Nuclear - Test Review Flashcards
How often is a dose calibrator checked:
- linearity
quarterly
A bar phantom is used to assess this?
How often is this checked?
- Linearity and Spatial Resolution
- Weekly
What is the equivalent dose of 1 Curie:
- Bq or becquerels
1 Curie = 3.7 x 1010 radioactive decays per second
What is the permissible breakthrough of Molybdenum-99 per mCi of Tc99m?
0.15 microcurie (μCi) of M-99 per 1 mCi of Tc99m
What is the half-life?
- Dobutamine
- Rubidium-82
- N13
- Dobutamine –> 2 minutes
- Rubidium-82 –> 75 seconds
- N13 –> 10 minutes
What radiotracer has the lowest extraction fraction?
Tc99m Tetrofosmin
What radiotracers act as potassium analogs when taken up into the myocardial cells?
- Rubidium
- Thallium
What is the next step:
- LBBB on EKG
- Exercise MPI –> perfusion defect in lateral wall
coronary angiogram
- perfusion defect in lateral wall not septum
What is the diagnosis in a patient with CABG who presents with chest pain and septal ischemia on MPI?
native vessel disease (not graft occlusion)
What can cause clear N13 perfusion images and blurry FDG-F18 metabolism images?
Diabetes
- insulin resistance?
What does gating improve when added to MPI?
specificity
Describe the difference in sensitivty/specificty between MPI radiotracers:
- Tc99m sestamibi
- Tl201 thallium
- Sensitivity –> similiar between the two
-
Specificity –> Tc99m significanty better
- further enhanced by gating
What is the effect on EF if you utilize 8 frames instead of 16 frames?
underestimate of EF
How do vasodilators work in stress testing?
differential hyperemia?
How do vasodilators induce ischemia?
vasodilatation of healthy arteries
Why can’t you image Tc99m and Tl201 at the same time?
Photopeak crossover
A ramp filter will remove this type of artifact?
star artifact
- marked streaking in an area with intense radionuclide emission
What is the effective half life of Tc99m if biological T1/2 = 3 hours?
TE = 1/3 + 1/6
TE = 1 / 0.5
TE = 2
TE = TB + TP
- TE = Effective half life
- TB = Biologic half life
- TP = Physical half life
What interaction occurs at a PMT?
photon converted to an electron
What is the units for diastolic function via MUGA?
end diastolic volumes / second???
How often is constancy checked?
daily
Describe recommendations for RNA (MUGA). Initiating and monitoring Adriamycin (Doxorubicin) therapy

Describe the finding:
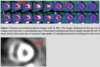
Pericardial effusion

What is the radiotracer for fatty acid metabolism?
C11-Palmitate
What is the effective annual dose limit for the public, infrequent exposure?
1 mSv (100 mRem or 0.1 Rem)
What is the diagnosis if:
- stress perfusion defect
- normal wall motion and EF
ischemia
- patients are imaged a while after stress so the EF recovers
What is the greatest determinant of radiation exposure?
radiotracer half-life
- shorter half life –> lower Sv
- don’t pick lower mCi administered
NTG enhances assessment of viability with which radiotracer?
Tc99m Sestamibi
What is one requirement of radioactive material delivery to a lab?
someone must receive it
What is the most frequently used radiotracer for linearity dose calibration?
Tc99m (Sestamibi)
If exposure rate is 1R / hr at 1 meter
What is the exposure rate at 3 meters?
0.111
I1 (d1)2 = I2 (d2)2
1 = I2 (9)
1 / 9 = I2
I2 = 0.1111
-
Inverse square law
- intensity (exposure, I1) = 1 / d2
- I1 (d1)2 = I2 (d2)2
How should the inverse square law be applied in patients with two separate distances and a set dose rate?
I1 (d1)2 = I2 (d2)2
Where is Tc99m sestamibi incorporated in the cell?
mitochondria
What chamber is used for dose calibration?
ionization chamber
What is the diagnosis of a hot spot in the LV cavity near the left lateral wall on SPECT?
papillary muscle
What happens to LVEF on MUGA if the background is over the spleen?
overestimated LVEF
What is the diagnosis of a patient with LAD and RCA stents presenting with chest pain?
MPI SPECT with ischemia in the anterolateral wall?
progressive disease of the RI
***Diagonal not a choice
What is the next step:
Patient preesents to ED with chest pain –> rest spect performed at this time shows AC corrected images with inferior defect
coronary angiogram
ERNA relies on this?
uniform labeling of the blood pool
Where is spatial resolution best in regards to the collimator?
at the face of the collimator
When can you dispose of radioactive waste?
when activity is similar to background radiation
Which Butterworth filter produces the most noise?
one with the highest frequency allowed
What is the effect as you move away from a collimator:
- Sensitivity
- Count density
- Resolution
- Sensitivity and Counts –> remain the same
- Resolution –> decreases
In the in vivo method of RBC labeling, when are stannous pyrophosphate and Tc99m pertechnetate injected?
Stannous pyrophosphate
given ~20 minutes prior to
Tc99m pertechnetate
What is one finding seen on patients with ASD repair?
Why?
Paradoxical septal motion
prior open heart surgery
What is the bias when a lab has:
- high sensitivity
- low specificity (40%)
Post-referral bias
- occurs when patients with abnormal stress test results are referred to cardiac catheterization at a higher rate than are patients with normal stress test results
What are the best radiotracers for quantitating myocardial blood flow and perfusion?
- O15
- N13
Describe the ischemic cascade
- Perfusion abnormalities
- Diastolic Dysfunction
- Strain abnormalities
- Systolic dysfunction
- EKG abnormalities
- Angina

