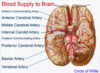
Lesson 12B: Brain Flashcards
(52 cards)
What are the membranes called that cover and protect the CNS?
Meninges
what are the three layers (types) of Meninges?
- Dura Mater: tough outer layer
- Arachnoid Mater: Has space filled with CSF below (ie is the roof to the space filled with CSF); impenetrable to fluid
- Pia Mater: Floor of space filled with CSF; intimate contact with brain cells themselves
The space below the arachnoid mater that is filled with CSF is called the:
Subarachnoid space
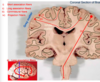
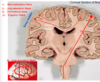
Label the layers of the brain:


Label the brain membranes seen


The arachnoid is an ______ layer
epithelium
The hills of the brain are called ______ (outer cortical tissue)
The spaces between the hills (valleys) are called _______
The hills of the brain are called Gyri (outer cortical tissue)
The spaces between the hills (valleys) are called sulci

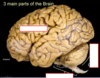
Label the three main parts of the brain:

What are the five main functions of the CEREBRUM?
- Higher cognitive functions
- thought, intellect, planning, creativity
- Language and speech
- Somatic motor function
- regulate skeletal muscle activity
- regulate and coordinate movement (basal ganglia)
- Somatic sensory function
- Interpret stimuli from environment
- Regulates emotional aspects of behaviour
The space separating the left and right hemispheres of the cerebrum is called the:

Longitudinal Fissure
The space between the Frontal Lobe and the Temporal lobe is called the:
Lateral (sylvian) fissure

The space between the Frontal lobe and the parietal lobe is called the:
Central Sulcus
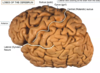
The central sulcus is the ________ (starts every signal to move muscle)
Primary motor cortex
Which lobe is associated with
- thinking, planning, personality
- motor planning
- has primary motor cortex
Frontal Lobe
The Parietal lobe contains what important cortex?
Primary Somatosensory Cortex
Which lobe of the brain is associated with:
- perception of self in space (proprioception)
- Houses the primary somatosensory cortex
Parietal Lobe
Which lobe is associated with vision?
Occipital lobe
Which lobe is associated with Learning and memory and hearing?
Parietal Lobe
The neurons reside in the ______ of the brain
Cerebral Cortex
(grey matter on outside of the brain)
What is the map of the primary motor cortex called?
Motor Homunculus
(the dark yellow border is the grey matter of the cortex)

The brain map of the somatosensory cortex is called:
Somatosensory Homunculus

Precentral gyrus you would find the:
primary motor cortex
Post central gyrus you would find the:
Primary sensory cortex (somatosensory cortex)
White matter is caused by:

White matter is caused by: Myelinated axons (myelinated by oligodendrocytes cns))