Mechanics of Ewe Obstetrics & Perinatal Conditions Flashcards
What are problems at lambing time
abortion
metabolic disease
dystocia
prolapses
metritis
mastitis
what are common themes of preventing lambing problems
Good Treatment of ewes/lambs
Selecting replacements
Strict culling policy
Good hygiene
Good nutrition
what are the pros of outdoor lambing
Usually more hygienic
Ewes more relaxed
Less mismothering
Less labour (1 shepherd to 600-1000 ewes)
what are the cons of outdoor lambing
Harder to catch ewes and lambs
Predation/crows
Risk of hypothermia
what are the pros to indoor lambing
Easier to handle ewes and lambs
Close monitoring day and night
Nutrition easier to manage
Less reliant on weather
Hypothermia is less common
what are the cons to indoor lambing
Increased risk of infectious disease
Poor ventilation = more pneumonia
Ewes can lie on lambs
More labour (1 sheered to 250-300 ewes)
what is the start of 2nd stage labour
Pass water bag (2nd stage labour)
how do you decide when to intervene
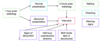
how do you minimize damage to the ewe
Lots of lubrication
Don’t hurry
Gentle manipulation
Avoid excessive traction
what situations can fetal manipulation and manual extraction be used for (4)
- correctable malpresentations/positions/posture
- tangled multiple lambs
- no fetomaternal disproportion (may change when corrected)
- no severe deformities
what situations can fetotomy be used for (2)
often not feasible in sheep
unless rotten lambs falling apart
what situations can caudal epidural, manual extraction be used for (4)
- ewe appears painful
- significant manipulation required
- dead lamb with only slight disproportion
- episiotomy needed
what situations can caesarean section be used for (7)
- no progress with lambing with 15 mins
- fetomaternal disproportion
- large lamb in posterior presentation or ewe with small pelvis
- vaginal prolapse – non reducable/swelling impeding pelvis
- severe deformities of ewe or lamb
- unresponsive ringwomb
- unresponsive uterine torsion
what situations can euthanasia be used for (2)
- dead putrid lamb(s) and sick ewe (can try fluids and meds)
- caesarean section but client not willing
what are causes of dystocia
- abnormal fetal placement
- maternal structural/functional factors
- fetomaternal disproportion
- deformities
what are fetal malpresentations (4)
- anterior
- posterior
- transverse
- verticle
what are fetal positions (3)
- dorsal
- ventral
- left or right lateral
what are postural abnormalities
head and limbs
what are signs of fetomaternal disproportion
- anterior presentation: forelimbs crossed in birth canal, head deviation
- posterior presentation: pelvis doesn’t fit into birth canal
what are maternal functional factors (3)
- uterine interia: lack of energy, lack of calcium, over-stretching of uterus
- uterine torsion: rare in sheep, often don’t see water bag, try rolling to correct
- ringwomb
what are possible causes of ringwomb
Prematurity/abortion
Disturbance in 1st stage labour
Malpresentation
Calcium deficiency
Exogenous estrogens (ex. fungal Fusarium in feed)
Inflammation/scarring from prolapse/historical injuries
Poor initiation of parturition by lamb?
what is ringwomb
cervix less than 5cm dilated 2 hours into 2nd stage labour
how is ringwomb treated
Attempt manual dilation, but risk trauma
Calcium injection
Hormonal (prostaglandin but CARE!)
- Pushing against a closed cervix can cause uterine ruptures
Caesarean section
what are maternal structural issues/deformaties
Pelvis narrow or shallow
Abnormal bony protuberances into canal
Previous damage (ex. pelvic fracture)






