3. Musculoskeletal System Flashcards
-blast
embryonic
-clast
breaking down
-cyte
cell
-physis
growth
-um
structure, thing
abduction
movement away from the midline
acetabulum
hip socket in distal pelvic girdle for head of the femur
achondroplasia
a kon droh PLAY zha
congenital disorder of the growth of cartilage at the epiphyses of the long bones and skull, resulting in dwarfism
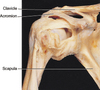
acromion process
highest point extending from the scapula
adduction
movement towards the midline
amphiarthroses
joints with limited range of motion (ROM)
Ex: vertebrae, female pubic bones during childbirth
ankyl/o
crookedness or stiffness
ankylosing spondylitis
chronic inflammatory disease of idiopathic origin, which causes a fusion of the spine
antrum
antr/o (also referred to as a sinus) a cavity or channel lined with a membrane
appendicular skeleton
append/o appendic/o shoulder bones, collarbones, pelvis bones, arms, and legs
arthrocentesis
surgical puncture of a joint to remove synovial fluid for analysis
arthrodesis
surgical binding or stabilization of a joint
arthrogram
x-ray of joint done after injection of contrast medium
arthrography
x-ray recording of a joint
arthroplasty
AR throh plas tee
general term meaning surgical repair of a joint
arthroscopy
ar THRAHS kuh pee
visual examination of a joint, accomplished by use of an arthroscope
arthrotomy
incision into a joint
articular cartilage
covers the ends of many bones and serves a protective function
axial skeleton
skull, rib cage, and spine
bone marrow
myel/o
bunion
fairly common, abnormal and painful enlargement and inflammation of the first metatarsophalangeal joint (base of the great toe)
bursa
burs/o (pl., bursae)
small, fluid-filled sac that allows easy movement of one part of a joint over another
calcium
calc/i calc/o
carpal
carp/o
wrist bones
carpal tunnel syndrome
compression injury that manifests itself as fluctuating pain, numbness, and paresthesias of the hand
In this condition, the median nerve is squeezed or constricted by a wrist ligament as it passes between that ligament and the bones and tendons of the wrist.
Numbness and burning pain have been reported in the fingers and hands, esp in the index and long fingers, sometimes extending all the way to the elbow.
cartilage
cartilag/o chondr/o
cervical
cervic/o neck bones (C1-C7)
chest
pector/o
chondroma
benign tumor of the cartilage, usually occurring in children and adolescents
chondrosarcoma
malignant tumor of the cartilage
occurs most frequently in adults
clavicle
clavicul/o
cleid/o
collar bone that connects the sternum to each scapula
closed reduction
no incision is necessary to align the bone
open reduction
proper alignment can occur only by making an incision
coccyx (KOCK sicks)
coccyg/o
coccygeal (kock sih JEE ul)
tailbone
Colles fracture
CALL-ees
break of the distal end of the radius at the epiphysis, often occurs when pt has attempted ot break his/her fall

comminuted fracture
the bone is crushed and/or shattered into many pieces
compact bone
hardest, densest layer just beneath the periosteum that contains blood vessels that deliver oxygen and nutrients to the bone while removing wastes such as CO2
complicated fracture
bone is broken and pierces an internal organ
compression fracture
the fractured area of bones collapses on itself
computed tomography (CT) scan
imaging technology that records transverse planes of the body for diagnostic purposes
condyle
condyl/o a rounded, knuckle-lick projection at the end of a bone that anchors ligaments and articulates with adjacent bones (aka near a joint)
contracture
chronic fixation of a joint in flexion caused by atrophy and shortening of muscle fibers after a long period of disuse
costals
ribs (12 pairs)
crest
a narrow, elongated elevation (such as the iliac crest)
