EKG pics Flashcards

-
VT
- Wide, bizarre QRS complex
- Not typical LBBB or RBBB complex
-
AV dissociation
- P-waves get in front of the ventricle far enough -→ fusion/capture complex


-
Atrial tachycardia
- P-waves (originating from the low RA, near the AV node)
- negative in II, III, aVF
- positive in I, aVL
- P-waves (originating from the low RA, near the AV node)
- RAD
- no need to code ST-T changes of ischemia


- Atrial Flutter
- AV block, 2:1
- P-wave immediately at the end of the QRS complex
- V-rate ~ 150 bpm


- NSR
-
Brugada Syndrome
- Type I and Type II pattern
- J-point elevation at end of the QRS complex + coved downward ST-segment + inverted T-wave → Type I
- V3 with saddleback ST-elevation → Type II
- not diagnostic if only finding


- NSR
- LVH
- Acute Pericarditis
- Do note code ST-T changes when coding pericarditis


- A-fib
- WPW


- Sinus arrhythmia
- LBBB
- ST and/or T wave abnormalities suggesting myocardial injury
- 1 mm inferior ST-elevation (II and aVF)
- 2-4 mm anterolateral concordant ST-elevation (V4-V5)
- location of acute infarction should not be coded int he presence of a LBBB


- NSR
- AV dissociation
- VVI - normal function
- AV interval at the end of the tracing is longer than at the beginning of the tracing (AV interval has prolonged by approximately 80 msec) indicating the atrial and ventricular rhythms are dissociated and the pacemaker is programmed VVI and not tracking atrial activity


- NSR
- Inferior MI - age recent or probably acute
- Posterior infarction injury pattern cannot be coded:
- R-wave does not exceed S-wave in V1-V2


- A-fib
- PVC’s
- Bi-V pacing
- V-sensed response
- R precordial leads → 2 pacing spikes
-
negative deflection → I and aVL
- activation from LV lead from lateral lead away from left side
- Pacing spike on PVC → designed to force Bi-V pacing and decrease the asynchrony caused by the PVC


- SR
- RAE
- Prolonged QT
- Hypokalemia


- MAT
RAE - not coded as large P-waves are ectopic in origin


- NSR
- Acute Pericarditis
- Pericardial effusion
- Electrical alternans


- NSR
- 2nd Degree AV Block - Mobitz I (Wenckebach)
- AV junctional escape complexes
- Inferior MI - age recent/acute


**29 year old female with dyspnea → Pulmonary hypertension
- NSR
- Sinus arrhythmia
- RAD
- RVH
- ST and/or T wave abnormalities secondary to hypertrophy


****24 year old male with bipolar disorder
- NSR
- PVC’s
- Prolonged QT
- Torsades de pointes
- T-wave becomes more complex following PVC/pause → increases risk of PVC on T wave → Torsades de pointes/malignant long QT


*** 74 year old female with 3 hours of chest pain and dyspnea
- NSR
- PVC’s
- 2nd degree AV block - Mobitz I
- Posterior MI - age recent/acute


***26-year old female with ascites and acute severe dyspnea
- ST
- RAE
- RAD
- RVH
- ST-T abnormalities secondary to hypertrophy
- PE/acute cor pulmonale

Describe the findings

Dual-chamber pacemaker (DDD), normally functioning
- Pacer spikes seen in I and III on the first beats of the tracing

Describe the findings

- A-fib (+4)
- LAD
- RBBB (+2)
- Anterior/anteroseptal age indeterminate/old (+2)
- Inferior age indeterminate/old (+2)

Describe the findings

- PAC’s
- Junctional rhythm/tachycardia (+2)
- LAD
- LVH (+2)
- ST/T abnormalities secondary to hypertrophy

Describe the findings

- NSR
- AIVR (+4)
- AV dissociation (+2)

Describe the findings:
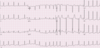
- A-fib
- ST and/or T wave abnormalities suggesting myocardial ischemia

Describe the findings:

- SVT
- PVC’s
- RAD
- IVCD, nonspecific type
- ST and/or T wave abnormalities suggesting myocardial ischemia

