Osteomyelitis Flashcards
1
Q
list the risk factors for osteomyelitis
A
- sexually active
- sickle cell disease
- prosthetic joint replacement
- vertebral involvement
- cat and dog bites
- IV drug abuse
2
Q
osteomyelitis–associated infection if there is no other information available
A
- S. aureus (most common overall)
3
Q
osteomyelitis–associated infection if sexually active
A
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae (rare)
- septic arthritis mor common
4
Q
osteomyelitis–associated infection if have sickle cell disease
A
- Salmonella
- S. aureus
5
Q
osteomyelitis–associated infection with prosthetic joint replacement
A
- S. aureus
- S. epidermidis
6
Q
osteomyelitis–associated infection with vertebral involvement
A
- S. aureus
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- Pott disease
7
Q
osteomyelitis–associated infection with cat and dog bites
A
- Pasteurella multocida
8
Q
osteomyelitis–associated infection with IV drug abuse
A
- Pseudomonas
- Candida
- S. aureus
9
Q
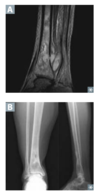
what is the best way to detect acute osteomyelitis, chronic osteomyelitis?
A
- elevated C reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate common, but a nonspecific MRI is best for detecting acute infection and detailing anatomic involvement (A)
- radiographs are insensitive early but can be useful in chronic osteomyelitis (B)