In the setting of acute MI what does a perfusion defect on rest SPECT represent?
Infarct; Ischemia; Stunning; Area at risk.???
What scale should always be utilized for interpretation of SPECT?
Linear scale
What is the downside of sigmoidal (nonlinear) vs. linear scales?
- gradual changes in uptake are seen better than when using sigmoidal (nonliear scales)
- small defects may be missed
When are logarithmic scales utilized?
regions with lower count density (RV)
- not used for evaluation of regional differences in LV tracer uptake
The principle of thickening assessment in gated SPECT images from end-diastole (count poor) to end-sytole (count rich) is based on what principle?
Partial volume averaging
- basis of assessing thickening of myocardial segments is based on the brightening between end-diastolic to end-systolic images related to partial-volume effect reflective of the limitations of spatial resolution of the gamma camera
- This results in relative increase in count intensity manifested as brightening used by different vendor programs to quantitate degree of thickening
Selective use of angiography after SPECT imaging as compared to direct angiography in patients with stable angina results in:
What is the effect of mortality/outcomes/cost?
lower cost
- END study
- showed that cost was significantly reduced in those who underwent cath-only based on MPI results
- direct catheterization group –>
- same mortality
- higher cost
When performing a dipyridamole stress MPI study, after the 4-minute dipyridamole infusion, what is the recommended time delay before injecting the radiotracer?
5 minutes
- maximum vasodilation of dipyridamole is 287 +/- 101 seconds
- radiotracer injection should not be injected until 3-5 minutes following dipyridamole injection
What tools/activities provide the greatest improvement in appropriate use of MPI?
- Clinician feedback regarding performance
- Clinical decision support tools
- probably the most powerful
What will be the result of increasing the number of frames from 8 to 16 in a gated MPI study (leaving all other parameters the same)?
decrease the counts per frame
- because the set number of counts are divided into double the number of frames
- there is a decrease in the counts per frame
What is the affect on the following as a result of increasing the number of frames from 8 to 16 in a gated MPI study (leaving all other parameters the same)?
- Temporal resolution
- Spatial Resolution
- Counts per frame
- Ejection fraction
- Temporal resolution –> increase
- more points sampled over a period of time
- Spatial Resolution –> unchanged
- Counts per frame –> decrease
- set number of counts divided by a double number of frames
- Ejection fraction –> increase
Describe the findings and next step:
- 45 year old male with pleuritic chest pain after exertion
- Serial EKG/Troponin negative
- Resting MPI (while having active chest pain) with LVEF 60%

