Lesson 12: Neuron Flashcards
The CNS is made up of the ____ and the ______
Brain and spinal cord
What are the three parts of the brain?
Cerebrum
Cerebellum
Brainstem
Cell bodies are called ______ when in the CNS and their axons are in ______
Cell bodies are in clusters called nuclei when in the CNS and their axons are in tracts
Cluster of cell bodies are called _____ when in the PNS and their axons are in ______
Cluster of cell bodies are called ganglia when in the PNS and their axons are in nerves
What are the two types of nerves in the PNS?
Cranial: come off the brainstem
Spinal: come off the spinal cord
What are the two divisions of the PNS?
- Somatic
- Autonomic
What are the two divisions of the Somatic division of the PNS?
Motor
Sensory - eg can feel when someone touches you

What are the two divisions of the Autonomic division of the PNS (remember, autonomic = visceral)
Motor
Sensory
The motor component of the autonomic nervous system can be _____ or ______
The motor component of the autonomic nervous system can be sympathetic (fight/flight) or parasympathetic (rest/digest)

All of the organs of your body have a _____ (afferent) component
Sensory
Difference between the somatic and autonomic sensory?
YOu can localize the sensation in somatic (can tell where someone touches you)
No localization in autonomic - can’t name which organ is hurting
Neuronal cell bodies in the peripheral system are called?
Peripheral ganglia
What are neurons?
Nerve cells that conduct signals
Support cells for neurons are called:
Neuroglia
Neurons form connections to other cells via ______
synapses
The functional unit of the brain is the ______
Neuron
What do neurons function to do?

Neurons encode information and conduct it over considerable distances and transmit it to other neurons or various non-neuronal cells

What produces myelination?
The neuroglial cell, Schwann cells
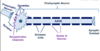
The gaps between schwann cells of the axon are called
Nodes of ranvier
The point of contact of an axon terminal with another cell is the
Synapse
The synapse transmits nerve impulse via ______
neurotransmitters
a neuron can synapse onto:
- other neurons
- muscle
- gland
A typical motor neuron is called a:
Multipolar neuron

Motor neurons cell bodies are found in the _______ forming a ______
Motor neurons cell bodies are found in the spinal cord forming a nucleus
(remember a collection of nerve cell bodies in the CNS is called a nucleus)












