Head and Neck 7 Flashcards
How many fossa is the floor of the skull divided into?
3
What do grooves and depressions in the skull indicate?
Where, in life, blood vessels and other structures ran
Which bone forms the posterior boundary of the anterior cranial fossas?
Sphenoid
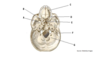
What is A?

Frontal bone
What is B?

Olfactory foramina
What is C?

Optic canal
What is D?

Foramen rotundum
What is E?

Foramen ovale
What is F?

Foramen spinosum
What is G?

Foramen lacerum
What is H?

Internal acoustic meatus
What is I?

Jugular foramen
What is J?

Hypoglossal canal
What is K?

Foramen magnum
What is L?

Occipital bone
What is M?

Parietal bone
What is N?

Posterior cranial fossa
What is O?

Temporal bone (petrous part)
What is P?

Middle cranial fossa
What is Q?

Hypophyseal fossa of sella turcica
What is R?

Greater wing of sphenoid
What is S?

Lesser wing of sphenoid
What is T?

Anterior cranial fossa
What is U?
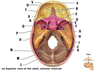
Crista galli of ethmoid bone