discharge and plan elective outpatient stress imaging
- Resting images –> no perfusion defects
- while having active chest pain –> nonischemic etiology
What study supports acute rest MPI studies in the ER?
ERASE
- normal perfusion –> very low event rate
- can be safely and quickly triaged for discharge
What are the recommended (ASNC guidelines) acquisition parameters when using a conventional SPECT system to acquire a MPI study utilizing Tc99m tetrofosmin:
- Collimator
- Seconds per step
- Energy window on PHA
- Frames per cardiac cycle
- Collimator –> Low-energy, High-Resolution (LEHR) collimator
- Seconds per step –> 20s / step
- Energy window on PHA –> 20% energy window
- Frames per cardiac cycle –> 8 frames per cardiac cycle
Describe the findings and next step:
- 50 year old male training for a marathon, presents for abnormal EKG: RBBB
- Exercise SPECT: 1 mm ST depression at peak exercise x 12 minutes. EF 61% –> 62%, TID 1.13

cardiac catheterization
- SPECT: perfusion abnormalities in septum from base to apex
- likely proximal LAD disease
- Exercise capacity good but EKG changes of ischemia
- patient training for a high-intensity event
What is the minimum time interval after the VQ scan when a stress Tc99m sestamibi MPI scan can be performed?
24 hours
- half-life = 6 hours
- 4 half lives = 24 hours
- this number of half-lives should elapse between studies with similar tracers

B - 49 yo DM male with atypical CP and CAC > 100
- appropriate to perform a seqeuential stress RNI for those patients with a prior abnormal CCT calcium and agtston > 100
What is the cause of the septal defect:
- EKG: LBBB
- SPECT: fixed septal defect, EF 58%, HR 64 –> 78
- CTA: no CAD

Partial volume effects
- Hayat et al. study
- patients with LBBB + no CAD –> reduced septal thickness and thickening compared to posterior wall
- resting MBF was preserved
- partial volume effects + limited spatial resolution of SPECT (10-12mm) –> areas with end-diastolic thickness < 10 mm show perfusion defects
- as the count intensity changes in systole dictates thickening assessment, asymmetric reductions in septal thickening during systole observed in LBBB reduced recovery coefficients of detected counts –> accounts for the septal defect at rest unrelated to HR

What is the difference in septal defects associated with LBBB in vasodilator and stress MPI?
- Exercise –> reversible septal defect
- HR related decrease in blood flow
- Vasodilator –> fixed septal defect
- partial volume effects + decreased spatial resolution
What is a disadvantage of new solid-state cameras compared to conventional (A-SPECT) cameras?
Incidence of diaphragmatic attenuation
- likely due to higher resolution of the cameras and artifact associated with breathing
- respiratory gating has been shown to help
What are the radiotracers utilized for:
- ATTR
- AL
- ATTR –> Tc99m pyrophosphate (PYP)
- AL –> F18 florbetapir
- taken up by both AL and ATTR amyloid but cannot distinguish between the two
Where is the greatest response to vasodilatory stimuli seen?
coronary arterioles
- most responsive as they possess smooth muscle
- venules have less vasodilatory capacity and capillaries do not possess smooth muscle
Describe coronary microcirculatory physiology as it relates to
- myocardial blood volume
- myocardial perfusion defects
- at rest approximately 90% of myocardial blood volume is in capillaries and
- capillary resistance is the primary determinant of coronary vascular resistance
- Perfusion defects (on SPECT) are primarily felt to be related to elevation of capillary resistance and reduction in myocardial blood volume at the capillary level
- This leads to reduced isotope uptake due to capillary decruitment, which happens in response to epicardial coronary stenosis

C - 55 yo woman, BMI 44, no cardiac history, new SOB
- 2 day protocol is best used in the patient with large body habitus where high-dose stress-and-rest imaging could provide image quality for diagnostic purposes
- mainly reserved for large BMI

B - 2 day high-dose stress, high-dose rest exercise MPI
- No limitations for exercise
- Imaging is appropriate –> baseline ST, T changes
- High BMI ( > 35 ) –> 2-day high/high is protocol is recommended

D - asymptomatic woman with anomalous RCA from left cusp with interarterial course
- interarterial course –> high risk for sudden death
- recommend evaluating for provocable ischemia with imaging
What is the recommended stress testing for a patient with:
- mild, chronic stable angina and a small, mild perfusion defect two years ago
no testing
- chronic stable angina + mild ischemia (on SPECT) + no change in symptomatology –> continue medical management

