Prca revision questions Flashcards
What mode of deveolpment does this species have?

Velvet worms have direct development
What form of deveopment does this species have what are the advantages of this development?

hemimetabolous: means there is no pupae stage where species can not acquire resouses or may be vunerable.
What form of deveopment does this species have what are the advantages of this development?

holometabolous development allows for the larva to be completely adapted to the function of food acquisition and adult stage to be completely adapted to dispersal/reproduction. allows the nymph and adult to live in different niches, reducing competition.
What form of deveopment does this species have what are the advantages of this development?

holometabolous development allows for the larva to be completely adapted to the function of food acquisition and adult stage to be completely adapted to dispersal/reproduction. allows the nymph and adult to live in different niches, reducing competition.
What form of deveopment does this species have what are the advantages of this development?

hemimetabolous: means there is no pupae stage where species can not acquire resouses or may be vunerable.
Match the following vertebrate gut diagrams to the list of likely diets?

Freshly, killed vertebrate flesh
Match the following vertebrate gut diagrams to the list of likely diets?

Almost exclusively flying insects
Match the following vertebrate gut diagrams to the list of likely diets?
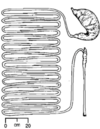
Fish and other large marine prey
Match the following vertebrate gut diagrams to the list of likely diets?

Reasonably good quality grass
Match the following vertebrate gut diagrams to the list of likely diets?

Poor quality leaves accessible only from within trees
Match the following vertebrate gut diagrams to the list of likely diets?

Extremely large quantities of very poor quality vegetation
What enviroments is internal fertilisation and planktonic larvae favoured as a stratergy?
Marine invertebrates with internal fertilisation and planktonic larvae are most likely to occur in cold, unpredictable environments.
What groups tend to have internal fertilisation and planktonic larvae?
Many marine gastropods exhibit this life history strategy.
What groups of marine invertibrates have direst devlopment and internal fertilisation?
direct devlopment occurs in advanced gastropods, some Crustaceans (e.g. Amphipods, Isopods), Cephalopods (i.e. octopus, cuttlefish, squid), and Chaetognathes (arrow worms).
What are the advatages of direct development in marine invertabrates?
- if the adults are very mobile and dispersal can be achieved despite the presence of non-dispersive immature stages.
- if ecological conditions are such that planktonic larvae would not be well-suited to the environment (e.g. the littoral zone).
- if ecological conditions are such that it is beneficial for offspring to mature in the same place as their parents (e.g. areas with localised or patchy resources)
What life history stratergy is the most common in marine invertibrates?
external fertilisation and planktonic larvae
What is the primary advantage of the external fertilisation and planktonic larvae statergy in marine invetebrates?
It allows sesslile organisms to disperse
What are the primary advantages and disadvantages of an exoskeleton?
Advantages
- Provides rigid external protection
- Strong
Disadvantages
- Must be shed to grow
- Very heavy at larger sizes
what does bein Plantigrade mean? What are its advantages?
Plantigrade: Animals that walk with their weight spread over the whole palm or sole of their manus and pes (hands and feet).
- Provides foot stability and weight bearing ability
What does being Digitigrade mean? what are its advatages?
Digitigrade: Animals that walk with their weight bearing on the pads of their phalanges (toes/fingers).
What does being Unguligrade mean? what are its advatages?
Animals that walk with their weight bearing on the ends of their nails/claws, which are often thickened to become hooves.
What are the advantages of being Digitigrade and Unguligrade?
Both digitigrade and unguligrade increase the efficiency of running by improving storage and recovery of energy.
What degree of sociallity does this animal likely have?

solitary
What degree of soliality does this animal likely have?

likely lives in groups as the teeth indicate it eats grass










