Histology - Respiration Images Flashcards

Hyaline cartilage and trachealis mm - patency support

Kulchitsky cells - Amine Precursor Uptake & Decarboxylation (AUPD) - neuroendocrine cells

Smooth muscle, no cartilage, and aveoli. Is a branchiole.

Visceral pleura - Mesothelium (M, simple squamous epithelium) and thin layer of loose connective tissue

Brounchus Associated Lymphatic TIssue - BALT

Phagocytotic cells - dust cells - TEM, c= capillar, e = RBC, m = macrophage

Emphysema - breakdown of interalveolar septum, ‘air trapping’ in large spaces, reduced air exchange.

Pseudostratified Epi, seromucous glands, hyaline cart. NO aveoli, so much be Trachea or Main Bronchus

Congenital Hiatal (diaphragmatic) Hernia - associated with Potter’s Sequence (Oligohydramnios)

Fibroblast - Synthesizes CT ECM

Clara cells (CC, Cl) - dome shaped. Increase as descend branchiolar tree, secrete surfactant, lysozyme, anti-inflammatory ptoreins

Cuboidal epithelial cells - account for 60% of alveolar lining cells - line 5% of alveolar lumen

Lung small cell carcinoma
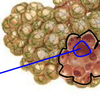
Opening of alveolar duct (into alveolar sac)

Bronchioles (incl. terminal bronchioles) - Simple cuboidal epithelium, NO goblet cells!

Alveolarstem cells - give rise to type I & II cells

Trachea


Thin Interalveolar Septum and RBC

Smooth muscle in branchioles, incl. terminal branchioles.

normal interalveolar septum

Smooth muscle in 2’ and 3’ bronchi

Endothelial cell injury - sepsis

Pulmonary hypoplasia (left lung) - associated with Congenital Hiatal (diaphragmatic) Hernia
