D - 70 yo male with typical angina, weighs 320 lbs
- stress imaging is usually performed on day 1, so rest imaging can be avoided if the stress study is normal
- patients with prior MI, known CAD, LV dysfunction are not optimal candidates for stress-first imaging given expected higher frequency of abnormal test results
What is the weight cut-off for 2-day protocol to be performed?
> 250 pounds and/or BMI < 35 (generally)
What is the advantage of stress first imaging studies?
if normal –> can avoid rest imaging
What patients are stress-first imaging studies generally not recommended?
- prior MI
- known CAD
- LV dysfunction
****not optimal candidates for stress-first imaging given expected higher frequency of abnormal test results
Describe the findings and next step:

- SPECT findings:
- marked flattening of the septum (Movahed’s sign) –> related to RV/LV interdependence
- RV strain
- no significant LV perfusion defects
- CT scan of chest

What concept describes LV dyssyncrhony assessment by gated SPECT?
partial volume effect
- there is a relatively linear relationship between myocardial counts and thickening –> time activity curve of the myocardium is essentially a thickening curve
- The low fidelity curve derived from 8-16 time points is transformed into a continuous thickening curve by Fourier transformation
- Phase analysis of curves derived from different myocardial regions is then used to measure dyssyncrhony (regional variation in mechanical activation).
What is the cutoff for I123-mIBG heart-to-mediastinum (H/M) ratio that correlates with a worse prognosis in patients with CHF?
H/M < 1.60
What is generally recognized as a disadvantage of CZT SPECT technology compared to traditional sodium iodide Anger gamma cameras?
cost of CZT SPECT technology
- up front hardware cost is greater than traditional cameras
- higher efficiency and speed of imaging likely makes this approach more cost effective
What are advantages of CZT SPECT technology compared to traditional sodium iodide Anger gamma cameras?
- Higher energy efficiency
- Higher sensitivity
- Higher spatial resolution
- similar to PET
- Ability to perform ultra low-dose imaging protocols
- high diagnostic accuracy for detection of CAD in morbidly obese patients
How long should dobutamine infusion be continued after radiotracer injection?
60 seconds
In myocardial perfusion SPECT, what problem does resolution recovery algorithms attempt to correct?
depth-dependent image blurring
- by decompensating for the loss of resolution with increasing depth from the face of a parallel-hole collimator
What is the most important advantage of iterative reconstruction, ordered-subset expectation maximization (OSEM) over filtered backprojection?
Avoid ramp filter artifact
- ramp filter is not applied in iterative reconstruction
How does iterative reconstruction improve resolution?
- uses image-modeling physics to update image reconstruction and
- considers depth-dependent loss of resolution and scatter
What are warning and precaution recommendations for Regadenoson?
- Bronchoconstriction
- CVA (stroke)
- Seizures
- Myocardial ischemia
- A-fib / A-flutter
- SA / AV nodal block
- Hypersensitivity (including anaphylaxis)
- Hypotension
- Hypertension

B - may be appropriate
- based on:
- 1-2 clinical risk factors (DM and TIA)
- < 4 METS for the last 12 months
- intermediate risk surgery

What is the desired injection-to-scan delay time in patients receiving Tc99m-labeled MPI agents?
30-60 minutes
- cleared by the hepatobiliary system
- take 30-60 minutes to reach desired 1:1 heart-to-liver ratio
What is the desired injection-to-scan delay time in patients receiving Tl201-labeled MPI agents?
< 10 minutes
- cleared by the kidneys
- must be imaged < 10 minutes of injection due to redistribution
Why can physical-exercise stress injections be performed sooner than pharmacologic-stress?
reach the desired heart-to-liver ratio faster
- due to redistribution of splanchnic blood flow to skeletal muscles
What is effect of setting the energy window outside of 126-154 keV 20% on a conventional SPECT camer with Tc99m?
introduces more scatter and noise
What is one major limitation of myocardial perfusion studies using currently available agents for routine clinical SPECT imaging?
limited ability to be extracted by the myocardium at high flow rates

B
- Tl201 has a more linear relationship with myocardial blood flow and higher tracer uptake than Tc99m with either sestamibi or tetrofosmin

What radiotracer uptake effectiveness is most efficient with regards to coronary blood flow?
- O15
- Tc99m Teboroxime
- Tl201
- N13
- Rb82
- Tc99m-sestamibi
- Tc99m-tetrofosmin