EKG Definition:
- LBBB
- Mean QRS duration
- ► 120 ms - Adults
- > 100 ms - Children 4-16 years
- > 90 ms - Children < 4 years
- Late forces of QRS complex should be negative (terminal S wave in V1)
-
Broad notched or slurred R wave in leads I, aVL, V5, V6 and
- occasional RS pattern in V5 and V6 attributed to displaced transition of QRS complex
-
Absent q waves in leads I, V5, V6
- but in lead aVL, a narrow q wave may be present in the absence of myocardial pathology
- Delayed onset of intrinsicoid deflection (> 60 ms from beginning of QRS complex to peak of R wave) in leads V5 and V6 but normal in leads V1-V3 when small initial r waves can be discerned in these leads

Describe the findings:

- Artifact
- NSR
- PVC’s
- RBBB, Complete
- Inferior MI, age indeterminant or probably old

Describe the findings:
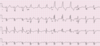
- NSR
- RVH
- in the setting of RBBB –> R-prime in V1 > 15 mm suggests RVH
- RBBB, complete
- Prolonged QT interval
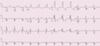
Describe the findings:

- Incorrect electrode placement
- abrupt change in R wave progression in lead V3 with immediate return of R wave forces in lead V4
- Sinus bradycardia (HR < 60 bpm)
- WPW

Describe the findings:

- Normal EKG
- NSR

Describe the findings:

- MAT
- PVC’s
- LVH
- LBBB, complete
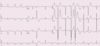
Describe the findings:

- NSR
- RAD
- LA enlargement
- IVCD, nonspecific type
- Pacemaker malfunction, not constantly capturing (atrium or ventricle)
- Pacemaker malfunction, not constantly sensing (atrium or ventricle)

Describe the findings:

- Atrial or coronary sinus pacing
- LVH (female)

Describe the findings:

- AT
- P-waves of sinus node origin should be positive in lead II, not negative as seen here.
- P-wave is secondary to an ectopic atrial focus
- Inferior MI, age indeterminant or probably old

Describe the findings:

- SB
- AV junctional rhythm/tachycardia
- AV dissociaton
- RBBB, complete
- LAFB
****P waves appear closer and closer to each QRS complex, until the P-wave becomes entirely hidden within the QRS complex.
*****P-waves in this tracing are actually not conducting the QRS complexes –> complete AV dissociation
*******When sinus rate is similar to junctional escape rhythm –> isoarrhythmic AV dissociation

Describe the findings:

- ST
- AV junctional rhythm/tachycardia
- AV block, 3rd degree
- Inferior MI, age recent or probably acute

Describe the findings:

- A-fib
- PVC
- Nonspecific ST and/or T wave abnormalities

Describe the findings:

- A-fib
- LAD

Describe the findings:

- NSR
- LA enlargement
- Nonspecific ST and/or T wave abnormalities

Describe the findings

- NSR
- 1st degree AV block
- IVCD, nonspecific
- ST and/or T wave abnormalities suggesting electrolyte disturbances (+2)
- Hyperkalemia (+4)

Describe the findings

- NSR
- RAD (+2)
- RVH (+4)

Describe the findings

- NSR
- PAC’s
- 1st degree AV block
- LBBB (+4)

Describe the findings

- SVT (+4)
- ST and/or T wave abnormalities suggesting myocardial ischemia
- > 1 mm of horizontal or downsloping ST-T segment depression and/or
- T wave inversion greater than or equal to 2 mm

Describe the findings
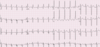
- LA enlargement
- ST
- RAD
-
RVH (+4)
- mean QRS axis > 100 degrees
- R/S ratio in V1 > 1, R/S ratio in V5 or V6 < 1, qR complex in V1, or R wave > 7 mm in V1
- ST and/or T wave abnormalities secondary to hypertrophy
*****42 year old male with history of severe PAH –> resuling in significant RVH

Describe the findings

- NSR
- LAD
- RBBB
- 2nd degree AV block - Type I (Wenckebach)
- Inferior MI, age old or indeterminate

Describe the findings

- Atrial tachycardia (+4)
- 2nd degree AV block - Type I (Wenckebach)

Describe the findings and diagnosis:

- EKG
- ST
- Acute Pericarditis
******Patient underwent left pneumonectomy and pericardial resection secondary to malignant mesothelioma. The patient developed post-operative EKG changes consistent with pericarditis.

