Behavioral Sciences 1: Biology and Behavior Flashcards
neuropsychology
the study of the connection between the nervous system and behavior
often focuses on the functions of various brain regions
Franz Gall
early psychologist
theorized that behavior, intellect, personality may be linked to brain anatomy - phrenology
false thought that development –> brain growth –> physical bulge
Pierre Flourens
studied the functions of the major sections of the brain through extirpation/ablation on rabbits and pigeons (removing parts and watching what happens)
learned that specific parts of the brain had specific functions
William James
father of American psychology
studied how the mind functioned in adapting to environment
helped form functionalism - how mental processes help individuals adapt to environments
John Dewey
helped form functionalism - how mental processes help individuals adapt to environments
studied the organism as a whole and not with discrete parts as it reacts to environment
Paul Broca
demonstrated that specific functional impairments can be linked to specific brain lesions
Hermann von Helmholtz
first person to measure the speed of a nerve impulse
transitioned psych into a natural science
Sir Charles Sherrington
first inferred the existence of synapses
organization of nervous system

parasympathetic nervous system effects
- acetylcholine
- constricts pupil
- stimulates saliva
- slow heartbeat
- stimulates peristalsis
- stimulates bile release
- contracts bladder
sympathetic nervous system effects
- adrenaline/noradrenaline
- dilates pupil
- inhibits saliva
- relaxes bronchi
- accelerates heartbeat
- inhibits peristalsis
- stimulates glucose production and release
- inhibits bladder contraction
- stimulates orgasm
three subdivisions of the brain
hindbrain, midbrain, forebrain
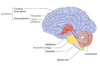
hindbrain
consists of the cerebellum, medulla oblongata, reticular formation
more primitive structure, has vital functions for survival
also called rhombencephalon divides during development to form myelencephalon (medulla) and metencephalon (pons and cerebellum)
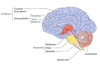
medulla oblongata

lower brain structure
breathing
heart rate
blood pressure
pons

lies above the medulla
sensory/motor pathways between cortex and medulla
cerebellum
above pons
maintain posture and balance
coordinates body movements

reticular formation
the portion that passes through medulla and pons and stops near midbrain
functions in arousal, alertness, attention

brainstem
consists of the midbrain and hindbrain
midbrain
mesencephalon
region of brain that receives sensory/motor information from the rest of the body
associated with involuntary sensorimotor reflex responses
have prominent nuclei

superior colliculus
nuclei in the midbrain that receives visual sensory input
inferior colliculus
nuclei in the midbrain that receives auditory input
has a role in reflexive reactions to loud noises
forebrain
proencephalon
divides to form telencephalon (cerebral cortex, basal ganglia, limbic) and diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, posterior pituitary, pineal glands)
associated with complex perpetual, cognitive, behavioral processes
greatest influence over human behavior, not needed for survival
number of pain receptors in the brain
none!
thalamus

relay center for all sensory input for smell, transmits to cerebral cortex
hypothalamus

serves homeostatic functions
key in emotion during high arousal, aggression, sex
helps control autonomic and endocrine functions through hypophyseal portal system to anterior pituitary
lateral hypothalamus (LH)
hunger center; detects when body needs more food or fluids – start eating
when destroyed, one lacks hunger
ventromedial hypothalamus (VMH)
satiety center – stop eating
when destroyed, one is very much hungry
anterior hypothalamus
sex center
when destroyed, one is asexual
posterior pituitary
comprised of axonal projections from hypothalamus
responds to hormones released by the hypothalamus
releases vasopressin and ADH
pineal gland
keeps biological rhythms
basal ganglia
coordinate muscle movement
receive info from cortex and relay info to brain and spinal cord
damage causes jerky movements and tremors (Parkinson’s)
extrapyramidal system
system in which the basal ganglia gathers info about the body position and carries the info to CNS
limbic system
interconnected structures looping around the central portion of the brain
primarily associated with emotion and memory
septal nuclei
amygdala
hippocampus
septal nuclei
contain a primary pleasure center
association between these neurons and addiction
amygdala
region that controls fear and aggression
hippocampus
consolidates memories and communications with other parts of limbic system through fornix extension
anterograde amnesia
amnesia in which a person cannot establish new longterm memory
retrograde amnesia
amnesia in which a person cannot remember events that happened before injury
cerebral cortex
heavily folded (many gyri/sulci) to increase surface area
two hemispheres
frontal lobe
parietal lobe
occipital lobe
temporal lobe
frontal lobe

made up of prefrontal cortex, primary motor cortex, and Broca’s area (on left hemisphere only)
executive function, impulse control, long-term planning, motor function, speech production
acts as an association area (receives input from diverse areas of brain)
central sulcus

landmark which separates the parietal and frontal lobes
parietal lobe

contains somatosensory cortex
receives sensory signals for touch, pressure, temp, pain
also involved in spatial orientation and manipulation
occipital lobe

