14.1 Eye Flashcards
conjunctiv/o
conjunctiva
ophthalm/o, ocul/o
eye
palpebr/o, blephar/o
eyelids
lacrim/o, dacry/o
tear
opt/o, optic/o
vision
supra-
above
ocular adnexa
the structure that surrounds and supports the function of the eyeball
oculus dexter (OD)
oculus dexter
oculus uterque (OU)
each eye
medial canthus
inner corner of the eye
lateral canthus
outer corner of the eye
palpebral fissure
point where upper and lower eyelids meet
palpebration
the act of blinking
conjunctiva
protective thin mucosal layer that lines the eyelids and spreads a protective coating across the anterior surface of the eyeball
meibomian glands
sebaceous glands in the eyelid that lubricate the eyelashes
meibomian = sebaceous
lacrimal gland
located above the eye and in the outer corners provide constant cleansing and lubrication of the eye itself

lacrimation
the process of creating tears
lacrimal punctus
small hole in the medial canthus where tears drain into the nasolacrimal ducts
nasolacrimal ducts
carry tears from lacrimal puncta in the medial canthi to the nasal cavity
extraocular muscles
move the eyes as directed by impulses from the cranial nerves

orbit
bony socket containing eyeball
choroid/o
choroid
cycl/o
ciliary body
kerat/o, corne/o
cornea
ir/o, irid/o
iris
phac/o, phak/o, lent/i
lens
macul/o
macula lutea
papill/o
optic disk
pupill/o, cor/o, core/o
pupil
retin/o
retina
scler/o
sclera
uve/o
uvea
vitre/o
vitreous humor, glassy
sclera
white of the eye
hard outer covering of the eye
cornea
transparent, anterior portion of sclera
site where refraction, or the bending of light, begins

limbus
border b/w cornea and sclera
uvea
the vascular middle coat of the eye that includes the iris, ciliary body, and choroid
AKA vascular tunic
iris
a colored, smooth muscle behind the cornea that contracts and relaxes to control the amount of light entering the eye

ciliary body
the thickened part of the vascular tunic of the eye joining the iris with the anterior part of the choroid
holds the lens in place

choroid layer
the thin vascular layer of the eye between the retina and the sclera

pupil
the dark area in the center of the iris, where light enters through the avascular lens

lens
the crystalline lens of the eye, the transparent biconvex body of the eye located between the posterior chamber and the vitreous body

aqueous humor
fluid produced by ciliary body to nourish the cornea, give the eye its shape, and maintain an optimal intraocular pressure
vitreous humor
holds the choroid membrane against the retina to ensure an adequate blood supply

retina
the inner layer of the eye that contains sensory receptors for the images carried by the light rays
AKA nervous tunic

rods
one of two types of sensory receptors that appear throughout the retina
responsible for vision in dim light

cones
one of two types of sensory receptors that are concentrated in the central area of the retina
responsible for color vision

macula lutea
spot near the center of the retina on which light rays focus during the daylight hours

fovea
a portion of the macula lutea that contains cones and provides the sharpest image

optic disc
point at which the optic nerve leaves the retina

blepharedema
swelling of the eyelid
blepharitis
inflammation of the eyelid
blepharochalasis
bleff ah roh KAL luh sis
hypertrophy of the skin of the eyelid
slackening of an eyelid
blepharoptosis
drooping of the upper eyelid
ectropion
eck TROH pee on
turning outward (eversion) of the eyelid, exposing the conjunctiva
the eyelid turns back “on” itself
entropion
turning inward of the eyelid toward the eye
the eyelid turns inward on (to) the eyeball
chalazion
kuh LAY zee on
hardened swelling of a meibomian gland resulting from a blockage
AKA meibomian cyst
Fig A

hordeolum
hor DEE uh lum
infection of one of the sebaceous glands of an eyelash
AKA stye
Fig B

conjunctivitis
inflammation of the conjunctiva, a highly contagious disorder
AKA pinkeye
dacryocystitis
dack ree oh sis TYE tis
inflammation of a lacrimal sac
epiphora
eh PIFF or ah
overflow of tears
excessive lacrimation
keratoconjunctivitis sicca
dryness and/or inflammation of the cornea and conjunctiva due to inadequate tear production
usually the result of an immune disorder
ophthalmia neonatorum
off THAL mee uh
severe, purulent conjunctivitis in the newborn, usually due to gonorrheal or chlamydial infection
routine introduction of an antibiotic ophthalmic ointment (erythromycin) prevents most cases.
xerophthalmia
zeer off THAL mee ah
dry eye
lack of adequate tear production to lubricate the eye
usually the result of vitamin A deficiency
amblyopia
am blee OH plee ah
dull or dim vision due to disuse
AKA lazy eye
diplopia
dip LOH pee ah
double vision
emmetropia (EM, Em)
normal vision
esotropia
turning inward of one or both eyes
AKA crossed eyes
exotropia
turning outward of one or both eyes
opposite of crossed eyes

