11. Respiratory System Flashcards
adenoid/o
adenoids
pneum/o
air
alveol/o
alveolus
spir/o
breathe
bronchiol/o
bronchiole
bronch/o, bronchi/o
bronchus
capn/o
carbon dioxide
steth/o, thorac/o
chest
diaphragm/o, diaphragmat/o, phren/o
diaphragm
salping/o
eustachian tube
laryng/o
larynx
lob/o
lobe
pulmon/o, pneum/o, pneumon/o
lung
mediastinum
mediastinum
or/o, stom/o, stomat/o
mouth
muc/o
mucus
naso, rhin/o
nose
ox/i
oxygen
pharyng/o
pharynx
pleur/o
pleura
cost/o
rib
sin/o, sinus/o
sinus
tonsill/o
tonsil
trache/o
trachea
phon/o
voice, sound
inspiration
lungs expand
diaphragm contracts downward, increasing volume of thoracic cavity
pressure within thorax falls below that of external environment and air flow from atmosphere into the lungs

expiration
lungs recoil
diaphragm relaxes back upwards, causing a reduction in the volume of the thoracic cavity and increasing the pressure within it - forcing air out of the lungs

nares
NAIR ees
sing., naris
nostrils
nasal septum
partition separating the nares, composed of cartilage and bone covered with mucous membranes
paranasal sinuses
any of the air cavities in bones surrounding the nose that warm and filter the air and help in the production of sound
pharynx
throat
extends from base of the skull to the esophagus

nasopharynx
uppermost of the three regions of the pharynx
located behind the nasal cavity and extending from the posterior nostrils to the soft palate

eustachian tubes
mucous membrane-lined tube joining the nasopharynx and the middle ear cavity
connects nasopharynx with ears to equalize pressure b/w the ears and the throat
adenoids
pharyngeal tonsils
lymphatic tissue located in the nasopharynx to protect against pathogens

palatine tonsils
pall uh tyne
one of two almond-shaped masses of lymphoid tissue located b/w in the oropharynx
composed of numerous lymph follicles and crypts

oropharynx
one of three divisions of the pharynx containing the palatine and lingual tonsils

laryngopharynx
one of three regions of the throat
extending from the hyoid bone to the esophagus

larynx
voice box, where the vocal cords vibrate to produce speech

epiglottis
flap of cartilage at the opening of the larynx
closes access to the trachea when food is being swallowed

trachea
windpipe, lies within the space b/w the lungs
cartilaginous, membranous tube extending from larynx and branching into the bilateral main bronchi

carina
lower end of the trachea where it bifurcates into the right and left bronchi
bronchi
bronchial tubes
any of the larger air passages of the lungs thorugh which inhaled and exhaled air passes

bronchioles
small airway of the respiratory system that extends from the bronchi into the lobes of the lung

alveoli
millions of small air sacs through which gas exchange takes place b/w pulmonary capillary blood and alveolar air
each alveolus is coated with a surfactant that keeps it from collapsing

lobes
right lung has 3
left lung only has 2

diaphragm
dome-shaped musculofibrous partition separating the abdominal and thoracic cavities
mediastinum
media STY num
central portion of the chest cavity, the space between the lungs that contains the heart, trachea, esophagus, bronchial tubes, major blood vessels, and other organs
pleura
serous membrane enveloping the lung and lining the thoracic cavity
made up of a single layer of flattened mesothelial cells on a membrane of connective tissue, and moistened with a serous secretion that facilitates lung movements in the chest
visceral pleura
the side of the membrane that coats the lungs

parietal pleura
side of the membrane that lines the inner surface of the rib cage

