CT - Chapter 6 Artifacts Flashcards
(60 cards)
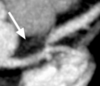
What is the arrow pointing at?

RV pacemaker leads - metal artifacts

What is one method of reducing image noise?
Increasing reconstructed slice thickness
- increases the amount of scintillation data used to construct each image –>
- image noise is reduced and overcome
What does the gantry rotation time define?
What artifacts does it affect?
- temporal resolution
- motion artifacts
- increasing rotation time –> reduces motion artifacts
How is tube current related to image noise?
increasing tube current –>
increases the photons per voxel –>
decreases image noise
How are image reconstruction kernels (filters) related to image noise?
smoother kernel/filter –> reduces image noise
sharper “edge-enhancing” kernels –> increase image noise
Describe the findings:

Beam Hardening Artifact
- occur when the photon beam is attenuated by a structure with especially high radiodensity (calcium, contrast, metal)
- A very low density hypoattenuated “streak” is seen adjacent to the high density structure

Describe the findings and diagnosis:
- 45 year old male with known CAD undergoes Cardiac CT to determine etiology of new onset cardiomyopathy
*

LV apical thrombus
- Important to distinguish this real finding from artifact, specifically beam hardening artifact (from mural calcium in this case)
- CT
- Batch reconstruction of sagittal sections through the LV
- LV apical thrombus which corresponds the the location of the patient’s wall motion abnormality (not shown)

Describe the findings:

Blood-contrast mixture
- SVC at the level of the insertion of the azygous vein
- serpiginous-appearing low-density within the SVC, and seeming to extend into the azygous, is not thrombus but the typical appearance of unopacified blood from one arm mixing with opacified blood from the other
- Common finding –> should not be mistaken for thombus

What artifacts typically degrade the quality of stent imaging?
- Beam Hardening artifacts
- Motion artifacts
- Partial volume artifacts
What is one artifact not typically associated with stent imaging?
Ring artifact
- seen when a detector is malfunctioning
What patient factor will always produce a non-diagnostic scan, and should always warrant pursuing an alternate testing modality?
inability to hold breath for the duration of the scan
- respiratory suspension is absolutely required during cardiac CT
- if a patient is unable or unwilling to hold their breath for the duration of the scan
- then the scan will be non-diagnostic and another testing modality should be used
Describe the findings related to reduced image quality:

Body habitus –> noise artifact
- example of excessive image noise –> renders coronary study non-diagnostic
- significantly increased “speckle” and noise within and surrounding each coronary image

Artifacts from dual chamber pacemaker leads MOST likely affect the image quality of the:
RCA
- one lead curls around in the RA and the second lead extends to the apex of the RV
Artifacts from Bi-V pacemaker leads MOST likely affect the image quality of the:
CFx
Describe the findings and most likely explanation for the discrepancy

The vessel line is incorrect
- such a stark discepancy between these orthogonal images should prompt a closer evaluation
- by examining the vessel line which is used to generate the curved MPR, one can see the vessel line is incorrect (travels outside of the contrast column)
- CT
- two images are orthogonal curved multiplanar reformats of the LAD and diagnoal branch
- Figure A - severe stenosis of proximal LAD
- Figure B - normal lumen caliber

Describe the findings:

Respiratory motion artifact
- coronary arteries are blurry and indistinct, indicating some kind of problem with the scan
- loss of detail is seen throughout the scan indicating most likely some kind of motion artifact
- Lung window:
- areas of streaking and “holes” (arrows) within the lung parenchyma adjacent to the contrast opacified vessels
- most consistent with motion of the lung parenchyma during the scan

Describe the findings:

Beam Hardening Artifact
- ventricular pacemaker lead that depicts two different artifacts:
- beam hardening
- motion
- due to high-density of metal skewing the energy profile of the incident photons
- error in reconstruction –> appears as very low-density (black) areas adjacent to the high density structure

Based on the comparative appearance of these two images, what element of the reconstruction was modified during the second reconstruction?
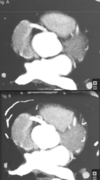
Slice Thickness
- Figure A is due to partial volume averaging –> the image has been reconstructed at a slice thickness of 5.0 mm, which is too thick for coronary imaging

Describe why slice thickness is so important in regards to coronary imaging
- Large slice thickness (typical thickness for non-coronary imaging) –> image depth is larger than the diameters of most of the coronary vessels –> other tissue and densities (perivascular tissue, epicardial fat) are incorporated into the image and averaged with the coronary arteries –> loss of distinction
- For coronary imaging, very thin sections ( < 1.0 mm) should be used in order to preserve distinct demarcation of the small coronary arteries
- this requires thin detector collimation as is typical for today’s multi-detector scanners
- but is not the case for 4-slice or older scanners
Describe the most likely finding:
- proximal (aortic) anastomosis of the SVG-LAD

Subtotal occlusion
- a bulky plaque is causing subtotal occlusion at the proximal anastomosis
- 80-year old male presented with acute chest pain at the ED, Troponin T was negative initially but spiked four hours later
- Angiography demonstrating subtotal occlusion

Define partial volume averaging
- occurs when adjacent structures with different CT-densities (calcium, endothelium) are averaged into one CT attenuation value of one voxel
- manifestation of the limited spatial resolution of CT
- adjacent, non-calcified structures are depicted as having an attenuation that is higher than actual, and this results in calcifications –> appear larger than they really are
- often influences ability to interpret CCTA
What is one way to minimize partial volume averaging?
sharp reconstruction kernal/filter
Describe the findings and best way to prevent this from occuring

Misalignment or Step artifacts (respiratory motion)
- clearly indicated by the step artifacts within the sternum
Ensure patient understands and follows the breath hold command

Describe the findings

Cardiac motion artifact due to ectopy
- EKG strip:
- two PVC’s during scan
- misgating of the rhythm (broken arrow) in which pat of the baseline was “tagged” as a QRS therefore adding a beat where none was present
- Incorporation of these beats will have disastrous consequences for the reconstruction
*****Usually not necessary to rescan patient –> EKG editing to correct for these arrhythmias and errors