Misregistration


cardiac catheterization
- SPECT study: normal
- Stress EKG: grossly abnormal
- submaximal stress
- High risk features on EKG
- ST elevation in VR and V1
- chest pain with exertion

After injection of Tc99m during stress MPI, patient develops flushing, chills, joint pain and SOB.
This is an example of failure of which quality control measure?
apyrogenicity
- allergic reaction typically caused by the presence of a pyrogen
- pyrogens include
- proteins or polysaccharide produced from metabolism of microbes
Define radionuclide impurity
presence of an additional radionuclide that does not cause an immediate reaction but may expose the patient to a significantly high radiation dose
Define chemical impurity
consists of the presence of unwated chemicals
- such as aluminum breakthrough from the Mo99 generator
- does not cause an immediate reaction
What will the radiation dose be at 2ft using 8mm lead?
- 1ft from point source = 32 mR/hr
- HVL lead = 4 mm
2 mR/hr
- I1 (d1)2 = I2 (d2)2
- 32 (1)2 = I2 (2)2
- I2 = 32/4 = 8
- 8 mm = 2 HVL (at 4mm)
- 8 mR/hr * 1/2 * 1/2 = 2 mR/hr
With positron decay, what happens to the number of protons in the nucleus?
decreases by 1
- proton is converted into a neutron (beta+ decay)
What Butterworth filter will produce images with the most noise?
higher frequency filter
- Butterworth is a low pass filter –> allows low frequency to pass through
- noise = high frequency
What is the effect of ramp filter on images?
Allows high frequency to pass through
- sharpens edges
- removes star artifact
- may introduce
- more noise
- ramp filter artifact
What is Butterworth filter used for?
Allows low frequencies to pass through
- blurs edges
- smoothens image
When using a parallel hole collimator, what happens to resolution when distance increases from 5cm –> 10 cm?
Resolution decreases
- number of counts –> unchanged
- sensitivity –> unchanged
- field of vision –> unchanged
What is the method by which radiotracers decay:
- Tl201
- Tc99m
- Tl201 –> electron capture
- Tc99m –> gamma decay
What is the half-life of F18-FDG?
110 minutes
What is the most important element for radiation exposure (for patient)?
physical half-life
What are thes steps if a major spill occurs?
- Close area and check for self-contamination
- Absorbent material over any spill
- Shield source if possible (only if can be done without further contamination)
- Close room and lock or secure area
- Inform radiation safety officer
- Survey and decontaminate (use mild soap…luke-warm water…surgical sponge)
What are the steps if a minor spill occurs?
- NOTIFY all persons in area a spill has occurred
- PREVENT - cover with absorben paper
- CLEAN - using gloves, tongs (remote handling)
- SURVEY - check spill and personnel
- RESPORT to RSO
What constitutes a major spill for the following radiotracers:
- Tc99m
- Tl201
- I123
- Tc99m –> 100 mCi
- Tl201 –> 100 mCi
- I123 –> 10 mCi
What is the prinicple of PET scanning?
conincidence imaging
What fluid is used to obtain Tc from Mo in the generator?
saline
Calculate the EF:
- EDV counts 25000 at 7.7 pixels
- ESV counts 10000 at 8.3 pixels
- Background counts 3000
LVEF = ED counts - ES counts / ED counts - background counts
- LVEF = 15 / 22 = 68%
What is the cause of an MPI study with excessive thyroid and stomach uptake?
Pertechnetate contamination
What is a normal resting LV myocardial blood flow?
- 0.7 - 1.2 mL/min/g
- parallels tissue O2 consumption
- Myocardial perfusion reserve > 2
- 1-year risk of cardiac death or MI is significantly lower
Describe the findings:

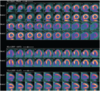
Inducibe ischemia in RCA distribution
- reversible prfusion defect consistent with stress-induced ischemia in the inferior and basal inferoseptal region
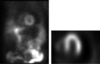
Describe the findings:

Severe perfusion defect in LAD distribution, with minimal reversibility on the rest images
- Perfusion defects of apical, apical septal, and apical anterior segments
- No hypoperfused myocardial regions with enhanced FDG uptake to suggest myocardial hibernation

Describe the findings:

