Biochemistry 11: Lipid and Amino Acid Metabolism Flashcards
how are lipids digested?
mechanical digestion occurs in the mouth and stomach (minimal) – enter the small intestine mostly intact
chemical digestion occurs in the small intestine through bile, pancreatic lipase, colipase, and cholesterol esterase
these enzyme hydrolyse lipids into 2-monacylglyerol, free fatty acids, cholesterol
digested lipids may form micelles for absoprtion or may be absorbed directly

how are lipids absorbed?
short chain fatty acids are absorbed across the intestine into the blood
long chain fatty acids are absorbed as micelles across the brush border into mucosa where they are converted to triacylglycerols and cholesteryl esters
assembled into chylomicroms for release into the lymphatic system via lacteals - re-enter bloodstream via thoracic duct
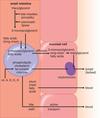
how are lipids mobilized from adipocytes and lipoproteins?
lipids are mobilized from adipocytes by hormone-sensitive lipase activated by a fall in insulin characteristic of a postabsorptive state, cortisol, or epinephrine
hydrolyzes triacyglycerols –> fatty acids and glycerol
lipids are mobilized from lipoproteins and chylomicrons by lipoprotein lipase
releases fatty acids from the triacylglycerols in lipoproteins

how are free fatty acids transported through the blood?
they are associated with albumin
lipoproteins
biochemical assemblies whose primary purpose is to transport hydrophobic lipid molecules in water, as in blood plasma or other extracellular fluids
aggregates of apolipoproteins and lipids
examples include chylomicrons, VLDL, IDL, LDL, HDL
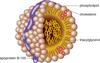
chylomicrons
least dense type of lipoprotein (hightest fat/protein ratio)
the transport mechanism for dietary triacylglycerol molecules, cholesterol, cholesteryl esters from intestine to tissues
transported via the lymphatic system
Very-Low-Density Lipoprotein (VLDL)
transports newly synthesized triacylglycerol molecules from the liver to peripheral tissues in the bloodstream
also contain fatty acids synthesized from excess glucose or retrieved from chylomicron remnants
Intermediate-Density Lipoprotein (IDL)
a VLDL remnant in transition between triacylglycerol and cholesterol transport (therefore is an intermediate between VLDL and LDL/HDL)
formed from a triacylglycerol removed from VLDL
sometimes reabsorbed by liver or sometimes further processed in bloodstream (like picking up cholesteryl esters from HDL to form LDL)
Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL)
primarily transports cholesterol for use by tissues (either biosynthesis or membrane structure)
can also be used to make bile salts in the liver or by other tissues for steroid hormone synthesis
High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL)
synthesized in the liver and intestines, released as dense, protein-rich particles into blood
has apolipoproteins for cholesterol recovery - excess cholesterol from blood vessels for excretion
involved in the reverse transport of cholesterol
apolipoproteins
form the protein component of lipoproteins
control interactions between lipoproteins
in what ways can cholesterol be obtained?
dietary sources of LDL or HDL
de novo synthesis in the liver driven by acetyl-CoA and ATP as well as insulin
3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl (HMG)-CoA reductase
the key enzyme (rate-limiting) in cholesterol biosynthesis
synthesizes mevalonic acid in the smooth endoplasmic reticulum
lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT)
enzyme in bloodstream activated by HDL apolipoproteins
catalyzes the formation of cholesteryl esters (cholesterol + fatty acid) for transport with HDL
cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP)
catalyzes the transition of IDL to LDL by transferring the cholesteryl esters from HDL





