L13- Bone introduction Flashcards
(28 cards)
bone is a type of
connective tissue
how many types of bone in the body
5
name the 5 types of bone in the body
1) long bones 2) short bones 3) flat bones 4) irregular bones 5) sesamoid
long bones
• Longer than wide • Function: support weight of the body and allow movement • e.g. Humerus, small bones in fingers
short bones
• As long as they are wide • Function: short bones provide stability and some movement • e.g. Trapezoid, wrist (carpals) bone, ankle (tarsals)
flat bones
• Flattened, with parallel edges • Function: protects internal organ- large area of attachment for muscle • e.g. Sternum and ribs , cranial bones, pelvis
irregular bones
• Vary in shape and structure (complex shape) • Function: protect internal organs • e.g. Vertebra protect spinal cord • e.g. Pelvis (sacrum) protects organs in the pelvic cavity
sesamoid (sesame like)
• Embedded in tendons • Function: protect tendons from stress and damage from repeated wear and tear • e.g. small round bones found in the tendons of the hands, knees and feet - Patella is a good example- forms postnatally
outer most layer of bone is called the
periosteum
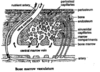
inner portion of the bone called
cancellous or spongy bone
features of cancellous/ spongy bone
- Strong - Light - Filled with bone marrow (trabeculae)
outer portion (external surface) of bone
compact bone
features of compact bone
80% of bone mass - Much more dense than cancellous bone o Fewer spaces
organisation of compact
Compact bone is tightly organised into osteons
osteons
Osteons are formed by layers of lamellae that wrap around each other.
in the centre of the osteon what is found
haversion canal
what is found within haversion canal
blood vessels and lymphatics and nerves
within sheets of lamella (in compact) are tiny channels called
Canaliculi
Canaliculi branch
out from the central/ haversian canal to empty spaces called lacunae.
Lacunae are empty spaces for
Osteocytes- branch through canaliculi to contract other osteocytes via gap junctions.
volkmanns canal
branch horizontally (unlike aversion which branch verticallY)
osteoblasts
make bone
osteoclasts
break down bone and reabsorbed
spaces between trabecular in cancellous bone
contain bone marrow and blood vessels