cranial sinuses
frontal ethmoidal sphenoidal maxillary

debridement
removal of debris from a wound
depression
general term for an opening, groove, or hollow space in bone
DEXA scan
dual energy x-ray absorptiometry
a procedure that measures the density of bone at the hip and spine
an x-ray detector measures how well the x-rays penetrate the bone
dia-
complete, through
diaphysis
middle shaft of a long bone
diarthroses
joints with movement in all planes with full range of motion (ROM)
also called synovial joints
Ex: hips, knees, elbows, shoulders, wrists, and ankles
dorsalgia
upper back pain
dorsiflexion
raising the foot and pulling the toes toward the shin
dystrophy
abnormal development
eat, swallow
phag/o
elbow
olecran/o
electromyography (EMG)
procedure that records the strength of muscle contraction as a result of electrical stimulation
endo-, end-
within
epi-
above
epiphyses
ends of a long bone
epicondyle
epicondyl/o projection on the surface of the bone above the condyle
ethmoid
ethmoid/o bone that forms part of the nose, orbit, and floor of the cranium
eversion
turning outward
Ewing sarcoma
most common bone cancer in children
extension
the act of straightening, to increase the angle of a joint
fascia
fasci/o
plural: fasciae
tough fibrous covering of the muscles (and of some nerves and blood vessels)
external fixation
immobilizing bone(s) externally, like with a cast
CREF = closed reduction and external fixation
femur
femor/o
fibromyalgia
disorder characterized by musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, muscle stiffness and spasms, and sleep disturbances
fibula
fibul/o
perone/o
the smaller of the two lower leg bones, runs parallel to the tibia
flared bony prominence at distal end is lateral malleolus (outside of ankle)
finger, toe (whole)
dactyl/o
fissure
a fairly deep cleft or groove, creating a slit-like opening (ex: inferior orbital fissure)
flat bones
sternum scapula
flexion (FLEK shen)
The act of bending, to decrease the angle of a joint
foramen (foh RAY men)
(plural: foramina) an opening or a hole for blood vessels and nerves
fossa
a hollow or shallow depression, especially on the surface of the end of a bone
frontal
front/o
greenstick fracture
bone is partially bent and partially broken
a common fracture in children bc their bones are still soft
hairline fracture
minor fracture that appears as a thin line on x-ray and may not extend completely through the bone
head
a rounded, usually proximal portion of some long bones
heart muscle
myocardi/o
herniated intervertebral disk
protrusion of the central part of the disk that lies between the vertebrae, resulting in compression of the nerve root and pain
humerus
humer/o
ilium
ili/o
blade-shaped section of the hip on each side of the pelvic girdle
impacted fracture
bone is broken, and the ends are driven into each other
inter-
between
internal fixation
immobilizing bones by fastening pins, screws, plates, etc. to maintain correct alignment
ORIF = open reduction and internal fixation
inversion
turning inward
irregular bones
verebra ossicles (bones of the ear) such as stapes
ischium
ischi/o
lower posterior part of the pelvic girdle
jaw
gnath/o
kyphoplasty
KYE foh plas tee
minimally invasive procedure designed to address the pain of fractured vertebrae resulting from osteoporosis or cancer
A balloon is used to inflate the area of fracture before a cementlike substance is injected. The substance hardens rapidly, and pain relief is immediate in most patients.
kyphosis
extreme posterior curvature of the thoracic area of the spine
AKA humpback or hunchback
lacrimal
bones at the corner of each eye that make up part of the orbit
lamina
lamin/o
Any thin, flat layer or stratum of membrane or other composite structure; sometimes used alone to denote the lamina arcus vertebrae.
