Biology 1: The Cell Flashcards
Epithelial Tissue
covers the body and line its cavities
providing a means for protection against pathogen and desiccation
sometimes polarized - facing different environments
form parenchyma - functional parts of organs
Facultative anaerobes
bacteria that can toggle between metabolic processes, aerobic metabolism and anaerobic metabolism
Anaerobes
bacteria that use fermentation or some other form of cellular metabolism that does not require oxygen
Basal body
complex structure that anchors the flagellum to the cytoplasmic membrane
Connective Tissue
supports the body and provides a framework for the epithelial cells to carry out their function
form stroma by secreting materials to form extracellular matrix (collagen, elastin)
ex. bone, cartilage, tendons, ligaments, adipose tissue, blood
Obligate aerobes
bacteria that require oxygen for metabolism
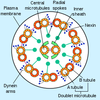
9+2 structure
only seen in eukaryotic organelles
make up with cilia and flagella
Filament
hollow, helical structure composed of flagellin
Obligate anaerobes
anaerobes that cannot survive in an oxygen-containing environment
Aerotolerant anaerobes
bacteria that are unable to use oxygen for metabolism
Microtubules
hollow polymers of tubulin
make up motile structures cilia and flagella
provide pathways for motor proteins to carry vesicles
attach to kinetochores during mitosis
Microfilaments
made up of solid polymerized rods of actin
interact with myosin for muscle contraction
organized into bundles and networks and are resistant to both compression and fracture
forms cleavage furrow during cytokinesis
Intermediate Filaments
kesmin, desmin, vimentin, and lamins
help anchor organelles in the cytoplasm
involved in cell-to-cell adhesion
able to withstand a tremendous amount of tension
cell theory
- all living things are composed of cells
- the cell is the basic unit of life
- cells rise only from other cells
- cells contain DNA, pass it on to their daughters
the cytoskeleton is made up of what three components?
microtubules
microfilaments
intermediate filaments