Pathology - Valve Disease Flashcards
What is this and what disease is this associated with?

Aschoff body (granulomatous-like histiocytes - phagocytic cells) - associated with rheumatic heart disease
Your 24 year-old patient from Kenya presents with a low-pitched, rumbling diastoic murmur heard best at the apex. They died because you are a med student that doesn’t know much, and you find that their myocardium looks like this…
What caused this?

Leukocytes in the myocardium is typical of rheumatic heart disease (more of an early event, though)
What is your diagnosis?

Rheumatic heart disease causing commisural fusion of the mitral valve –> mitral stenosis
What’s up wit it? What caused it?
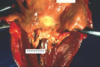
Fused chordae tendinae from rheumatic heart disease
What valve is this? What is wrong with it?

Aortic valve - commisural fusion from rheumatic heart disease
Name four pathologic findings associated with rheumatic heart disease.
- Pancarditis
- Fish-mouth valves
- Fused commisures
- Aschoff bodies
What’s your Dx?
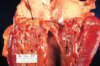
Infective endocarditis
What is your Dx?

Infective endocarditis causing valve ulceration (it’s a prosthetic valve)
Name these lesions and the heart condition that they are associated with.
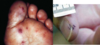
Janeway lesions on the left
Splinter hemorrhages on the right
Associated with infective endocarditis
What is your Dx?

Non-bacterial thrombotic endocarditis (smaller vegitations around the rim of the valve)
Describe the murmur associated with this condition.
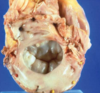
Systolic murmur with a mid-systolic click (mitral prolapse)
Myxomatous degeneration of the mitral valve as seen in the photo are characteristic of what valvular disease?

mitral valve prolapse
What is your Dx? How do you know this?

Fibrocalcific aortic stenosis - you know it isn’t rheumatic heart disease because there is no commisural fusion