Left Cfx
- Perfusion defects
- moderately severe lateral wall defect extending from the apex to the midcavity
- TID 1.33 - increased
- Angiography –> 70% stenosis in large OM1


D - Dual-isotope Tl201 / Tc99m
- Tl 201 given in 3-4 mCi dose with 72 hour half life –> ~27 mSv of radiation
- other 3 choices will give radiation exposure of < 15 mSv
- MDCT may be as low as 1-2 mSV
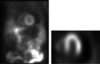
Describe the findings and diagnosis:
Pericardial Effusion
- lateral and right ventricular halo surrounding the heart on the projection image and can be seen on the HLA image
- distended stomach bubble below the heart
*

Why is water given after radiotracer injection (sometimes)?
distended stomach bubble below the heart –>
- usually result of giving the patient fluids to get greater separation between the inferior wall and gastric/intestinal activity that may be close to the heart
What radiotracers can be utilized for detection of a recent ACS?
-
Tc99m pyrophosphate
- retained in areas of healing infarction
- has been used to detect infarcts 3-7 days old
-
Tc99m Myoscint
- antibody directed to myosin that is exposed following acute damage
- detects earlier than Tc99m PYP
-
I-123 BMIPP
- fatty acid analog that is not taken up in areas of infarction due to cell damage
- areas surrounding ischemia at the the time of infarction also fail to use fatty acids and may overestimate the area of actual infarction

in vitro
- image shows excellent delineation of the ventricular blood volumes with very low background activity
- Based on excellent image quality, “in vitro” method is likely to give the best results and is the best answer

What is the most appropriate cardiovascular test to order for this patient?
- 35 yo female with atypical chest pain
- No CV risk factors
- EKG: NSR
Stress treadmill EKG
- Low pre-test probability –> could argue no testing needs to be done
- Stress EKG avoids risk of radiation and contrast reactions
Describe the findings:
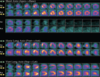
Abnormal due to CFx ischemia
- Images:
- moderate perfusion defect involving the entire inferior and inferolateral wall
- Angiography:
- LIMA-LAD: patent
- SVG-CFx: severe disease
- SVG-RCA: occluded


RCA and CFx infarct and ischemia
- Images:
- severe fixed perfusion defect in the inferior and inferolateral wall
- reversible peri-infarct ischemia as depicted by semi-quantitative analysis


No further studies are indicated
- excellent functional capacity
- MPI images:
- no evidence of ischemia or infarcts
- Semi-quantitative analysis of rest/stress images below

In the presence of hibernating myocardium, What EF indicates a decreased benefit from revascularization?
Why?
LVEF < 20%
extensive remodeling
What is the role of nitrates-enhanced Tc99m sestamibi testing to evaluate for hibernating myocardium?
Compare this to Tl201 rest/redistribution.
- reasonable test to evaluate for hibernating myocardium
- better positive and negative predictive value when compared to Tl201 rest/redistribution

What is the best test to predict improvement of LV function and survival?
- severe LV dysfunction and CAD
- scheduled for bypass surgery
no advantage of one test over the other
- MA (3,088 patients)
- no statistically significant difference in prediction of survival benefit with revascularization was detected between testing methods
- Improvement in survival was a function of:
- size of viable myocardium
- degree of LV dysfunction