Describe the findings:

- NSR
- SA exit block
- Nonspecific ST and/or T wave abnormalities

Describe the findings
- 65 year old who is post anterior-STEMI (day 3) with revascularization
- No residual disease on cath
- Asymptomatic

LV aneurysm
- EKG: persistent ST-elevations post anterior STEMI –> consistent with LV aneurysm

Describe the findings

- Sinus tachycardia
- Dual-chamber pacemaker (DDD), normal functioning (+4)
- Paced morphology consistent with biventricular pacing/cardiac resynchronization (+2)
***Notice the dual ventricular pacing spikes best seen in lead V3, indicating a bi-ventricular pacing device

Describe the findings

- NSR
- Dual-chamber pacemaker (DDD), normal function (+2)
- Bi-V pacing/cardiac resynchronization (+4)
***dual ventricular pacing spikes occurring just after each other (best seen in lead V2) with the upright (RBBB morphology) QRS complex in V1 –> suggests the presence of a bi-ventricular pacing (cardiac resynchronization therapy) device

Describe the findings

- NSR
- Dextrocardia, mirror image
- P wave, QRS complex, and T wave in leads I and aVL are inverted or “upside down”
- Reverse R wave progression (R wave amplitude is largest in V1 and gets smaller as you move towards V6)
- Lead reversal can give the appearance of dextrocardiain the limb leads. However, reverse R wave progression should not exis in the setting of limb lead reversal

Describe the findings

- NSR
- 1st degree AV block
- RAD
- IVCD, nonspecific (+2)
- ST and/or T wave abnormalities suggesting myocardial ischemia (+2)
****QRS complex in V1 demonstrates characteristics of both right (RSR prime) and lef (negative late forces) bundle brach block, making nonspecific IVCD the most accurate answer

Describe the findings

- A-flutter (+4)
- 2:1 AV block (+1)

Describe the findings

- NSR
- AV/junctional rhythm/tachycardia (+2)
- 3rd degree AV block (+4)
- RAD
- RBBB, complete
- LPFB

Describe the findings
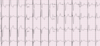
- Dual-chamber pacemaker (DDD), normally functioning (+4)

Describe the findings

- NSR
- RBBB, incomplete
- LAFB
- Prolonged QT interval (+4)
- CNS disorder (+4)
***Patient suffered from an intracranial hemorrhage
***CNS disorders commonly result in EKG abnormalities
- Prolonged QT
- Diffuse ST-depression
- Deep T-wave

Describe the findings

- ST
- LA abnormality/enlargement
- RAD
- RBBB, complete (+2)
- Nonspecific ST and/or T wave abnormalities
- Mobitz II - 2nd degree AV block (+4)
***High-grade AV block, specifically 2nd degree AV block, Mobitz type II, with 3:1 conduction (every third atrial P-wave conducts through the AV node)

Describe the findings

- A-fib (+4)
- RBBB, complete (+2)
- LAFB (+1)

Describe the findings

- NSR
- LAD
- LVH (+4)
- ST and/or T wave abnormalities secondary to hypertrophy
- Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (+4)
***Marked LVH with repolarization abnormalities in a patient with this clinical scenario suggests diagnosis of HCM

Describe the findings

- SB
- AV junctional rhythm/tachycardia (+2)
- P wave, with typically a superior and leftward axis, if seen, may be seen immediately before or after the QRS complex
- Junctional rhythm slows, the P-wave finally has time to conduct, resultling in the sinus beat (last beat on the tracing) with normal AV conduction
- AV dissociation (+2)
- Isorhythmic dissociation
***P-waves marching through can be seen in lead II
***P-wave is initially immediately following the QRS complex (1st beat) and slowly extends further away from the QRS complex with each of the next 4 beats
***Junctional rhythm is slightly faster than the underlying sinus rhythm during these beats, and no association exists between these two rhythms