contains visual cortex for visual processing
temporal lobe

contains auditory cortex for sound processing
contains Wernicke’s area for language reception and comprehension
what does it mean for the brain to be contralateral?
the hemispheres of the brain control movement in opposite sides of the body
what does it mean for the brain to be ipsilateral?
the hemispheres of the brain process hearing on the same side of the input
dominant hemisphere
usually the left
primary in analytic functions, details
language, logic, math
letters/words, complex voluntary movement
nondominant hemisphere
usually the right
intuition, creativity, music recognition, spatial processing
faces, emotions, sense of direction
acetylcholine
neurotransmitter…
PNS - used by somatic to move muscles; parasympathetic, sympathetic sweat glands
CNS - alertness and arousal
linked to Alzhimers - loss of cholinergic neurons connecting hippocampus = memory loss
dopamine
neurotransmitter that maintains smooth movements and posture
heightened levels found in basal ganglia
endorphins/enkephalins
neurotransmitters that act as natural painkillers
epinephrine
neurotransmitter that controls alertness/wakefulness
primarily in sympathetic
can act as hormone when secreted by adrenal medulla
norepinephrine
local neurotransmitter that controls alertness/wakefulness
primarily in sympathetic
low levels = depression
high levels = anxiety and mania
gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glycine
neurotransmitter that produces IPSPs - hyperpolarization
stabilizes neural activity in brain
glutamate
neurotransmitter that produces EPSPs
serotonin
neurotransmitter that modulates mood, eating, sleeping, dreaming
imbalances can lead to depression and mania
neuropeptides
neurotransmitters that create a longer chain of events than most others
- > slower effect –> longer lasting
ex. endorphins and enkephalins
adrenal glands

located at the top of the kidneys, divided into the adrenal medulla and adrenal cortex
adrenal medulla

part of the adrenal gland that releases epinephrine and norepinephrine as part of the sympathetic nervous system
adrenal cortex
part of the adrenal gland that produces corticosteroids and sex hormones
cortisol
a stress hormone released by the adrenal cortex
sex hormones
hormones that increase libido, contribute to mating behavior and sexual function
made in both the adrenal cortex and the gonads
innate behavior
behavior that is genetically programmed as a result of evolution and is seen in all individuals regardless of environment or experience
learned behavior
behavior that is not based on heredity but instead on experience and environment
adaptive value
the extent to which a trait or behavior positively benefits a species by influencing the evolutionary fitness of the species
leads to adaptation through natural selection
family studies
genetic studies that look at the frequency of a trait within a family compared to the general population
limited because members of a family share environment and genes, so its hard to distinguish between genetic factors and environmental factors
twin studies
genetic studies that compare concordance rates between monozygotic (identical) and dizygotic (fraternal) twins
since both MZ and DZ twins share environment, differences between them must be genetic
sometimes look at MZ raised apart
adoption studies
genetic study that compares similarities between adopted children and their adoptive parents, relative to similarities with their biological parents
neurulation
ectoderm overlying the notochord begins to furrow, forming a neural groove surrounded by two neural folds

neural crest

cells at the leading edge of the neural fold
eventually spread out throughout the body and differentiate into many different tissues
neural tube
becomes the CNS of the organism
has an alar plate - sensory neurons
basal plate - motor neurons
umbilical cord
attaches the fetus to the uterine wall and placenta
placenta
organ in the uterus that transmits food, oxygen, and water to the fetus while returning water and waste to the mother
primitive reflexes
reflexes that exist in infants and should disappear with age
often protective
can occur in adults as a result of demyelination
rooting reflex
reflex in which the infant turns his/her head toward anything that brushes the cheek
Moro reflex
reflex in which the infant extends the arms and slowly retracts them and cries in response to a sensation of falling
Babinski reflex
reflex in which an infant’s big toe is extended and the other toes fan in response to the brushing of the sole of the big foor
grasping reflex
reflex in which the infant grabs anything put into his/her hand
gross motor skills
motor skills that incorporate movement from large muscle groups and whole body motion
ex. sitting, crawling, walking
often develop from head to toe
fine motor skills
motor skills that involve the smaller muscles of the fingers, toes, and eyes, providing more specific and delicate movement
ex. tracking motion, drawing, catching, waving
often develop in the core before the extremities
stranger anxiety
a fear and apprehension of unfamiliar individuals
develops at 7 months
separation anxiety
a fear of being separated from the parental figure
develops at one year
development of playtime
solitary -> onlooker -> parallel play
parallel play
a playstyle in which children play alongside each other without influencing each other’s behavior
what developmental roles occur at age three?
child gains awareness of gender identity
engages in gender-specific play
knows full name
what developmental roles occur at age five?
conformity to peers and romantic feelings begin to develop