Why should MPI be performed in asymptomatic diabetics?
- Higher risk for development of CAD
- CV disease is the leading cause of mobidity and mortality in diabetics
- Myocardial ischemia is more likely to be silent in diabetics
- Diabetic patients who sustain a MI are at higher risk for mortality than nondiabetic patients
What is the relationship between CAC score, mortality and DM
higher CAC score and higher mortality in patients with DM vs. non-DM
Patients with DM and CAC = 0 demonstrate:
very low and similar event rates at 5 years
- no further risk stratification is needed
- similar in patients with and without DM
What is one abnormal resonse to vasodilator (adenosine or regadenoson) MPI could you see in patients with DM?
bluted heart rate response compared to patients without DM
- attributed to cardiac autonomic neuropathy
When undergoing vasodilator MPI, what is the the relationship between:
- blood surgar
- HRR
direct relationship between blood sugar level and HRR
What are the effects of cardiac autonomic neuropathy that may be seen in diabetic patients?
- increase in the risk of heart failure progression
- increased incidence of diastolic dysfunction
- increased presence of silent ischemia
- impaired myocardial flow reserve
Describe the process of calcium deposition in the coronary arteries:
- sensitivity
- specificity
- calcium deposition is a late phenomenon in the atherosclerotic process
- reflection of earlier soft plaque rupture and subsequent healing
-
High specificity: indicator of plaque burden
- correlates well with extent of atherosclerotic plaque burden
- Poor sensitivity
When CAC is utilized in risk assessment of asytmpomatic patients, explain the relationship:
- Framingham risk score
- traditional risk markers
- Ethnic minority populations
- CAC provides incremental value for favorable or unfavorable risk stratification as compared to traditional risk factors like FRS
- MESA study
- this concept has been validated in ethnic minorities
-
CAC = 0
- predicts very low event rates irrespective of other risk factors
What is the difference in prediction of short-term event (1 year) rates between:
- CAC > 1,000
- MPI - very abnormal
- CAC > 1,000 –> 25%
- MPI - very abnormal –> 7.5%
****symptomatic or asymptomatic patients
What is the relationship between CAC and MPI SPECT in terms of risk prediction?
complementary in multiple studies
- normal SPECT MPI have low event rate irrespective of their calcium score
- high risk MPI SPECT + high CAC –> mortality 42%
- compared to 30% when only one abnormal
What is the event rate associated with normal MPI and CAC:
- < 100
- > 400 and < 1000
- > 1000
- < 100 –> no events
- > 400 and < 1000 –> 2.9x the event rate for CAC > 400
- > 1000 –> event rate > 10%
What are medications that should be held prior to pharmacologic stress testing?
- Caffeine
- Aminophylline
- Theophylline
- Dipyridamole
- L-arginine (nitrate precursor)
What are the benefits of combination of exercise with pharmacologic stress testing?
- decrease duration of side effects
- decrease liver activity
- improve sensitivity to detect ischemia
- provide incremental information about functional capacity
What is the most common adverse event with adenosine when used for pharmacologic stress testing?
Second-degree AV block (4.1%)
- Hypotension (1.8%)
- 3rd-degree AV block (0.8%)
- Bradycardia (0.2%)
What is the most common adverse event (although uncommon) with dipyridamole when used for pharmacologic stress?
Chest Pain (20%)
What is likely to cause an artifact in the inferior wall when a loop of bowel is close to the heart?
Filtered back projection
- use of a ramp filter during filtered back projection reconstruction will result in decreased counts in the wall of the LV closest to the hot area
Describe the effects of a hot liver or bowel and use of iterative reconstruction
will lessen the effect of a hot liver or loop of bowel
Describe the effects of a hot liver or bowel and use of resolution recovery
correction for the loss of resolution the further an object is from the detector
- should not influence the counts in an area
Describe the effects of a hot liver or bowel and use of scatter correction
- correction for the overrepresentation in counts due to misregistration of counts coming from a hot area close to the heart
- will decrease the total counts in the inferior wall
What type of patient / stress acuisition and processing will most likely result in normalization or scaling artifacts?
1-day rest/stress in an obese female patient
- scaling or normalization artifacts occur with greater frequency in low-count studies using fixed threshold filtering during reconstruction
- obese patients have greater attenuation resulting in lower counts, and this effect is greater when doing 1-day studies with split doses as opposed to 2-day studies when equal and higher doses are gien
- females have greater anterior wall attenuation due to the presence of breast tissue –> most likely to result in normalization problems or the creation of hot spots
How is the image quality improved when centering the heart in the gamma camera field of view during SPECT MPI acquisition?
Greatest uniformity
- center generally has the greatest unifromity of crystal and PMT’s
- at the edges of the field, light leaks due to poor contact between the PMTs and the crystal
How are the following affected when centering the heart in the gamma camera field of view during SPECT MPI acquisition?
- counts
- scatter
- attenuation
not affected - all are generally uniform across the field of view
What camera crystal materials gives the highest counts using the same injected dose of Tc99m?
CZT - highest response rate for SPECT
***BGO and LSO used in PET
What does TID threshold depend on?
- type of stress
- protocol used
- gender (or size of the LV)
What are the TID cutoff’s (in general)?
- Older systems:
- Exercise TID –> 1.14
- Vasodilator TID –> 1.23
- New (CZT camera) system:
- Exercise TID –> 1.16
- Vasodilator TID –> 1.29
Daily uniformity tests should acquire a minimum of how many counts?
- small field-of-view cameras
- large field-of-view cameras
- Small FOV cameras
- > 3,000,000 counts
- Large FOV cameras
- > 5,000,000 counts
How often is the QC measure performed:
- Energy peaking
daily
How often is the QC measure performed:
- Uniformity
daily
How often is the QC measure performed:
- SPECT phantom
quarterly
How often is the QC measure performed:
- Planar resolution and
- four quad linearity (bar) phantoms
weekly
How often is the QC measure performed:
- Plexiglass (Jaszczak) phantoms
quarterly
What is a common characteristic of radioisotopes disposed of with “Decay-In-Storage”?
What are common isotopes disposed of in this manner?
half-life < 120 days
- Tc99m, Tl201, F18, Mo99, Sr89
How often is the QC measure performed on a survey meter:
- calibration
annually
- to ensure that the meter responds appropriately to radiation
How often is the QC measure performed on a survey meter:
- source check
daily
- verifies that the instrument responds to a radioactive source
Radioactive packages must be monitored within what period following delivery?
3 working hours
- should be surveyed and wipe tested withiin 3 hours of receipt if during normal working hours
Radioactive packages must be monitored within what period following delivery when the facility is closed?
surveyed and wipe tested within 3 hours of the next business day