Describe the findings and diagnosis:
- 52 year old male with previous MI (3 weeks prior) who is admitted with CVA (two different arterial territories)
- PE: S1, S2, S3, 1+ pretibial lower extremity edema

- Cardioembolic CVA
- Large anterior MI
- PE –> evidence of heart failure with resultant systolic dysfunction
- EKG –> Anterior Q waves

Describe the findings and diagnosis:
- 64 year old male with 1 day of intermittent chest pain
- PMH: HTN, HLD, cholelithiasis, hip osteoarthritis
- Meds: Amlodipine, Chlorthalidone, Rosuvastatin, Ibuprofen
- Labs: Troponin 1.6

Ostial OM occlusion / High-Lateral MI
- 1st EKG
- ST depression in inferior leads, but not in lateral leads
- subtle ST-elevation in aVL
- 2nd EKG
- new Q-wave in aVL with TWI –> high lateral MI

Describe the findings:

RV infarct
- ST elevation in II, III, aVF and V1-V-3
- ST elevation III > II –> suggests involvement of RCA rather than CFx

EKG Definition:
- Anterior or anteroseptal, age recent or probably acute

- Anterior (V3-V4) or anteroseptal (V1-V3) leads
- Pathological Q waves must be ► 30 ms wide and 0.1 mV deep in amplitude or
- Q wave width may only be 20 ms wide in V2-V3
- QS complexes
- Pathological Q waves must be ► 30 ms wide and 0.1 mV deep in amplitude or
- Evidence of acute or evolving myocardial injury
- ST elevation in two contiguous leads ► 2mm - men or 1.5mm - women in V2-V3 and 1mm in V1 or V4

Describe the findings:

- AV junctional rhythm/tachycardia
- Wide-complex rhythm is junctional in origin.
- PVC’s
- Additional PVC’s are seen throughout the tracing as well.
- Intraventricular conduction disturbance, nonspecific type
- Q waves seen in the lateral leads (aVL) are not typical of a LBBB, so this wide-complex represents a non-specific IVCD.
- Nonspecific ST and/or T wave abnormalities

Describe the findings:

- NSR
- RAD
- Prolonged QT interval
- lengthening of the ST-segment
- Hypocalcemia
- inferred from prolonged QT interval and
- parasthesias on clinical exam

EKG definition:
- ST and/or T wave abnormalities suggesting myocardial ischemia
- > 1mm of horizontal or downsloping ST-T segment depression
and/or
- TWI ► 2mm

Describe the findings:

- A-fib
- LAD
- RBBB, complete
- Anterior or anteroseptal, age indeterminant or probably old

EKG definition:
- Anterior or aneroseptal, age indeterminant or probably old
- Anterior (V3-V4) or anteroseptal (V1-V3) leads
- Pathological Q waves must be ► 30 ms wide and 0.1 mV deep in amplitude or
- Q wave width may only be 20 ms wide in V2-V3
- QS complexes
- Pathological Q waves must be ► 30 ms wide and 0.1 mV deep in amplitude or
- No evidence of acute or evolving myocardial injury (no ST elevation)
Describe the findings:

- A-flutter
- AV block, 2:1
- LAD
- LBBB, complete

Describe the findings:

- Sinus bradycardia
- LAD
- Inferior MI, age indeterminant or probably old
- Nonspecific ST and/or T wave abnormalities

Describe the findings:

- AV block, third degree
- Ventricular escape complexes/rhythm
- Two ventricular escape complexes are present in this tracing
- Ectopic atrial rhythm
- P waves marching throughout are negative in lead II, suggesting ectopic orgin (P-waves originating from the sinus node should be positive in lead II)
- Ectopic atrial rhythm does not conduct through the AV node indicating the presence of 3rd degree (complete) heart block.

