Nuclear - Physics Flashcards
(106 cards)

X-direction (horizontal) patient motion
- in the mid-portion of the sinogram diplayed there is abrupt discontinuity of the septal and lateral borders, indicative of lateral cardiac/patient motion
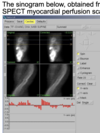
Describe how a signogram works
- sinogram is a stack of y-axis compressed (usually approximately 64) images obtained throughout the 180-degree SPECT acquisition
- the sinogram thereby tracks the motion of the heart throughout the 180-degree SPECT acquisition
- left border of the sinogram –> tracks the epicardial border of the septum
- right border of the sinogram –> tracks the epicardial boder of the lateral wall

What are the findings in a sinogram with:
- arrhythmic beat rejection
horizontal lines of decreased count density due to decreased count density in those individual frames
What can a linogram be used to detect
Y-direction motion
How should flood field non-uniformity be evaluated?
daily flood fields
For a Tc-99m sestamibi tetrofosmin myocardial perfsuion scan, setting the pulse height analyzer to 160 keV with a +/- 10% energy window:
- What will be the most apparent result?
Decreased image count density
- if the photopeak is set above the primary Tc-99m gamma ray energy (140 keV) most photons will be rejected, and image count density will markedly decrease
- 160 +/- 10% window accepts photons 144-176 keV
What is the standard energy window and peak for Tc-99m?
Why?
- Symmetric energy window: 15-20% centered around the
- Energy peak: 140keV
- this window width provides an appropriate tradeoff between
- accepting unscattered-photons
- and
- rejecting the scattered photons
- accepting unscattered-photons
What is the standard energy window and peak for most modern detectors:
- Tc99m
- Tl201
- Tc99m
- 9-10% for 140keV photons from Tc99m
- Tl201
- 15-17% for 72keV photons from Tl201
What is the standard energy window and peak for Tc-99m utilizing a CDZ detector?
energy resolution of 5-6%
For an ECG-gated post-stress myocardial perfusion SPECT scan acquired on a two-headed scintillation camera, rejection of 30% of cardiac cycles due to arrhythmic beat rejection will result in approaximately:
- what reduction in count density?
30% decrease in overall image count density
- when arrhytmic beats are rejected the camera stops acquiring data from the entire field of view (FOV), not just the myocardium
- percentage of rejected beats is roughly equivalent to the percent decrease in overall image count density, irrespective of the number of camera heads or stops
What defines definite infective endocarditis according to the Modified Duke Criteria?
- Pathological Critiera
- Microorganisms demonstrated by culture or histological examination of a vegetation, a vegetation that has embolized, or an intracardiac abscess specimen
- Pathological lesions; vegetation or intracardiac abscess confirmed by histological examination showing active endocarditis
- Clinical Criteria
- 2 major criteria; or
- 1 major and 3 minor criteria or
- 5 minor criteria
What are the minor criteria used in the Modified Duke Criteria for IE?

What are the major criteria used in the Modified Duke Criteria for IE?

Explain the difference between cameras:
- CZT-based SPECT cameras
- conventional sodium-iodide-based SPECT cameras
CZT-based cameras have a lower uniformity defect contrast trade-off
- CZT detector modules are smaller than conventional photon multiplier tubes (PMT) –> smaller pixel size
- smaller pixel size = improved spatial resolution
- Energy resolution is two-fold higher in CZT-based cameras
Describe the difference in crosstalk between:
- CZT-based SPECT cameras
- conventional sodium-iodide-based SPECT cameras
- Sodium-iodide-based SPECT cameras
- utilize photon multiplier tubes (PMT)
- PMT’s share photon signals because of the spreading of light between the PMT’s (crosstalk)
- crosstalk –> degrades effective pixel size
- CZT-based SPECT cameras
- utilize CZT detector modules (instead of PMT’s)
- have negligible crosstalk (due to direct conversion into an electric charge –> improved spatial resolution
Tc-99m sestamibi myocardial perfusion SPECT was performed in a 65 year old man. The VLA post-exercise tomograms below were processed without (A) and with (B) low-dose XR attenuation correction.
The decrease in anterior wall count density in the AC images (B) is attributable to?

Scatter from subdiaphragmatic radiotracer concentration
- by eliminating attenuation of the overlying abdominal wall, attenuation correction often accentuates subdiaphragmatic activity
- such increased activity may scatter into the inferior wall of the LV
- When myocardial tomograms are normalized to a resulting “hot” inferior wall, the contralateral anterior wall appears to have relatively decreased activity
- this may simulate an anterior perfusion defect in AC-corrected images
***In this case, non-AC images are normal for a male

Metal artifact reduction in the CT component of a PET/CT is advantageous in the assessment of PET myocardial perfusion imaging because such artifacts may:
impair PET relative uptake and quantitation
- the map of attenuation coefficients for PET attenuation correction scales is a monotonically increasing function of the CT Hounsfeld units (usually a bilinear function)
- higher HU’s –> higher attenuation coefficients
- PET image reconstruction compensates for the loss of signal (absorbed photons) in its AC algorithm
- Consequently, regions of artifactually high or low HU’s typically can translate to regions of artifactually high or low radiotracer uptake in AC PET images
The AC quality control figure shown, displays a fused image: the CT used for the attenuation map overlaid with a red contour showing the outlines of the myocardium on SPECT. What AC-induced artifact is most likely created if the MPI SPECT/CT misregistration shown?

Apparent uptake decrease in the lateral wall
- higher CT numbers (in units of Hounsfeld units) give areas in the attenuation map that are assigned higher attenuation coefficients
- misalignment is associated with an artifactual decrease in the apparaent uptake in the lateral wall of the ventricle –> amount of AC from this region will be underestimated during AC SPECT reconstruction –> artifactually photon deficient region

What will MPI SPECT/CT misregistration show?
- Septum
- Apex
- Septum
- artifactual increase in radiotracer uptake
- Apex (misregistration with AC map or motion with respect to AC map)
- causes apparent apical thinning
When using a CT scan for PET attenuation correction, voxel A has a CT number of zero Hounsfield units (HU) and voxel B has a CT number of 400 HU. What best describes the linear attenuation coefficients, μ(A) and μ(B)?
μ(B) > μ(A)
- HU are obtained from a linear transformation of the measured attenuation coefficients
- materials denser than water have positive pixel values
- Pixel with a higher positive value in CT consists of more dense materials with higher linear attenuation coefficient
- higher pixels = denser material –> higher HU’s = higher linear attenuation coefficient
How are pixel values in CT images expressed?
usually expressed in Hounsfield units (HU) on a normalized scale with respect to the values for water
What effect does attenuation correction in SPECT MPI have:
- Specificity
- Sensitivity
- Specificity –> improved
- Sensitivity –> not affected
Define attenuation coefficient
characterizes how easily a volume of material can be penetrated by a beam of light, sound, particles or other energy or matter
What affects does AC SPECT MPI have in obese patients?
- Increases specificity in all patients
- Greater effect in obese patients






