exophthalmia
eck soff THAL mee ah
protrusion of the eyeball from its orbit
may be congenital or the result of an endocrine disorder

strabismus
general term for a lack of coordination b/w the eyes, usually due to a muscle weakness or paralysis
sometimes called a “squint,” which refers to the patient’s effort to correct the disorder

asthenopia
visual impairment due to weakness of ocular or ciliary muscles
astigmatism
malcurvature of the cornea leading to blurred vision
if uncorrected, asthenopia may result
hyperopia
farsightedness
refractive error that does not allow the eye to focus on nearby objects

myopia (MY)
nearsightedness
refractive error that does not allow the eye to focus on distant objects

presbyopia
progressive loss of elasticity of the lens (usually accompanies aging), resulting in hyperopia
corneal ulcer
trauma to the outer covering of the eye, resulting in an abrasion
keratitis
inflammation of the cornea
keratoconus
kair uh toh KOH nus
malformation of the cornea that appears as a protrusion of the center of the cornea
more prevalent in females than males, this condition may cause astigmatism

anisocoria
an nye soh KORE ee ah
condition of unequally sized pupils, sometimes due to pressure on the optic nerve as a result of trauma or lesion
hyphema
blood in the anterior chamber of the eye as a result of hemorrhage due to trauma
iritis
inflammation of the iris
AKA iriditis

uveitis
yoo vee EYE tis
inflammation of the uvea (iris, ciliary body, and choroids)
aphakia
ah FAY kee ah
condition of no lens, either congenital or acquired
cataract
progressive loss of transparency of the lens of the eye

glaucoma
abnormal intraocular pressure (IOP) due to the obstruction of the outflow of the aqueous humor

chronic or primary open-angle glaucoma
characterized by an open anterior chamber angle
angle-closure glaucoma
characterized by an abnormally narrowed anterior chamber angle
AKA narrow-angle glaucoma
synechia
sin ECK kee ah
adhesion of the iris to the lens and the cornea
achromatopsia
ah kroh mah TOP see uh
impairment of color vision
inability to distinguish b/w certain colors bc of abnormalities of the photopigments produced in the retina
AKA colorblindness
age-related macular degeneration (ARMD or AMD)
progressive destruction of the macula, resulting in a loss of central vision
most common visual disorder after the age of 75

diabetic retinopathy
damage of the retina due to diabetes
leading cause of blindness

