Vascular Disease Flashcards
Describe the findings

DVT
- US images:
- thin walled vein + not collapsible with compression –> DVT

What are other significant doppler/US findings of LE DVT?
- anechoic thrombus
- increased venous diameter
- loss of phasic flow with breathing
- augmentation with calf squeeze
- absence of color flow
Describe US findings:
- Baker’s cyst
well-circumscribed mass + echolucent center
Describe US findings:
- arterial stenosis
- atheroma and stenosis are visualized
- confirmed by spectral Doppler –>
- significant increase in velocities (flow accelearation)
Describe US findings:
- Polyarteritis nodosa
- small aneurysms
- beads of a rosary (“rosary sign”)
- most commonly involved organ = kidney
How does large artery atherosclerosis lead to cerebral ischemia?
- thromboembolism from the atherosclerotic plaque
-
direct occlusion of the penetrating arteries by the plaque
- especially in the case of intracranial atherosclerosis
- hemodynamic perturbations <– plaque related stenosis
What is the Class I indication for carotid endarterectomy?
TIA / CVA « 6 months secondary to –>
moderate to severe ( ► 50% stenosis ) extracranial carotid stenosis
What is an alternative to carotid endarterectomy?
- symptomatic ( CVA / TIA « 6 months)
- moderate-severe ( ► 50% stenosis)
Endovascular stenting (Class IIa)
- should be reserved for highly selected cases with:
- extracranial vertebral artery stenosis
- limited evidence
Describe the difference in treatment and outcomes for intracranial atherosclerotic disease:
- medical therapy
- endovascular stenting
- stenting has worse outcomes compared to best medical therapy
- should only be performed when best medical therapy has failed
What are the recommended first line antiplatelet therapies for secondary prevention of ischemic stroke?
- ASA
- Clopidogrel
- ASA/extended-release dipyridamole
****DAPT is not recommended over monotherapy with any of these agents
What is the mortality rate associated with?
- Type A aortic dissection
- aortic root / SoV involvement
- Without operation:
- First 24 hours –> 1-2% / hour
- First 48 hours –> 50%
What is the mortality associated rate?
- Type B aortic dissection
- In-hospital –> 8%
- 5 years –> 60-80%
Describe the initial treatment strategy for acute aortic dissection?
- Decrease wall stress by controlling:
- HR
- LV contractility
- change in pressure / change in time [dP / dT]
- Beta blockers
What BB’s are utilized in the acute aortic dissection?
- Metoprolol
- Labetalol
- Esmolol
- Propanolol

What are the indications for TEVAR in type B aortic dissection?
- Malperfusion syndrome (end-organ ischemia)
- Early expansion
- Rupture
- Refractory pain
What are the indications for surgery?
- Acute
- Type A dissection
All patients
What are the indications for surgery?
- Acute
- Type B dissection
- Rupture
- Rapid Aneurysm Expansion
- Extension
- Malperfusion syndrome
- Marfan Syndrome?

What are the indications for surgery?
- Chronic
- Type A dissection
- ► 5.5 cm
- ► 1 cm / year increase in dimension
- Severe AR
- Symptoms suggestive of:
- expansion or
- compression

What are the indications for surgery?
- Chronic
- Type B dissection
- ► 6 cm
- ► 1 cm / year increase in dimension
- Symtpoms suggestive of:
- expansion or
- compression

What are three genetic risk factors / mutations for aortic aneurysm and dissection?
- FBN1
- fibrillin-1 gene
- Marfan’s syndrome
- TGFB1-2
- transforming growth factor beta 1 and 2 gene
- Loeys-Dietz syndrome
- COL3A1
- Collagen type 3 alpha 1 gene
- Vascular Ehlers-Danlos
What patients are at increased risk of PAD?
- Age ► 65 years
- Age 50-65 years + risk factors (DM, tobacco abuse, dyslipidemia, HTN) or FH PAD
- Age < 50 years + DM and 1 additional risk factor for atherosclerosis
- Known ASCVD in another bed
- coronary, carotid, subclavian, renal, mesenteric artery stenosis, AAA
Describe the diagnostic testing algorithm for suspected PAD?