eupnea
good, normal breathing
dyspnea
DISP nea
abnormal, difficult, or uncomfortable breathing
tachypnea
tack ip NEE uh
rapid, shallow breathing
bradypnea
brad ip NEE uh
abnormally slow breathing
orthopnea
breathing that is difficult unless in an upright position
apnea
abnormal, periodic cessation of breathing
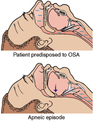
obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)
sleep disorder characterized by periods in which the person makes no attempt to breathe, resulting from a physical obstruction in the upper airways
cough
sudden, audible expulsion of air from the lungs
Cheyne-Stokes respiration
deep, rapid breathing followed by a period of apnea
cyanosis
blue, gray, or purple discoloration of skin and mucous membranes
clubbing
abnormal enlargement of the distal phalanges as a result of diminished O2 in the blood
hypoxemia
deficiency of oxygen in the blood
hypoxia
deficiency of oxygen in the tissues
hypercapnia
condition of excessive CO2 in the blood
aphonia
ah FOH nee ah
loss of ability to produce sounds
dysphonia
impairment of speaking, hoarseness
epistaxis
ep ih STACK sis
nosebleed
fatigue
overhwelming sense of exhaustion
hemoptysis
hee MOP tih sis
coughing up blood or blood-stained sputum
hyperventilation
abnormally increased breathing
pleurodynia
ploor oh DIN ee ah
pain in the chest caused by inflammation of the intercostal muscles and their points of attachment of the diaphragm to the chest thorax
precordial pain
chest pain over the heart and lower thorax
rhinorrhea
rye noh REE ah
discharge from the nose
shortness of breath (SOB)
breathlessness
inability to fill the lungs adequately
sputum
mucus coughed up from the lungs and expectorated through the mouth
if abnormal, may be described as to its amount, color, or odor
thoracodynia
thor uh koh DIN ee ah
chest pain
tympany, chest
TIM puh nee
bell-like, low-pitched, resonant sound from the chest
friction sounds
sounds made by dry surfaces rubbing together
hiccup
sound produced by the involuntary contraction of the diaphragm, followed by rapid closure of the glottis
AKA hiccough, singultus
rales
an abnormal lung sound heard during inspiration when the alveoli are filled with secretions
characterized by discontinuous bubbling noises
AKA crackles
rhonchi
RONG kye
abnormal rumbling sound heard on auscultation, caused by airways blocked by secretions or muscle contractions
stridor
STRY dur
high-pitched inspiratory sound from the larynx
a sign of upper airway obstruction
wheezing
whistling sound made during breathing
often associated with asthma
asthma
respiratory disorder characterized by recurrent episodes of paroxysmal (sudden, episodic) dyspnea
symptoms include coughing, wheezing, and SOB
if attack becomes continuous (status asthmaticus), it may be fatal
croup
CROOP
acute viral infection of early childhood, marked by stridor caused by spasms of the larynx, trachea, and bronchi
symptoms include labored breathing; a harsh, barking cough; and stridor
deviated septum
deflection of the nasal septum that may obstruct the nasal passages, resulting in infection, sinusitis, SOB, headache, or recurring epistaxis
epiglottitis
eh pee glah TYE tis
inflammation of the epiglottis

laryngitis
inflammation of the voice box
pharyngitis
inflammation of infection of the pharynx, usually causing symptoms of a sore throat

polyps, nasal and vocal cord
small, tumorlike growth that projects from a mucous membrane surface, including the inside of the nose, the paranasal sinuses, and the vocal cords
rhinitis
inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nose
rhinomycosis
abnormal condition of the fungus in the nose
rhinosalpingitis
inflammation of the mucous membranes of the nose and eustachian tubes
sinusitis
inflammation of one or more of the paranasal sinuses
upper respiratory infection (URI)
inflammation and/or infection of structures of the upper respiratory tract
AKA coryza (kore EYE zuh, a head cold)
atelectasis
at ih LECK tuh sis
collapse of lung tissue or an entire lung
incomplete dilation of the lungs
bronchiectasis
brong kee ECK tuh sis
chronic, abnormal dilation of the bronchi
typically caused by bacterial infection, which weakens the walls of the bronchi. Pus-filled (purulent) material then collects within pockets of the damaged bronchial walls
may be caused by an obstruction, below which the bronchial walls become distended
symptoms include dyspnea, expectoration of foul-smelling sputum, and coughing