How is extrinsic uniformity of a gamma camera evaluated?
collimator (using a)
Extrinsic procedures using a gamma camera are performed using this?
sheet source
How is intrinsic uniformity of a gamma camera evaluated?
point souce (without a collimator)
How often is the QC measure performed:
- area surveys
at the end of each working day
How do Tc99m radiotracers causes scatter in MPI?
they are excreted into the duodenum where they cause scatter if they are close to the heart
What practice is utilized to give the greatest separation to give the greatest separation between the heart and GI tract with the least amount of attenuation?
soda
- increases intestinal motility or push the loops of bowel toward the pelvies when the patient is supine during acquisition and gravity causes layering
- Food, water and coffee have greater attenuation thatn carbonated beverages (mixture of liquid and gas causes less attenuation)
What is the recommendation for vasodilator stress testing in the setting of rapid A-fib?
cancel testing
- diagnose and manage A-fib prior to stress testing
- based on patient safety and lack of diagnostic accuracy as there is not a true baseline blood flow measurement
- Rest/stress studies should be performed under the same conditions
What is the diagnosis in patients with abnormal TID + normal perfusion?
usually normal
- Patients with DM and known CAD –> may represent higher risk
- High risk –> consider LHC
- Low risk –> medical management
What are the causes of TID with normal perfusion?
- Hypertension with LVH
- especially hypertensive BP response to stress
- Differences in HR between rest and stress acquisition
- Technical factors related to differences in acquisition, slice selection, tracer doses
What are the cut-offs and special considerations for TID?


C - Stress Echo
- exercise with nuclear imaging is not the best test due to low specificity associated with exercise-induced septal perfusion defects
- PET study will give the lowest radiation exposure but exercise may still be a problem

C - insist on repeat imaging
- repeating the study is the best method to get accurate results
- already exposed to radiation dose
- interpreting the study will not be diagnostic based on the large distance moved
- it is not possible to correct for side-to-side or horizontal motio
What are the effects of a ultra-high resolution collimator on total counts?
decreases the total counts
What gamma camera system is optimal for obtaining the LAO views of the heart on equilibrium radionuclide angiography or multiple gated acquisition (MUGA)?
single-headed small field of view
- Single-headed, SFOV
- not generally utilized for SPECT due to long acquisition times
- but provide greatest flexibility for angulation in MUGA studies
- Single-headed, LFOV
- extends too far toward the abdomen to allow angulation
- Dual-headed systems do not allow optimal positioning of the camera head relative to the patient that permits the best septal view LAO
- most are in a fixed 90-degree configuration and do not allow caudal tilt angulation, this limits the rotation
What is the diagnosis in a pateint who undergoes stress testing:
- EKG (pre-testing): normal
- EKG (post-testing): ST elevation in inferior leads
transmural ischemia
- ST elevations can localize territory of ischemia
- ST depressions –> do not localize


