Nervous 3 Flashcards
(153 cards)
What kind of fibres pass through the corpus collosum?
Commissure fibres
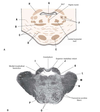
What are the 4 parts of the corpus collosum?
Rostrum
Genu
Body
Splenium
What is A?

Body
What is B?

Genu
What is C?

Rostrum
What is D?

Spleenium
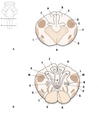
What is the septum pellucidum?
Thin sheet that lies in the mied sagittal plane and seperates the anterior horns of the two lateral ventricles

What is the septum pellicuidum inferior to?
Corpus collosum

What is inferior to the septum pellicudum?
Fornix

What is the fornix?
Bundle of fibres that linkes the hippocampus with the mammilary bodies
What is the connection between the lateral ventricles and III ventricle?
Interventricular foramen
What is E?

Septum pellicidum
What is F?

Fornix
What are the black spaces at each side?

Lateral ventricles
What is the bulbous projection on the floor of the lateral ventricle?
Caudate nucleus

Caudate nucleus is one of what?
The basal nuclei
What is the thalamus?
Sensory relay area made up of smaller masses of gray matter nuclei, each with a different function
What of the general sensory information from the body relays to what nucleus?
Ventro-postero-lateral (VPL) nucleus of the thalamus
What are the functions of the hypothalamus? (x6)
Releasing hormone
Regulating temperature
Regulating hunger
Managing sexual behaviour
Regulating emotional response
Regulating thirst
A fold of what immediately overlies the pituitary gland?
Dura mater (called Diaphragma sellae)
What fold overlies the pituitary gland?
Diaphragma sellae
What gland is immediately posterior to the thalamus?
Pineal gland
Where are the colliculi in relation to the pineal gland?
Inferior
The colliculi are a component of what?
Midbrain