laminectomy
removal of the bony arches of one or more vertebrae to relieve compression of the spinal cord
leiomyoma
lye oh my OH mah
benign tumor of smooth muscle
the most common leiomyoma is in the uterus and termed “fibroid”
leiomyosarcoma
lye oh my oh sar KOH mah
malignant tumor of smooth muscle
most commonly appearing in the uterus
ligament
ligament/o
syndesm/o
flexible, tough band of fibrous connective tissue that attaches one bone to another at the joint
long bones
humerus (upper arm bone) femur (thigh bone)
lordosis
exaggerated anterior curve of the lumbar spine
AKA swayback
lumbar
lumb/o
lower back (L1-L5)
lumbago
lum BAE goh
lower back pain
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
procedure that uses magnetic properties to record detailed information about internal structure
malleolus
malleol/o
mandible
mandibul/o lower jaw bone that contains sockets, or alveoli, for holding lower teeth
malunion
when a bone does not mend and realign correctly
mastoid process
mastoid/o
matrix
material between osteocytes that stores calcium and phosphorus for the body to use as needed in the form of mineral salts
maxillary
maxill/o plural: maxilla upper jaw bone that contains sockets, or alveoli, for holding upper teeth
meta-
beyond
metacarpal
metacarp/o
hand bones
metatarsal
metatars/o
bones of the foot

muscle
muscul/o
my/o
myos/o
muscle
muscul/o my/o myos/o
muscular dystrophy (MD)
group of disorderes characterized as an inherited progressive atorphy of skeletal muscle without neural involvement
myasthenia gravis (MG)
mye ah STHEE nee ah / GRAV us
a usually severe condition characterized by fatigue and a progressive muscle weakness, especially of the face and throat
thought to be caused by a defect in the transmission of impulses from nerve to muscle cells
myelogram
MYE eh lo gram
x-ray of spinal canal done after injection of contrast medium
myorrhaphy
mye ORE rah fee
suture of a muscle
nonunion
when no healing takes place after a bone is broken
nose
nas/o
occipital
occipit/o
olecranon
olecran/o
proximal projection of the ulna that forms the tip of the elbow
osteoarthritis (OA)
joint disease characterized by degenerative articular cartilage and a wearing down of the bones’ edges at a joint; considered a ‘wear and tear’ disorder
AKA degenerative joint disease (DJD)
operative ankylosis
procedure used in the treatment of spinal fractures or after diskectomy or laminectomy for the correction of a herniated vertebral disk; also used to describe surgical fixation of a joint
osteoblasts
smaller, immature osteocytes; form bony tissue that replaces cartilage
osteoclasis
OS tee oh klay sis
refracture of a bone, usually done if a bone has a malunion
osteoclasts
bone phagocytes; reabsorb, or digest, bony tissue inside each bone, thus enlarging the inner cavity This process prevents the bone from becoming too thick and heavy. The continual tearing down and rebuilding of bony tissue helps keep the body’s bone structure strong and in good repair
osteoma
benign bone tumor, usually of compact bone
osteomalacia
softening of bone caused by a loss of minerals from the bony matrix as a result of vitamin D deficiency
osteomyelitis
infection of the bone and bone marrow
osteopenia
a severe form of bone deficiency
osteoplasty
OS tee oh plas tee
surgical repair of a bone
osteoporosis
loss of bone mass, which results in the bones being fragile and at risk for fractures
osteosarcoma
malignant tumor of bone
AKA Ewing sarcoma (most common children’s bone cancer)
osteotome
instrument used to cut into bone
palatine
palat/o cranial bones that forms the hard palate of the mouth and suppose the floor of the nose
parietal
pariet/o two bones - one on each side of the head - form the roof and upper sides of the cranium
patella
patell/o
kneecap; largest sesamoid bone in the body
pathologic fracture
any fracture occurring spontaneously as a result of disease
peri-
surrounding
periosteum
tough, fibrous structure that surrounds the bone and comprises the outermost surface of the long bones except for the ends of the epiphyses
phalanx
phalang/o
plural: phalanges
finger or toe bones
phosphorus
phosph/o phosphat/o
plantar flexion
lowering the foot, pointing the toes away from the shin
point of insertion
bone at the movable end of the muscle, farthest from the trunk
point of origin
unmovable bone at the more stable end nearest the trunk
process
general term for any raised or projected area
polydactyly
pall ee DACK tih lee
condition of more than five fingers or toes on each hand or foot
pronation
turning the palm or foot downward (face down)
protraction
moving a part of the body forward
pubis or pubic bone
pub/o
distal anterior part of the pelvic girdle; fused at midline to form the pubic symphysis joint
radius
radi/o
lateral lower arm bone in line with the thumb
reduction
the process of alignment for a broken bone
retraction
moving a part of the body backward
rhabdomyoma
benign tumor of striated/voluntary/skeletal muscle
rhabdomyosarcoma
highly malignant tumor of striated/voluntary/skeletal muscle
AKA rhabdosarcoma or rhabdomyoblastoma
rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
inflammatory joint disease believed to be autoimmune in nature; occurs in a much younger population (ages 20-45) than OA
In this autoimmune reaction against the joint tissues (especially the synovial membrane), these inflamed synovial membranes thicken and damage the articular cartilage. This makes movement difficult and painful.