bronchiolitis
viral inflammation of the bronchioles
more common in children <18 mos
bronchitis
inflammation of the bronchi
may be acute or chronic
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
respiratory disorder characterized by progressive and irreversible diminishment in inspiratory and expiratory capacity of the lungs
symptoms include dyspnea on exertion (DOE), difficulty inhaling or exhaling, and a chronic cough
cystic fibrosis
inherited disorder of the exocrine glands resulting in abnormal, thick secretions of mucus that cause COPD
emphysema
abnormal condition of the pulmonary system in which alveoli are distended and destroyed after exposure to tobacco smoke or environmental toxins
most common cause is tobacco smoking, but exposure to environmental particulate matter may also cause the disease
Fig A

flail chest
condition in which multiple rib fractures cause instability in part of the chest wall
the lung under the injured area contracts on inspiration and bulges out on expiration
hemothorax
blood in the pleural cavity, which causes the lung to collapse
Fig A

influenza
acute infectious disease of the respiratory tract caused by a virus
AKA flu
avian flu is caused by type A influenza virus
pleural effusion
abnormal accumulation of fluid in the intrapleural space
Fig C

pleurisy
PLOOR ih see
inflammation of the parietal pleura of the lungs
may be caused by cancer, pneumonia, or TB
pneumoconiosis
noo moh koh nee OH sis
loss of lung capacity caused by an accumulation of dust in the lungs
types may include:
- asbestosis - abnormal condition of asbestos in the lungs
- silicosis - abnormal accumulation of glass dust in the lungs
- anthracosis - abnormal accumulation of coal dust in the lungs (AKA black lung disease, coal workers’ pneumoconiosis [CWP]) - Fig B

pneumonia
inflammation of the lungs caused by a variety of pathogens
if infectious, pneumonia
if noninfectious, pneumonitis
the names of the lobes are used to describe the extent of the disease (e.g., RML pneumonia is pneumonia of the right middle lobe). if both lungs are affected, termed double pneumonia
pneumothorax
air or gas in the pleural space causing the lung to collapse
Fig B

pulmonary abscess
localized accumulation of pus in the lug
pulmonary edema
accumulation of fluid in the lung tissue
often present in congestive heart failures, it is caused by the inability of the heart to pump blood
pyothorax
pus in the pleural cavity
AKA empyema (em pah ee ma)
respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
sin SISH uhl
acute respiratory disorder usually occurring in the lower respiratory tract in children and upper respiratory tract in adults
most common cause of bronchiolitis and pneumonia in infants and highly contagious in young children
severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)
viral respiratory disorder caused by a coronavirus
usually results in pneumonia
tuberculosis (TB)
chronic infectious disorder caused by an acid-fast bacillus, Mycobacterium tuberculosis
transmission is normally by inhalation or ingection of infected droplets
multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR TB) is fatal in 80% of cases
chronic bronchitis
repiratory disorder in which there are inflammatory changes to and narrowing of the bronchi, causing airflow limitation
distinguished by excessive production of mucus and a recurrent cough
onset is slow, progressive, and continuous
associated with cigarette smoking, infection, and inhaled irritants
treatment involves avoidance of irritants and use of expectorants and bronchodilators to help decrease the inflammation and any further production of mucus. If not initiated early, then disease progresses much more rapidly
expectorants
agents that help expel mucus
mucous gland adenoma
a benign tumor of the mucous glands of the respiratory system
papilloma
a benign tumor of epithelial origin named for its nipplelike appearance
pulmonary hamartoma
a benign tumor of limited abnormal tissue formed in the respiratory tract
AKA chondroadenoma
non-small cell carcinoma (NSCLC)
most prevalent type of lung cancer
adenocarcinoma
a type of NSCLC derived from the mucus-secreting glands in the lungs
large cell carcinoma
a type of NSCLC originating in smaller bronchial lining
squamous cell carcinoma
a type of NSCLC originating in the larger bronchial squamous epithelium
mesothelioma
a rare malignancy of the pleura or other protective tissues that cover the internal organs of the body
often caused by exposure to asbestos
small cell carcinoma (SCLC)
2nd most common type of lung cancer
usually associated with smoking
AKA oat cell carcinoma
-ectasis
dilation
-ptysis
spitting
tel/o
complete
hamart/o
defect
coni/o
dust
-drome
to run
auscultation
aw skull TAY shun
the process of listening to sounds within the body
percussion
the process of tapping the body for diagnostic purposes
stethoscope
a commonly used instrument to listen to sounds within the body, especially the chest
chest x-ray (CXR)
one of the most common imaging techniques for the respiratory system
used to visualize abnormalities of the respiratory system
lung perfusion scan
nuclear medicine test that produces an image of blood flow to the lungs
used to detect pulmonary embolism