What is the next step?
- history or PE suggestive of PAD
- ABI > 1.4 (noncompressible vessels)
Toe-brachial index (TBI)
- « 0.70 = abnormal
What is the mortality associated with a diagnosis of PAD?
- 5- year risk of CV death –> 25-30%
- Nonfatal MAACE –> 20%
What are the benefits of exercise ABI?
- Diagnosing PAD in patients with:
- claudication and
- normal ABI at rest
- Discriminating claudication from pseudoclaudication
- Assessing functional capacity
What constitutes further anatomic assessment in PAD?
When should this be performed?
- Duplex US, CTA, MRA or invasive angiography
- Performed with revasculrization is planned
What patient should be screened for PAD?
- 52-year old woman with pale feet when lying in bed, reddish color when standing
- 84-year-old woma with a draining ulcer over the medial malleolus
- 73-year-old man with pain and tingling in both legs while walking, reduced with bending forward
1. - 52-year-old woman with pale feet when lying in bed, reddish color when standing
- elevation pallor and dependent rubor –> PAD
- 84 year old with draining ulcer –> venous insufficiency ulcers
- arterial ulcers tend to be dry
- 73-year old with tingling in both legs bending over
- neurogenic claudication –> spinal stenosis
Describe the findings

Raynaud phenomenon
- exaggerated vascular response to cold temperature or emotional stress
- Secondary RP - triggers:
- Autoimmune diseases
- systemic sclerosis
- SLE
- mixed connective tissue disease
- Sjogren syndrome
- dermatomyositis/polymyositis
- Drugs / Toxins
- BB
- Clonidine
- Sympathomimetics
- Stimulants (Methamphetamines)
- Cyclosporine
- Cisplatin
- Bleomycin
- Autoimmune diseases

What are the indications for carotid duplex prior to CABG?
- > 65 years of age
- LM stenosis
- PAD
- Tobacco abuse (history of)
- TIA/CVA (history of)
- Carotid Bruit
Describe the findings

Cholesterol emboli syndrome (CES)
- nonspecific symptoms
- livedo reticularis
- renal failure
- mesenteric ischemia
- Treatment:
- supportive
- increase statin therapy

What is the most common cause of atheroembolism?
iatrogenic - > 70%
- secondary to catheter-based angiography or vascular surgery
What is diagnostic of obstructive PAD on exercise ABI?
decrement of > 20%
- functional testing is important to evaluate for PAD in patients with exertional symptoms (Class I)
What is the BP goal in acute ischemic stroke?
- no thrombolytics
< 220 / 110 mmHg
- should be tailored based on comorbid conditions
What is the BP goal in acute ischemic stroke?
- thrombolytics given
- prior to administration of thrombolytics = < 180 / 110 mmHg
- 24 hours post-thrombolysis = < 180 / 105 mmHg
What is the window for tpa in acute ischemic stroke?
< 4.5 hours
Define acute limb ischemia (ALI)
- vascular emergency
- requires rapid assessment of, to determine limb viability and salvageability:
- arterial perfusion
- venous perfusion
- sensory function
- motor function
- revascularization is performed emergently
Describe diagnostic testing, findings and treatment of ALI:
- Category I: Viable limb
- Dopplers:
- Audible arterial
- Audible venous
- Category I: Viable limb
- Normal motor function
- No sensory loss
- Intact capillary refill
- Urgent (Class I)
- Anticoagulation
- Revascularization

When should limbs be revascularized in ALI?
- Viable limbs –> within 6-24 hours
- Threatened limbs –> « 6 hours
Describe the diagnostic/treatment algorithm for ALI

Describe diagnostic testing, findings and treatment of ALI:
- Category IIa: Marginally threatened
- Dopplers:
- Inaudibale arterial
- Audible venous
- Motor/Sensory function assessment:
- Intact motor function
- Sensory loss limited to toes if present
- slow-to-intact capillary refill
- Emergent (Class I) - salvageable if treated promptly
- Anticoagulation
- Revascularization

What is the diagnosis?
- acute ischemic cerebral syndrome (R hemiparesis)
- preceded by:
- neck pain
- ptosis
- miosis
carotid dissection
- Horners syndrome –>
- Ptosis and Miosis
- symptoms are the result of distension of nerve fibers on the outer surface of the internal CA
- 25% of cases
Describe diagnostic testing, findings and treatment of ALI:
- Category III: Irreversible
- Dopplers:
- Inaudibale arterial
- Inaudible venous
- Motor/Sensory function assessment:
- Complete loss of motor function
- Complete sensory loss
- Absent capillary refill
- Emergent (Class I)
- Primary amputation

Describe the findings post-PCI?
What is the best way to confirm the diagnosis?

