production due to age-linked decline in number of ovarian follicles.
- Usually preceded by 4–5 years of abnormal menstrual cycles.
- Age
- Average age at onset is 51 years (earlier in smokers).
- Menopause before age 40 can indicate premature ovarian failure.
- Menopause causes HAVOCS
- Hot flashes
- Atrophy of the Vagina
- Osteoporosis
- Coronary artery disease
- Sleep disturbances
13
Q
Menopause
- Hormones
- Estrogen
- FSH
- Hormonal changes
A
- Hormones
- Source of estrogen (estrone) after menopause becomes peripheral conversion of androgens, increased androgens –> hirsutism.
- Really increased FSH is specific for menopause (loss of negative feedback on FSH due to decreased estrogen).
- Hormonal changes
- Decreased estrogen
- Really increased FSH
- Increased LH (no surge)
- Increased GnRH.
14
Q
Spermatogenesis (572)
- Timeline
- Location
- Produces…
A
- Timeline
- Spermatogenesis begins at puberty with spermatogonia.
- “Gonium” is going to be a sperm
- Full development takes 2 months.
- Spermatogenesis begins at puberty with spermatogonia.
- Location
- Occurs in seminiferous tubules.
- Produces…
- Spermatids that undergo spermiogenesis (loss of cytoplasmic contents, gain of acrosomal cap) to form mature spermatozoon.
- “Zoon” is “Zooming” to egg
- Spermatids that undergo spermiogenesis (loss of cytoplasmic contents, gain of acrosomal cap) to form mature spermatozoon.

15
Q
Androgens
- Examples
- Source
A
- Examples
- Testosterone, dihydrotestosterone (DHT), androstenedione.
- Source
- DHT and testosterone: testis
- AnDrostenedione: ADrenal
- Potency: DHT > testosterone > androstenedione.


