Physics, Artifact, M-mode Flashcards
(155 cards)
What are the types of cavitation?
- Squeeze flow
- acceleration of blood as occluder approaches stop causing drop in pressure
- Vortex flow
- turbulence at edge of rapidly moving occluder
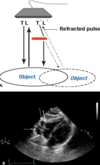
What is velocity (propagation speed) error artifact?
- sound propogates through some structures at velocity other than 1540 m/sec
- takes longer to travel through a structure - which is assumed by the ultrasound machine
What is specular reflection?
- mirror-like reflection of waves from a surface, in which waves from a single incoming direction (a ray) is reflected into a single outgoing direction.
- angle of reflection equals angle of incidence for objects > 1 wavelength diameter (~0.5mm)
What is cavitation?
- rapid formation of vaporous microbubbles in a fluid due to a local reduction in pressure
What are High Intensity Transient Signals (HITS)?
- under some conditions (vortices), vaporous microbubbles can coalesce into larger bubbles
- degassing: removal of gasses (principally CO2 in blood) from liquid medium
- larger bubbles persist and ar visible on echo
- no demonstrated neurologic sequelae from HITS microbubbles
Why are bubbles such good reflectors? Why do we see them with prosthetics?
- they have a very low acoustic impedance
- acoustic impedance (velocity x density)
- interface between materials with dissimilar acoustic impedances (velocity x density) reflects sound
- 23 (air) vs. 1465 (water)
To reduce aliasing on color-flow Doppler, a sonographer should perform this action?
- Changing the baseline shift
- allows velocities to be displayed up to twice th original Nyquist limit
What is pulse repetition frequency (PRF)?
- number of pulses of a repeating signal per unit time
- inversely related to PRP (PRF = 1 / PRP)
- inversely related to imaging depth (PRF x 1/d)
What environment can sound waves not travel through?
- vacuum
- pressure waves can only be transmitted through physical media consisting of molecules that interact with each other
What is the upper limit of human hearing?
20,000 Hz or 20 kHz
The frequency of a sound wave is measured in Hz as the:
- number of times particles vibrate each second in the direction of wave propogation
- 1/s
- the number of times a particle in a conducting medium vibrates per unit time
Ultrasound imaging is usually performed in what frequency range?
- 1-30 MHz
- lower frequencies (greater penetration) –> larger organs or deeper structures
- higher frequencies (better spatial resolution) –> smaller, more superficial structures
Define wavelength
the distance a wave travels during a single cycle
What type of tissue results in the fastest loss of ultrasound wave strenght?
- Lung
- because of the high content of air and the abundance of highly reflective tissue/air interfaces, the sound waves dissipate in the lung so fast that the lungs are virtually opaque to ultrasound
What is the main goal of the gel used during ultrasound imaging?
- Improve contact between the transducer surface and the skin
- eliminates any tissue/air interfaces which are highly reflective and thus prevent ultrasound transmission
What are Piezoelectric crystals?
materials that respond to electric signals by vibrating and generating acoustic waves and vice versa
To better assess rapidly moving structures, a sonographer should perform this action?
- Narrow scan sector width and decrease imaging depth = increased frame rate
- Higher frame rate is required to increase temporal resolution
- some machines enable direct manipulation of frame rate, others can be adjusted by sector width and imaging depth
- Higher frame rate is required to increase temporal resolution
How do Piezoelectric crystals generate ultrasound images?
- transmit waves by “exciting” the crystals in the transducer by an electrical stimulus,
- then receiving the ultrasound waves reflected by structures inside the body,
- translating them back into electrical signals that are used to form an image of the reflecting structures
Define Doppler shift?
- change in the frequency of a sound wave reflected by a moving target
- negative / red shift
- object moving away
- wavelength made longer (increased)
- frequency decreased
- positive / blue shift
- object moving toward transducer
- frequency incerased
- wavelength decreased
- negative / red shift

Define doppler angle?
- angle between:
- the direction of flow
- ultrasound beam
With time gain compensation, the machine is generally preset to perform this action?
- Decrease signal in near field, increase signal in far field
- increasing depth = increased attenuation
- TGC accounts for this signal loss by effectively incresing gain in parallel with increase in depth
- many modern systems automatically account for this so the knobs should be left in neutral position to start with then adjusted as needed
Define Harmonic imaging?
Echocardiogaphic images are formed from returning echoes at twice the insonifying frequency (second harmonic)
When does aliasing occur?
when doppler shift of high-velocity flow exceeds the Nyquist limit (1/2 the Pulse Repetition Frequency)