The Ear Flashcards
Divisions of the Ear
External (outer)

Auricle, external auditory meatus, external surface of the tympanic membrane

Divisions of the Ear
MIddle

Internal surface of the tympanic membrane, tympanic cavity, ossicles, pharyngotympanic tube

Divisions of the Ear
Internal (inner)

Auditory apparatus, vestibular apparatus, internal auditory meatus, vestibulococchlear nerve (CN VIII), oval window, round window

Relations of the Ear


External Ear
Auricle

Elastic cartilage
Muscles of facial expression but vestigal in humans
Lymph to parotid and cervical lymph nodes

Auricle Arteries


Auricle Innervation


External Ear
External Auditory Meatus
About 2.5cm long
Lateral third has elastic cartilage, hair follicles, sweat and sebaceous glands
Medial two-thirds is bone lined with stratified squamous epithelium
Blood from branches of external carotid (auricular)
Nerves are mainly auriculo-temporal from CN V3 but also auricular branches from CN VII and CN X
Tympanic Membrane

Roughly 8mm diameter circle
Outer is stratified squamous and inner is mucous membrane
Chorda tympani across medial surface
Malleus attached to inner surface
Lateral surface - auriculotemporal nerve (CN V3) and auricular branch of vagus (CN X)
Medial surface - tympaic branches of glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)

Tympanic Cavity


Internal Ear


Muscles and Neuro-vascular supply to ear


Bones of Middle Ear


Facial Nerve


Chorda Tympani

Crosses medial surface of tympanic membrane and handle of malleus
Leaves tympanic cavity via petrotympanic fissure
Joins lingual nerve
Parasympathetic - sub-lingual and sub-mandibular salivary glands
Special sense of taste for the anterior 2/3 of the tongue

Auditory Tube

Connects nasopharynx with tympanic cavity
Lateral - Bony canal lined with mucosa
Medial - Cartilagenous and membranous tube
Normally closed but lumen opens when tensor veli palatini contract (swallow, yawn etc)
Equalises pressure on both sides of tympanic membrane
Sensory via CN IX

Inner Ear


Ear overview


Labrynths
Bony
Surrounded by otic capsule
Otic capsule very dense bone within petrous temporal bone - not bony labyrinth but surrounds it
System of canals filled with perilymph
Cochlea
Vestibule
Semicircular canals
Labrynths
Membranous
Continuous system of ducts and sacs inside bony labyrinth
Suspended in perilymph but contains endolymph
Perilymph and endolymph conduct sound vibrations and respond to mechanical forces (movement and acceleration)
Cochlea


Cochlea


Semi-Circular Canals
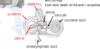
Lie posterior and lateral to vestibule
Each canal 2/3 of a circle
Anterior, posterior and lateral
Anterior posterior sit at right angles with lateral being horizontal
Contain semi-circular ducts (continuous with utricle)
Each duct swells at the end (amupullae)

Ampulla, Utricle and Saccule

Each ampulla houses crista ampullaris which respond to angular movements of head
Vestibule is a bony labyrinth, inside of which are two membranous sacs - the utricle and saccule
These house equilibrium receptors called maculae which respond to the pull of gravity and changes in head positon
Otoliths