hemianopsia
hem ee an NOP see uh
loss of half the visual field, often the result of a cerebrovascular accident
nyctalopia
nick tuh LOH pee uh
inability to see well in dim light
may be due to a vitamin A deficiency, retinitis pigmentosa, or choroidoretinitis
retinal tear/detachment
separation of the retina from the choroid layer
may be due to trauma, inflammation of the interior of the eye, or aging
a hole in the retin allows fluid from the vitreous humor to leak b/w the 2 layers
retinitis pigmentosa
hereditary, degenerative disease marked by nyctalopia and a progressive loss of the visual field
scotoma
skoh TOH muh
area of decreased vision in the visual field
AKA blind spot
nystagmus
nis STAG mis
involuntary, back-and-forth eye movements due to a disorder of the labyrinth of the ear and/or parts of the nervous system associated with rhythmic eye movements
optic neuritis
inflammation of the optic nerve resulting in blindness
often mentioned as a predecessor to the development of multiple sclerosis
intraocular melanoma
malignant tumor of the choroid, ciliary body, or iris that usually occurs in individuals in their 50s or 60s
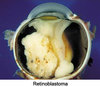
retinoblastoma
cancer of the retina
an inherited condition that arises from embryonic retinal cells and is present in an infant at birth
chala/o
to relax
trop/o
turning
scot/o
darkness
presby/o
old age
sicca, xer/o
dry
eso-
inward
glauc/o
gray, bluish green
ambly/o
dull, dim
sthen/o
strength
-chalasis
relaxation, slackening
Amsler grid
test to assess central vision and to assist in the diagnosis of age-related macular degeneration
diopters
measurement of refraction errors, including the amount of nearsightedness (-), farsightedness (+),
and astigmatism
fluorescein angiography
floo RES see un
procedure to confirm suspected retinal disease by injection of a fluorescein dye into the eye and use of a camera to record the vessels of the retina
fluorescein staining
floo REH see un
use of a dye dropped into the eyes that allow differential staining of abnormalities of the cornea
gonioscopy
goh nee AH skuh pee
visualization of the angle of the anterior chamber of the eye
used to diagnose glaucoma and inspect ocular movement
ophthalmic ultasonography
use of high-frequency sound waves to image the interior of the eye when opacities prevent other imaging techniques
may be used for diagnosing retinal detachments, inflammatory conditions, vascular malformations, and suspicious masses
ophthalmoscopy
off thal MAH skuk pee
any visual examination of the interior of the eye with an opthalmoscope
Schirmer tear test
SHURR mur
test to determine the amount of tear production
useful in daignosing dry eye (xerophthalmia)
slit lamp examination
part of a routine eye exam
used to examine the various layers of the eye
medicated may be used to dilate the pupils (mydriatics), numb the eye (anesthetics), or dye the eye (fluorescein staining)
tonometry
measurement of intraocular pressure
used to diagnose glaucoma
Goldmann applanation tonometry
eye is numbed and intraocular pressure measurements are taken directly on the eye
air-puff tonometry
a puff of air is blown onto the cornea to determine intraocular pressure
visual acuity (VA) assessment
test of the clearness of sharpness of vision
AKA Snellen test
normal vision is 20/20: top figure is # of feet a normal person would be from the chart and still be able to read the smallest letters
20/40 means that the highest line the individual can read is what a person with normal vision could read at 40 feet
visual field (VF) test
test to determine the area of physical space visible to an individual
normal visual field is 65 degrees upward, 75 degrees downward, 60 degrees inward, and 90 degrees outward
blepharoplasty
surgical repair of the eyelids
may be done to correct blepharoptosis or blepharochalasis
blepharorrhaphy
bleff ah ROHR ah fee
suture of the eyelids
enucleation of the eye
removal of the entire eyeball
evisceration of the eye
removal of the contents of the eyball, leaving the outer coat (sclera) intact
exenteration of the eye
removal of the entire contents of the orbit
astigmatic keratotomy (AK)
corneal incision process that treats astigmatism by creating a more rounded cornea
corneal incision procedure
any keratotomy procedure in which the cornea is cut to change shape, correcting a refractive error (AK, RK, PRK)
flap procedure
any procedure in which a segment of the cornea is cut as a means of access to the structures below (LASIK, LASEK)
laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis
flap procedure in which an excimer laser is used to remove material under the corneap flap
corrects astigmatism, myopia, and hyperopia
laser epithelial keratomileusis (LASEK)
flap procedure that differs from the LASIK procedure only in the amount of tissue cut
LASEK incises the epithelium and only part of the stroma, with an advantage of the opportunity for more easily treated possible infections
photoablation
use of UV radiation to destroy and remove tissue from the cornea
photorefractive keratectomy (PRK)
treatment for astigmatism, hyperopia, and myopia that uses and excimer laser to reshape the cornea
radial keratotomy (RK)
corneal incision process that treats myopia by incising the cornea in a spoke-like pattern
anterior ciliary sclerotomy (ACS)
incision in the sclera to treat presbyopia
corneal transplant
transplantation of corneal tissue from a donor or the patient’s own (autograft) cornea
may be either full- or partial-thickness grafts
AKA keratoplasty
epikeratophakia
eh pee kair uh toh FAY kee ah
replacement of lens function with the use of a donor corneal graft
may be used for myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, and occasionally keratoconus
implantation of corneal ring segments
procedure to correct myopia with the addition of pieces to the cornea

laser thermal keratoplasty (LTK)
KAIR uh toh plasty
use of heat and a holmium laser to treat hyperopia in patients over 40
limbal relaxing incision (LRI)
incision of the limbus to treat astigmatism
extraction of the lens
removal of the lens to treat cataracts
may be intracapsular, in which the entire lens and capsule are removed; or extracapsular, in which the lens capsule is left in place
implantable contact lenses (ICL)
use of an artificial lens implanted behind the iris and in front of the natural abnormal lens to treat myopia and farsightedness
phacoemulsification and aspiration of cataract
fack koh ee MULL sih fih KAY shun
vision correction accomplished through the destruction and removal of the contents of the capsule by breaking it into small pieces and removing them by suction
coreoplasty
surgical repair to form an artificial pupil
goniotomy
incision of Schlemm’s canal to correct glaucoma by providing an exit for the aqueous humor
iridotomy
eye rih DOT tuh mee
incision of the iris to treat postoperative glaucoma or to gain access for cataract surgery
trabeculotomy
external incision of the eye to promote intraocular circulation in glaucoma
surgical procedure used in the treatment of glaucoma to relieve intraocular pressure by removing part of the eye’s trabecular meshwork and adjacent structures

retinal photocoagulation
destruction of retinal lesions using light rays to solidify tissue
scleral buckling
reattachment of the retina with a cryoprobe and the use of a silicone sponge to push the sclera in toward the retinal scar
includes the removal of fluid from the subretinal space
vitrectomy
removal of part or all of the vitreous humor

ton/o
tone, tension
Acc
accommodation
Astigm, As, Ast
astigmatism
IOP
intraocular pressure
s. gl
correction without glasses
accommodation
a process through which the lens adjusts to see