- Cholesterol Embolization Syndrome (CES)
- Biopsy
- only for clinical situations in which diagnosis is unclear

What is the appropriate screening recommendation for AAA based on size at diagnosis?
- > 2.5 cm - < 3 cm –> 10 years
- 3 cm - 3.9 cm –> every 3 years
- 4 cm - 4.9 cm –> every 12 months
- 5 cm - 5.4 cm –> every 6 months
What are the indications for elective repair of an asymtpomatic AAA?
- > 2.5 cm - « 5.5 cm;
-
► 5.5 cm –> repair
- women (consider) ► 5.0 cm
-
► 5.5 cm –> repair
- Rapid expansion; and
- AAA associated with peripheral arterial aneurysms or PAD
What are treatments to improve symptoms of claudication in PAD?
- supervised exercise program
- Cilostazol
- contraindicated in heart failure
- Endovascular therapy
- effective and reasonable in patients with inadequate response to exercise and medical therapy
Describe diagnostic testing, findings and treatment of ALI:
- Category IIb: Immediately threatened
- Dopplers:
- Inaudibale arterial
- Audible venous
- Motor/Sensory function assessment:
- Mild or moderate muscle weakness
- Sensory loss more than toes and with rest pain
- slow-to-absent capillary refill
- Emergent (Class I) - salvageable if treated emergently
- Anticoagulation
- Revascularization

Define critical limb ischemia (CLI)
- chronic ( > 2 week) ischemic rest pain
- nonhealing wound/ulcers or gangrene in one or both legs
- attributable to objectively proven arterial occlusive disease

What are the requirements to proceed with PFO catheter closure?
- embolic-appearing ischemic stroke
- without other etiology despite adequate testing
- 18-60 years of age
What is the recommendation for anticoagulation in cryptogenic stroke with presence of PFO?
Not recommended (Class III harm)
- unless other indication present (A-fib, h/o DVT, mechanical heart valve)
Describe the findings

- Incorrect electrode placement ( +1 )
- abrupt R-wave increase in lead V2 followed by much smaller R wave in V3
- V2 is actually V6
-
Atrial tachycardia ( +4 )
- P-waves of sinus origin should be positive in lead II
- PVC’s ( +1 )
- Inferior MI, age indeterminant or probably old ( +1 )
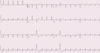
Describe the findings

- Atrial flutter ( +4 )
- LAD ( +1 )
- LVH ( +1 )
- RVH ( +1 )
- RBBB, incomplete ( +1 )

Describe the findings

- NSR ( +1 )
- LAE ( +1 )
- AV block, second degree, Mobitz I (Wenckebach) ( +4 )

Describe the findings

- NSR ( +1 )
- AV block, second degree, Mobitz I (Wenckebach) ( +4 )
- LAD ( +1 )
- IVCD, nospecific type ( +1 )
- QRS slightly widened (approximately 115 ms) but criteria for LBBB are not met

Describe the findings

- NSR ( +1 )
-
PAC’s ( +2 )
- single dropped beat toward the end of the tracing
- T-wave preceding this dropped beat has a slightly different morphology
- PAC burried within the T wave –> dropped beat