lung ventilation scan
test using radiopharmaceuticals to produce a picture of how air is distributed in the lungs
measures the ability of the lungs to take in air
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
computerized imaging that uses radiofrequency pulses to detect lung tumors, embolisms, and chest trauma
pulmonary angiography
imaging of the lungs with a dye injected into the blood vessels of the lung, followed by subsequent x-ray imaging to demonstrate the flow of blood through these vessels
bronchoscopy
endoscopic procedure use dto examine the bronchial tubes visually

laryngoscopy
endoscopic procedure used to visualize the interior of the larynx
mediastinoscopy
endoscopic procedure used for visual examination of the structures contained within the space b/w the lungs
arterial blood gases (ABG)
blood test that measures the amount of O2 and CO2 in the blood
Mantoux skin test
mon TOO
intradermal injection of purified protein derivative (PPD) used to detect the presence of tuberculosis antibodies
sputum culture
cultivation of microorganisms from sputum that has been collected form expectoration
sweat test
method of evaluating sodium and chloride concentration in sweat as a means of diagnosing cystic fibrosis
throat culture
cultivation of microorganisms from a throat swab to determine the type of organism causing a disorder
pulmonary function tests (PFT)
procedures for determining the capacity of the lungs to exchange O2 and CO2 efficiently
peak flow meter
instrument used in a pulmonary function test (PFT) to measure breathing capacity
pulse oximetry
ock SIM uh tree
test to measure oxygen in arterial blood, in which a noninvasive, cliplike device is attached to either earlobe or the fingertip
spirometry
spy ROM uh tree
test to measure the air capacity of the lungs with a spirometer (spy ROM ih tur)
ventilator
a machine that assists a patient with respiration
positive pressure breathing (PPB) is the delivery of air at greater than atmospheric pressure to the lungs using a ventilator
continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP)
ventilation therapy that keeps airways open by providing air at greater than normal atmospheric pressure
may be accomplished through a cannula or a facial mask
endotracheal intubation
passage of a tube through the mouth into the trachea to ensure a patent (open) airway
bronchoplasty
surgical repair of a bronchial defect
rhinoplasty
surgical repair of the nose for either health care or cosmetic reasons
septoplasty
surgical repair of the wall between the nares
sinusotomy
incision of a sinus
thoracocentesis
thor ah koh sen TEE sis
aspiration of a fluid from the pleural space
AKA pleruocentesis, thoracentesis
tracheostomy
opening through the neck into the trachea, through which an indwelling tube may be inserted either temporarily or permanently

tracheotomy
incision made into the trachea below the larynx to gain access to the airway
usually as an emergency procedure
cannula
CAN yoo luh
a flexible tube for insertion into a duct, cavity, or vessel to drain fluid or deliver medication
adenoidectomy
excision of the pharyngeal tonsils, or adenoids
laryngectomy
excision of the voice box
pulmonary resection
excision of a portion or a lobe of the lung or the entire lung
lobectomy = when an entire lobe is excised
pneumonectomy = when the entire lung is excised

tonsillectomy
excision of the palatine tonsils
pneumonectomy
the excision of an entire lung
lobectomy
excision of an entire lobe
CWP
coal workers’ pneumoconiosis
LLL
left lower lobe
LUL
left upper lobe
MDR TB
multidrug-resistant tuberculosis
PPB
positive pressure breathing
delivery of air at greater than atmospheric pressure to the lungs using a ventilator
PPD
purified protein derivative
RLL
right lower lobe
RML
right middle lobe
RUL
right upper lobe


