Heme1b Flashcards
(17 cards)
How old is this patient? Where is the megakaryocyte?

To whom, how old, would this marrow be hypoplastic? What are some causes of hypoplasticity?

This marrow would be hypoplastic to anyone below 40. Causes: toxins, viral infection, fanconia anemia (congenital), myelodysplastic dynrome, paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. EBV, CBV, parvovirus, idiopathic.
What are the large cells? Are they increased in number?

The large cells are megakaryocytes, and they increased in number.
What are the two large cells? What are the small “black” cells. Which cells are more mature?

The two large cells are two megakaryocytes. The dark black could be lymphocytes or darkly nucleated RBCs. As a cell matures, it gets smaller and the Nucleus:Cytoplasm ratio decreases.
How can you tell that you’re in the bone marrow? Which cell is the pro-erythroblast? What is a nurse cell?

Bone marrow = lots of cell types in different stages of development. The pro-erythroblast is the big, dark purple cell with little cytoplasm. Nurse Cells are macs that have Fe that is transferred to surrounding immature RBCs.
What disease does this suggest?

This happens in infection and also chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML).
What do you see here? What is a primary/secondary granule? Why are proerythroblasts blue?
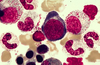
You see lots of band cells here. The red dots are the primary granules, and the clear granules are the secondary. Proerythroblasts are blue from the RNA.
What is this cell. What are the faint circles inside the nucleus? What will this cell become.

This is a myeloblast. The faint circles inside the nucleus are nucleoli with dispersed chromatin. This cell will become a band cell next.
What disease is this? What is the hallmark?

This is acute myelo leukemia. These myeloblasts are all stuck in this early phase of differentiation.
What is the content of the two types of granules?

Primary: myeloperoxidase, acid phosphatase, and esterase enzymes
Secondary: lysozymes, gelatinase, CD35 and Cytochrome B558 (all are anti-microbials)
What is the maturation time for granulopoiesis? How long do mature granulocytes circulate in the peripheral blood?

It takes 1-3 weeks to mature, and they circulate for only hours.
What is RBC:Platelet:WBC?

1000:100:1
How do you describe this smear?
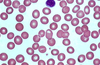
Normocytic, normochromatic, 1/3 central palor.
What type of cell is this? What is in the granules? What are possible causes of increased numbers in circulation?

Basophil.
Granules: histamine, IgE, heparin, IL4.
Allergic reactions and chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) can increase their numbers.
What type of cell is this?
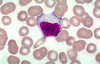
This is an activated LYMPHOCYTE. Can be hard to differentiate bc it looks like a monocyte.
What is this?
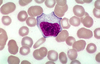
Cytotoxic T Cell.
What are these, and what is their function?

These are eosinophils, and they see them fight parasites. They can also work on drugs and allergies.


