Pelvic Contents Flashcards
Female Peritoneum


Male Peritoneum


Bladder

Partial covering of peritoneum - stuck against pubic bones
Transitional epithelium and rugae
Rises into suprapubic region as it fills
Apex is posterior to the pubic symphysis

Trigone

Triangular base of bladder - internal area of smooth mucous membrane
Urethra exit and ureters enter at trigone
Sphincter vesicae not complete

Prostate and urogenital diaphragm


Bladder Supply
Arteries, veins and nerves

2x superior arteries and inferior vesical from each side - corresponds to vaginal in females
Vesical plexus of veins
ANS inferior hypogastric plexus

Lymphatic Drainage of Bladder
Ureter

Lumbar, common iliac, external iliac, internal iliac nodes as they descend towards bladder

Lymphatic Drainage of Bladder
Urinary bladder

Main drainage to internal iliac nodes (some superior to external iliac and some lymph from neck to sacral nodes)

Lymphatic Drainage of Bladder
Urethra

Main drainage to internal iliac.
Males: Spongy urethra to deep inguinal
Females: Some to sacral nodes

Rectum

Upper 1/3 covered by visceral peritoneum, middle 1/3 by peritoneum on anterior surface and lower 1/3 is infraperitoneal.
3rd sacral vertebra to tip of coccyx

Rectum

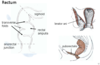
Rectum Supply
Arterial

Superior rectal artery (from inferior mesenteric)
Middle rectal artery (from internal iliac)
Inferior rectal artery (from internal pudendal)

Rectum Supply
Veins

Superior (to portal)
Middle ( to internal iliac)
Inferior (to internal pudendal)

Rectum Supply
Lymph

Pararectal to inferior mesenteric and internal iliac

Rectum Supply
Nerve

Inferior hypogastric plexus

Lymphatic Drainage of Rectum
Superior rectum

Aortic nodes at L3 (inferior mesenteric)

Lymphatic Drainage of Rectum
Inferior rectum

Internal iliac nodes

Lymphatic Drainage of Rectum
Anal canal superior to pectinate line

Internal iliac nodes

Lymphatic Drainage of Rectum
Anal canal inferior to pectinate line

Superficial inguinal nodes

Uterus - Broad Ligament

Big sheet formed in middle and either side of body of uterus. Overy sits on posterior surface.
Carries nerves, vessels and lymphatics mostly

Uterus Features

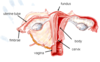
Cervix


Uterine Tube

Isthmus is a small, narrowed area

Uterine Ligaments












