Hemodynamics Flashcards
(46 cards)
What is the formula for Fick CO?
CO = O2 consumption (mL/min) / VO2 difference (mL/100mL blood) x10
- O2 consumption estimated using 3 mL O2/kg or 125 mL/min/m2
- VO2 difference = difference (0.95 - 0.65) x 1.36 x Hgb x 10
**** Larger difference between A and V O2 content –> lower CO
What is the formula for cardiac index (CI)?
CI = CO (L/min) / BSA (m2)
- normal = 2.5 - 4 L/min/m2
When is Fick (CO) most accurate?
- low output states (valvular heart disease)
- TR
- multivalvular heart disease
- steady state
What is the problem with Fick (CO)?
estimate of O2 consumption
What PA sat correlates with low CO (on Fick)?
< 65%
What are quick estimates of Fick (CO) utilizing PA sats?
- PA sat 70-80% –> Normal CO
- PA sat < 65% –> Low CO
- PA sat > 80% –> High CO (or L-R shunt)
- AV graft for HD
When is TD (CO) more accurate?
Least accurate?
- Most accurate –> High Output States
- Inaccurate –> TR or AF
What is the formula for PVR (pulmonary vascular resistance, Woods units)?
PVR = mPAP - mPCWP / CO
**Normal range = 80-130 dynes
***Woods units x 80 = dynes
**** TPR = mPAP / CO
What is the formula for SVR (systemic vascular resistance)?
What is normal range?
SVR = mean systemic arterial pressure - mRAP x 80 / CO
- Normal range = 700-1600 dynes-sec/cm5
Describe the finding

Severe TR
- monophasic “CV” wave
- CV wave lifted completely off the baseline
- monophasic event in systole, occurring within the RA
- ventricularization of RA waveform

What constitutes a pathologic or abnormal “v” wave in PCWP tracings?
What are causes?
- “v” wave more than 10 mmHg than PCWP
- PCWP “v” waves
- MR
- VSD
- Noncompliant LA
- previous A-fib ablation procedures

Describe the findings

Pericardial Tamponade
- Rapid x only
- Blunted ‘y’ descent (no early diastolic RV filling)

Describe the findings

Pericardial constriction
- Rapid x and y descents
- y = early rapid diastolic RV filling

Describe when step-up O2 saturations are significant?
What does this imply?
Intra or Extra cardiac shunt may be present

Describe the findings

- a = atrial systole
- x = atrial relaxation, decrease of pressure
- c = closure of the TV
- v = ventricular systole, atrial diastole
- y = passive filling of the RV

Describe the findings

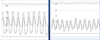
HOCM - Brockenbrough sign
- PVC –> ventricular contraction will be more forceful, and the pressure generated in the LV will be higher
- reduction in pulse pressure in a post-PVC beat
*
- reduction in pulse pressure in a post-PVC beat

How can you differentiate AS and HOCM on intracardiac pressure tracings?
Post-PVC
-
Pulse Pressure
- HOCM –> decrease
- AS –> increase
Valsalva
-
Gradient
- HOCM –> increase
- AS –> decrease

Describe the findings

AS

Describe the findings

HOCM: L heart pullback

Describe the findings

Provocable Gradient: Valsalva Maneuver

Describe locations for mixed venous O2 sats in shunt calculations:
- No L-R shunt
- L-R shunt present
- ASD
- No R-L shunt
- No L-R shunt
- Mixed venous = PA sat
- L-R shunt present
- Mixed venous = O2 sat in chamber proximal to shunt
- ASD
- Mixed venous = Caval O2 sat = (3 x SVC) + (1 x IVC) / 4
- No R-L shunt
- Mixed venous = PV O2 sat = FA O2 sat
What is a normal BP response to exercise?
25-70 mmHg
Describe the findings

ASD

Describe the findings

AR
- Corrigan’s pulse
- absence of dicrotic notch