rheumatoid factor test
lab test that looks for rheumatoid factor (RF) present in the bloo dof those who have rheumatoid arthritis
rib
cost/o
Rickets
osteomalacia occurring during childhood
rotation
revolving a bone around its axis
sacrum
sacr/o
5 bones fused together (S1-S5) below the lumbar spine
Salter-Harris fracture
fracture of the epiphyseal plate in children
scapula
scapul/o
shoulder blade
sciatica
inflammation of the sciatic nerve, usually marked by pain and tenderness along the course of the nerve through the thigh and leg
may result in wasting of the muscles of the lower leg
scoliosis
lateral “S” cure of the spine, causing a loss of height in inches
serum calcium (Ca)
test to measure the amount of calcium in the blood
sesamoid bones
small rounded bones found near any joint to increase the efficiency of the joint around them patella (kneecap)
short bones
carpal (wrist bone) tarsal (ankle bone)
sinus
sin/o sinus/o (also referred to as an antrum) a cavity or channel lined with a membrane; a hollow cavity within a bone
skeletal/striated muscle
rhabdomy/o
skull
crani/o
smooth/visceral muscle
leiomy/o
sphenoid
sphenoid/o cranial bone that forms part of the floor and walls of the eye sockets, extending to form part of the base of the skull between parietal and temporal bones (extends from back of the eye to sides of skull)
spina bifida occulta
SPY nah / BIFF ih dah / oh KULL tah
congenital malformation of the bony spinal canal without involvement of the spinal cord
spinal column
rachi/o spin/o vertebr/o
spinal stenosis
abnormal condition of the narrowing of the spinal canal with attendant pain, sometimes caused by osteoarthritis or spondylolisthesis
spine
a thorn-like projection, such as the spinous process of a vertebra
spondylolisthesis
spon dih loh liss THEE sis
condition resulting from the partial forward dislocation of one vertebra over the one beneath it
spondylosis
a stiffening of the vertebral joints
spondylosyndesis
spon dih loh sin DEE sis
fixation of an unstable segment of the spine by skeletal traction, immobilization of the patient in a body cast, or stabilization with a bone graft or synthetic device
Also called spinal fusion and spondylodesis
sprain
traumatic injury to a joint involving the soft tissue: muscle, ligaments, and tendons
sternum
stern/o
subluxation
bone is partially out of joint

sulcus
a groove or depression in an anatomical structure (not as deep as a fissure)
supination
turning the palm or foot upward (face up)
synarthroses
immovable joints
Ex: fontanelles of the skull
syndactyly
sin DACK tih lee
condition of the joining of the fingers or toes, giving them a webbed appearance
talipes
TALL ih peez
congenital deformity resulting in an abnormal twisting of the foot
AKA clubfoot

tarsal
tars/o
ankle bones
talus is the first of the tarsal bones

temporal
tempor/o
temporomandibular joint
where the mandible and temporal bones meet
temporomandibular joint disorder (TMJ)
dysfunctional temporomandibular joint, accompanied by gnathalgia (jaw pain)
tendon
ten/o
tend/o
tendin/o
band of fibrous connective tissue that attaches muscle to bone
tenomyoplasty
ten oh MYE oh plas tee
surgical repair of a muscle and a tendon
thorax
thorac/o
upper back (T1-T12)
also called dorsal spine by some specialties
tibia
tibi/o
shin bone that forms a joint with femur at patella
flared bony prominence at distal end is medial malleolus (inside of ankle)
torticollis
tore tih KOLL lis
congenital or acquired condition that manifests itself as a contraction of the muscles of the neck
AKA wryneck
trochanter
one of two tuberosities (bony projections/processes) on the proximal ends of the femurs that serve as points of attachment for muscles
tubercle
a nodule or a small raised area (projection) for tendon or muscle attachment
tuberosity
an elevation or protuberance; a large, rounded process used to attach muscles or tendons (larger than a tubercle)
ulna
uln/o
medial lower arm bone
ultrasonography (US)
procedure in which high-frequency sound waves form an image of the body
vertebra
spondyl/o
vertebr/o
26 vertebrae separated by cartilage pads called disks
vomer
vomer/o thin, flat cranial bone that forms the nasal septum
x-ray
imaging technique using electromagnetic radiation for recording internal structures
zygoma
zygom/o zygomat/o cheekbone


