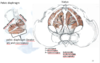
Pelvic Walls and Floor Flashcards
Innominate


Pelvis


Sacrum


Pelvic Boundaries


Pelvic Ligaments
Sciatic Foramen

The sacrotuberous and sacrospinous ligaments for the greater sciatic foramen and lesser sciatic foramen by making the notches in the innominate into proper gaps

Sacroiliac Joints
Joint types

Plain synovial at the front and more fibrous at the back

Wall Muscles - Iliacus
Attachments

Iliac fossa to join psoas as iliopsoas and insert into lesser trochanter of femur

Wall Muscles - Iliacus
Function

Hip flexion

Wall Muscles - Iliacus
Innervation

Femoral nerve

Wall Muscles - Psoas
Attachments

T12-L4 bodies and intervertebral discs (superficial). L1-L5(deep) to join iliacus as iliopsoas -> lesser trochanter of femur

Wall Muscles - Psoas
Function

Hip flexion. Bends trunk laterally (one) and raises trunk from a supine position (two)

Wall Muscles - Psoas
Innervation

Lumbar plexus diect branches L2-4 anterior rami

Wall Muscles - Obturator Externus
Attachements

Outer surface of the obturator membrane to the trochanteric fossa of the femur

Wall Muscles - Obturator Internus
Attachments

Inner surface of obturator membrane to the medial surface of the greater trochanter of the femur

Wall Muscles - Obturator Internus
Function

Lateral rotation of the hip

Wall Muscles - Obturator Internus
Innervation

Nerve to obturator internus direct from sacral plexus (L5,S1)

Wall Muscles - Piriformis
Attachments

Pelic surface of the sacrum to the greater trochanter of the femur

Wall Muscles - Piriformis
Function

Lateral rotation of the hip joint

Wall Muscles - Piriformis
Innervation

Nerve to piriformis direct branch of sacral plexus (S1,S2)

Pelvic Diaphragm
Made up of

Muscular diaphragm with fascial elements supporting - Levator ani and Coccygeus

Coccygeus
Attachments

Ischial spine and sacrospinous ligament to the coccyx and inferior sacrum

Coccygeus
Function

Supports pelvic viscera and can flex coccyx very slightly

Coccygeus
Innervation

Direct branches from sacral plexus (S4,S5)

Levator Ani
Pubococcygeus

Most medial fibres. attaching to and supporting the vagina/prostate gland and rectum.
Usually divided into puborectalis, levator prostate and pubovaginalis