Core Lecture Series Flashcards
(50 cards)
Describe the image

RAO Caudal
- LAD (on top)
- CFx (coming towards front)

Describe the image

LAO Cranial

Describe the findings
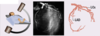

Describe the findings

LAO Straight

Describe the findings

LAO Cranial

Describe the findings

RAO Straight

What are the branches of the SMA?
- inferior pancreaticoduodenal
- intestinal
- ileocolic
- right colic
- middle colic
What are the branches of the celiac trunk?
- Left gastric
- Common hepatic
- Splenic
Describe the views and imaging of the left coronary system

Describe the image


Describe the image

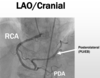
Describe the image


Describe the image


Describe the image


Describe the image

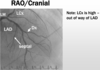
Describe the image


Describe the views and imaging of the right coronary system

Describe the image


Describe the image


Describe the image


Describe the findings of the LV gram


What is the most common challenge in regards to radial access?
vasospasm
What tests should be performed before attempting radial access?
Why?
- Barbeau or Allen’s Test
- To assess ulnar and radial flow in the superficial palmar arch
What is the best treatment for radial artery vasospasm during cath?
- Intra-arterial vasodilators
- verapamil, Nitrates
- Sedation
- Minimizing catheter manipulation and catheter exchanges