Describe the findings:

- Sinus bradycardia
- Sinus pause or arrest
- AV junctional escape complexes
- LBBB, complete

EKG definition:
- Sinus pause or arrest
> 2 second pause without a p-wave
- may be the result of:
- sinus arrhythmia
- SA exit block
- non-conducted PAC
- sinus arrest
EKG definition:
- SA exit block
- failure of the electrical impulse to leave the sinus node
- resulting in the pause duration being a precise multiple (2 or 3 times) of the usual P-P interval
Describe EKG axis:

- Normal Axis
- QRS axis between -30 and +90
- LAD
- QRS axis < -30
- RAD
- QRS axis > +90
- Extreme axis deviation
- QRS axis between -90 and 180 (AKA “Northwest axis”)

Describe the findings and diagnosis:

Stress Cardiomyopathy with LVOTO
- new murmur due to LVOTO can be seen in apical variant, due to hyperkinesis of the basal anteroseptum
- M-Mode
- anterior leaflet of the mitral valve moving towards the LV setpum during systole (systolic anterior motion)
- Treatment:
-
Beta-blockers –> can be used to treat outflow tract obstruction
- reduce contractility of the basal segments
- slow HR –> allows more diastolic filling of the LV
- Class IIa
-
Beta-blockers –> can be used to treat outflow tract obstruction

Describe the findings

- Dual-chamber pacemaker (DDD), normally functioning (+4)

Describe the findings:

- NSR
- 1st degree AV block
- Low voltage, precordial leads
- Anterior or anteroseptal, age indeterminant or probably old ( +2 )

Describe the findings:

- ST
- Anterior or anteroseptal, age recent or probably acute ( +4 )

Describe the findings:

- Atrial fibrillation ( +2 )
- Functional (rate-related) aberrancy ( +4 )

Describe the findings:

- LAE
- SB
- 1st degree AV block
- LAD
- LVH ( +2 )
- RBBB ( +4 )
- ST and/or T wave abnormalities secondary to hypertrophy ( +2 )

Describe the findings:

- NSR
- PAC’s
- LVH
- RBBB, incomplete
- Inferior MI, age recent or probably acute ( +4 )

Describe the findings:
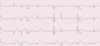
- NSR
- AV junctional rhythm/tachycardia
- PVC’s
- 3rd degree AV block ( +4 )
- Inferior MI, age recent or probably acute ( +4 )

Describe the findings:
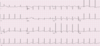
- ST
- occurs starting at 5th beat
- AV junctional rhythm/tachycardia ( +2 )
- Nonspecific ST and/or T wave abnormalities
****Atrial activity preceding QRS complexes in the first 4 beats (best seen on lead II)
****P-wave is of a different morphology (inverted) with slighly shorter PR interval than the P-waves found on the rest of the tracing.
****Represent retrograde atrial conduction from a junctional (or possibly low ectopic atrial) rhythm

Describe the findings:

- SVT ( +4 )
- Low Voltage, limb leads
- < 5 mm
- Low Voltage, precordial leads
- < 10 mm
- LAD

Describe the findings:

- AV junctional rhythm/tachycardia
- LBBB, complete
- ST and/or T wave abnormalities suggesting electrolyte disturbances
- Hyperkalemia ( +4 )
***Serum potassium - 8.5 mEq/L
***P-waves absent/loss of amplitude, QRS widening expected with hyperkalemia

Describe the findings:

- ST
- RAD
- RVH ( +4 )
- ST and/or T wave abnormalities secondary to hypertrophy
****Murmur consistent with pulmonary stenosis and was diagnosed with tetralogy of fallot
****Characteristic EKG findings:
- RAD
- RVH
- Varying degrees of RBBB

Describe the findings:

- NSR
- 2:1 AV block ( +4 )
- RBBB, complete
- ST and/or T wave abnormalities suggesting myocardial ischemia

Describe the findings:

- NSR
- LAD
- LVH
- Anterolateral MI, age reent or probably acute ( +4 )

What EKG findings preclude a diagnosis of LAFB?
Absence of causes of marked LAD
- Inferior MI
- LVH
Describe the findings:

- A-fib ( +4 )
- LAD
- LBBB ( +2 )

Describe the ST/T wave changes in presence of LBBB
- ST and T waves are usually opposite in direction of QRS complex
- Positive T waves in leads with upright QRS complexes may be normal (positive concordance)
- Depressed ST segments and/or negative T waves in leads with negative QRS complexes (negative concordance) are typically abnormal and may even represent myocardial injury
- LBBB may change the mean QRS axis in the frontal plane (to the right, left or superior axis) and in some cases, this may occur in a rate-dependent manner

Describe the findings:

- Artifact
- NSR
- PVC’s
- LBBB ( +4 )

Describe the findings:

- NSR
- Age indeterminate, or probably old
- Anterolateral
- q-waves in V5, V6
- Inferior
- Posterior
- R > S in V1, V2
- Anterolateral
***Upright T-waves suggest the infarctions are old

Describe the findings:

- NSR
- Prolonged QT
- Hypocalcemia
- normal T-wave morphology
- QT prolongation the result of ST-segment lengthening

Describe the findings:
- 75 year old male with syncope

- NSR
- 2nd degree AV block - Mobitz II
- RBBB

Describe the findings:

- SB
- one sinus capture beat (5th QRS complex)
- complete heart block should not be diagnosed in setting of sinus capture complex
- AV junctional rhythm/tachycardia
- AV dissociation
- isorhythmic AV dissociation - sinus and junctional pacemakers have a similar rate

Describe the findings:

- NSR
- ST/T abnormalities suggesting myocardial ischemia
- Prolonged QT
****Strong suspicion for, based on ST elevation > 1 mm in aVR and ST-depression across the precordial leads
- LM stenosis
- 3-vessel disease

Describe the findings:

- AT
- AV block 2:1

Describe the findings:

- A-fib
- Age recent/probably acute
- Lateral MI
- Anterolateral MI
- Failure to sense

Describe the findings:

- NSR
- Dextrocardia
- R-wave amplitude decreases from V1 to V6

Describe the findings:

- Sinus arrhythmia
- P-P interval varying by > 10%
- Normal variant, juvenile T waves

Describe the findings:

- NSR
- RBBB
- Age indeterminate, or probably old
- Anterolateral MI
- Inferior MI
**** No posterior MI because RBBB is present

Describe the findings:

- NSR
- Age old, indeterminate:
- Inferior
- Anterolateral
- q-waves in V5, V6
- Posterior
- R > S in V1, V2
- Upright T-waves

Describe the findings:

- NSR
- Prolonged QT
- Hypocalcemia
- ST-segment prolongation
- Normal T-wave morphology

Describe the findings:

- Atrial fibrillation
- Aberrant conduction
- RBBB beats - Ashmann’s beats

Describe the findings:

- SB
- MI - Age old or indeterminate:
- Inferior
- Posterior
- ST-T abnormalities suggesting myocardial ischemia (subtle)

Describe the findings:

- NSR
- 3rd degree AV block
- Ventricular escape rhythm
- PVC

Describe the findings:

- MAT

Describe the findings:

- ST
- Acute PE (S1Q3T3)

Describe the findings:

- AV dissociation
- AV/junctional rhythm/tachycardia

Describe the findings:

- Atrial flutter
- p-waves at end of QRS complex
- 2:1 AV block

Describe the findings:

- ST
- Low-voltage, limb leads
- Age acute or recent MI:
- Inferior
- Anterolateral

Describe the findings:

- SB
- Age acute or recent MI:
- Inferior
- Posterior
- Anterolateral

Describe the findings:

- SR
- AV dissociation
- VVI normally functioning
****No low-voltage****

Describe the findings:

- NSR
- Inferior MI - age acute or recent
***Posterior MI - not diagnosed as R/S < 1 in V1-V2
***Anterolateral MI - not diagnosed due to only 1 q-wave in V6

Describe the findings:

- NSR
- Lateral MI - Age acute or recent
- Low voltage
- Limb leads
- Precordial leads
- iRBBB
- QRS < 120 ms



