Biology 11: Muscloskeletal System Flashcards
what are the three subtypes of muscle
skeletal
smooth
cardiac
skeletal muscle
muscle responsible for voluntary movement - somatic
striped/striated bc alternating actin and myosin sarcomeres
multinucleated bc individual muscle cells fuse in long rods
nuclei are found at cell periphery
red fibers / slow-twitch fibers
fibers in skeletal muscle
have high myoglobin content and derive most of their energy aerobically
have lots of mitochondria to carry out oxidative phosphorylation
numerous in muscles that contract slowly and can sustain activity
white fibers / fast-twitch fibers
fibers in skeletal muscle
contain less myoglobin, less iron, lighter color
numerous in muscles that contract rapidly but fatigue quickly
myoglobin
an oxygen carrier that uses iron in a heme group to bind O2, imparting a red color
smooth muscle
muscle responsible to involuntary action - autonomic
cells have a single nucleus in the center
contain actin and myosin in fibers not well organized - not striated
can do tonic contraction - constant low-level contraction
myogenic activity - responds directly to stretch and other stimuli
myogenic activity
the ability of muscle to contract without nervous system input
present in smooth and cardiac muscle
cardiac muscle
muscle found in the heart - involuntary - autonomic
appears striated
primarily uninucleated but sometimes w two nuclei
can define and maintain rhythm through myogenic activity
intercalated discs
connect cardiac muscle cells and contain gap junctions
gap junctions - connections between the cytoplasm of adjacent cells, allowing for the flow of ions directly between cells
allows for rapid and coordinated muscle cell depolarization and efficient contraction
allows progressive depolarization to spread via ion flow across
pathway of electrical depolarization through the heart
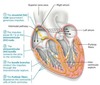
sinoatrial node –> atrioventricular node –> bundle of His –> Purkinje fibers

what provides parasympathetic outflow to heart?
vagus nerve
what neural innervations increases heart rate?
norepinephrine from sympathetic neurons or epinephrine from adrenal medulla binds to adrenergic receptors in heart
increases heart rate and greater contractility
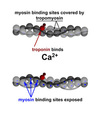
which filament in a sarcomere is composed of actin?
thin or thick
thin
thin filaments also consist of troponin and tropomyosin to regulate interaction between the two filaments

which filament in a sarcomere is composed of myosin?
thin or thick
thick

titin
protein in sarcomeres that acts as a spring and anchors the actin and myosin filaments together
prevents excessive stretching of muscle

M-line
line that runs down the center of the sarcomere, through the middle of the myosin filaments

middle of the myosin filaments
Z-line
defines the boundaries of each sarcomere

z is the end of the alphabet, the end of the sarcomere
I-band
the region containing exclusively thin filaments (actin)

I is a thin layer, thin filaments only
H-zone
region containing exclusively thin filaments (myosin)

H is a thick letter, thick filaments only
A-band
region that contains the thick filaments in their entirety, including any overlap with thin filaments

all of the thick filament whether overlapping or not
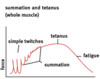
how do the H-zone, I-band, Z-lines, M-lines, A-lines of a sarcomere change during contraction?

H zone, I band becomes smaller
distance between Z lines and M lines all become smaller
A band’s size remains constant

myofibrils
end-to-end attachment of sarcomeres
surrounded by sarcoplasmic reticulum

sarcoplasmic reticulum
a modified endoplasmic reticulum that contains high concentrations of Ca2+ ions
sarcoplasm
modified cytoplasm located just outside sarcoplasmic reticulum
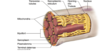
sarcolemma
cell membrane of a myocyte
capable of propagating an action potential and can distribute the action potential to all sarcomeres through T-tubules

transverse tubules / T tubules
tubes oriented perpendicularly to myofibrils
propagates action potentials to all sarcomeres in a muscle