Define May-Thurner syndrome
- rarely diagnosed condition in which patients develop ileofemoral DVT and recurrent DVTs
- anatomical defect:
- the R common iliac artery overlies and compresses
- the left common iliac vein against the lumbar spine
- present in > 20% of the population
What are common risk factors / presenting symptoms in May-Thurner syndrome?
- scoliosis
- pregnancy (recent)
- OCP
- LLE DVT’s (rather than RLE DVT’s)
- LLE swelling (in the absece of DVT’s)
- female sex
What is the best method of diagnosis in suspected May-Thurner syndrome?
CT or MR venography of the pelvis
- gold standard –> contrast venography
- has been replaced due to its invasive nature
What is the recommendation for screening in family members of a patient with?
- bicuspid aortic valve
- aortic aneurysm
CTA or MRA of aorta in first-degree relatives
- especially when a family history of thoracic aortic aneurysm and/or aortopathy
Define critical limb ischemia (CLI)
severe PAD associated with:
- rest pain
- nonhealin ulcers
- gangrene
What is the recommendation for DAPT in severe PAD (CLI)?
not recommended
- has not been demonstrated to provide incremental benefit
What is the diagnosis and next best step?
- 78 year old woman
- HA’s, visual disturbances, jaw fatigability with chewing, shoulder stifness
- Giant cell (temporal) arteritis
- large-vessel vasculitis
- Temporal biopsy
What is the diagnosis and next best step?
- 38 year old woman
- tobacco abuse and ulcers on fingertips
Buerger’s disease (thromboangitis obliterans)
- most important therapy = smoking cessation
What is the diagnosis and next best step?
- 28 year old Asian woman
- mild fevers and arm fatigue when brushing her hair
Subclavian stenosis / possible Takayasu arteritis
What are the recommendations for surgery for TAA disease based on size and rate of growth of aneurysm?

What are the recommendations for medical thearpy in TAA?
- BB (atenolol)
- ARB/ACE (losartan)
Describe Takayasu Arteritis
- < 50 years of age
- 80-90% are women
- inflammation (thickening) of:
- aortic arch
- and stenosis of its branches
What laboratory test may help in the diagnosis of cholesterol embolization syndrome?
Urine eosinophils
When calculating ABI, what brachial BP should be used?
higher of the two
- subclavian stenoses may cause decreases BP in one arm
What is the diagnosis and next best step?
- 75 year old woman with severe substernal chest pain
- PMH: HTN, dyslipidemia, prior carotid endarterectomy
- Meds: ASA, Rosuvastatin, Carvedilol, HCTZ
- VS: HR 98, BP 169/102
- Labs: Troponin negative
- CT: crescentic, high attenuation area measuring approximately 3 mm in diameter in the posterior ascending aorta, that does not enhance with contrast. No involvement of the great vessels or arch. No intimal flap or compression of the lumen.
- Type A intramural hematoma (IMH)
-
Emergent surgical consultation
- high risk of rupture
- mortality with medical therapy alone ~40%
What medications are contraindicated in acute aortic syndromes?
Vasodilating drugs - Hydralazine
- should not be given prior to adequate beta-blockers
- Class III recommendation
What are the “5 Ps” of limb ischemia?
- pain
- pallor
- paralysis
- pulselessness
- paresthesia
What are the types of acute aortic syndromes?
- Aortic dissection
- Intramural hematoma
- Penetrating aortic ulcer
- Rapid Aneurysm expansion
- Aortic Rupture

Why is vitamin K not the reversal agent of choice in intracranial hemorrhage?
- slow reversal
- earliest effect on INR in 2 hours
- peak effect 6-12 hours
What is the agent of choice for reversal?
- acute cerebral hemorrhage
- warfarin use
- INR 3
4F-PCC 1500 units
- contains purified vitamin K-dependent clotting factors
- do not require ABO compatibility and can be stored at room temperature
- dosing:
- INR and
- bodyweight

What is the reversal agent for Dabigitran?
Idarucizumab
Describe the findings

- NSR ( +1 )
- AV junctional rhythm / tachycardia ( +1 )
- AV block, third degree ( +4 )
- Inferior MI, age recent or probably acute ( +4 )

Describe the findings

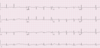
- NSR ( +1 )
- LAE ( +1 )
- AV block, second degree, Mobitz II ( +4 )
- Nonspecific ST and/or T wave abnormalities ( +1 )
Define posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES)
- acute encephalopathy that appers to be related to disordered cerebral autoregulation and endothelial dysfunction
- acute severe hypertesion (beyond upper limits of cerebral autoregulation) –> Vasogenic edema
-
MRI brain
- focal bilateral areas of cerebral edema
- posterior portion of the brain (particularly occipital lobes)


