Biochemistry 5: Lipid Structure and Function Flashcards
lipids
biomolecules that are insoluble in water and soluble in nonpolar organic solvents
phospholipids
polar head = phosphate and alcohol
joined to fatty acid tail with phosphodiester linkages

glycerophospholipids
phospholipids with a glycerol backbone
bonded by ester linkages to 2 fatty acids
bonded by a phosphate linkage to a polar head group

phosphatidylcholine
a glycerophospholipid with a choline head group

phosphatidylethanolamine
a glycerophospholipid with an ethanolamine head group

sphingolipids
lipids with a sphingosine or sphingoid backbone
linked to fatty acids and a polar head group
some can be phospholipids because of their phosphodiester linkage
others can be glycolipids because of their glycosidic linkage

ceramides
sphingolipids with a single H as it’s head group

sphingomyelin
sphingolipids with phosphatidylcholine or phosphatidylethanolamine head have a phosphodiester bond, so are sphingophospholipids
have no net charge
highly present in membranes of cells that produce myelin

glycosphingolipids
sphingolipids with head groups of sugars bonded with glycosidic linkages

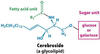
cerebrosides
glycosphingolipids attached to a single sugar moiety
globosides
glycosphingolipids attached to two or more sugar moieties
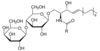
gangliosides
sphingolipids with polar head groups of oligosaccharides with one or more N-acetylneuraminic acid (NANA/sialic acid)
have glycosidic linkages so they are glycosphingolipids

waxes
esters of long-chain alcohols used as protection against evaporation and parasites in plants and animals
terpenes
odiferous steroid precursors made from isoprene subunits
protective compounds made by plants and insects
a single compound has two isoprene units

sesquiterpenes
have 3 isoprenes
terpenoids
derived from terpenes that underwent oxygenation or rearrangement and addition have similar odiferous characteristics
steroids
compounds composed of 4 cycloalkane fused rings
3 hexane and 1 pentane ring

steroid hormones
steroids with high affinity receptors
work at low concentrations affect gene expression and metabolism
cholesterol
steroid important in membrane fluidity and stability
serves as a precursor to many other molecules
prostaglandins
autocrine and paracrine signaling molecules that regulate cAMP levels
affect smooth muscle contractions, body temp, sleep-wake cycle, fever, pain, inflammation
inhibited by NSAID derived from arachidonic acid - 20 carbons, one 5-carbon ring produced by almost all cells
fat-soluble vitamins
vitamins A, D, E and K
vitamin A (carotene)
vitamin metabolized to retinal, stored as retinol, for vision
oxidized to retinoic acid for gene expression during epithelial development
vitamin D (cholecalciferol)
vitamin consumed or made from UV
metabolised to calcitrol in kidneys and liver and regulates calcium and phosphorus homeostasis (increases calcium and phosphate absorption in intestine)
promotes bone formation
vitamin E (tocopherols)
vitamin that acts as an antioxidant
aromatic rings with isoprenoid sidechain
vitamin K (phylloquinone and (menaquinone)
vitamin important for formation of prothrombin, a clotting factor
also performs post-translational modifications to create Ca2+ binding sites
why are lipids so great for energy storage?
carbons in the fatty acid are more reduced
hydrophobic nature prevents water weight, so the molecules are lighter
also good for insulation
triacylglycerol
lipids with one glycerol attached to three fatty acids with an ester bond
travel between liver and adipose tissue

free fatty acids
unesterified fatty acids with free carboxylate group
traveling in bloodstream noncovalently bound to albumin
form salts called soaps

saponification
the ester hydrolysis of triacylglycerol using a strong base like NaOH or KOH
soap can be a surfactant


isoprene


