Pharynx and Pre-vertebral Flashcards
Pharynx
Shape
Upper funnel end shaped at base of skull - joins oesophagus at C6
Pharynx
Mucous membrane
Nasal, mouth, larynx, tympanic cavity
Pharynx
Ciliated columnar epithelium
Superiorly to stratified squamous inferiorly
Pharynx
Fibrous layer
Under epithelium - connects to base of skull and into submucous coat of oesophagus
Pharynx
Muscular layer
Under fibrous layer and has almost circular constrictor muscles and longitudinal muscles
Pharynx Divisions


Nasopharynx
Position

Behind nasal cavities, above soft palate

Nasopharynx
Boundaries

Roof - Sphenoid, occipital and pharyngeal tonsil
Floor - Soft palate - pharyngeal isthmus
Anterior - Nasal passages
Posterior - Roof and CI level
Lateral - Auditory/Eustacian tube, salpingopharyngeal fold

Oropharynx
Position

From soft palate to upper border of epiglottis

Oropharynx
Boundaries

Roof - soft palate
Floor - Posterior third of tongue, lingual tonsil and glossoepigottic folds
Anterior - Mouth
Posterior - C2/3 level
Lateral - Palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal folds with palatine tonsil

Palatoglossus, palatine tonsil and palatopharyngeus


Laryngopharynx
Position

Behind larynx and laryngeal opening

Laryngopharynx
Boundaries

Anterior - Larynx
Posterior - C vertebrae 3-6
Lateral - Supported by thyroid cartilage, aryepiglottic fold and thyrohyoid membrane

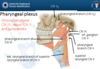
Superior Constrictor
Attachments

Lower part (posterior) medial pterygoid plate, hamulus, pterygomandibular ligament, mandible, side of tongue
To pharyngeal tubercle of occipital bone, fibrous raphe and middle constrictor

Superior Constrictor
Function

Upper fibres pull posterior pharyngeal wall anteriorly to close off nasopharynx
Propel food to middle constrictor.

Superior Constrictor
Innervation

Pharyngeal plexus (vagus)

Middle Constrictor
Attachments

Lower part of the stylohyoid ligament to the greater and lesser cornua of the hyoid bone
To raphe but also blend with superior and inferior constrictor

Middle Constrictor
Function

Propel food towards inferior constrictor

Middle Constrictor
Innervation

Pharyngeal plexus (vagus)

Inferior Constrictor
Attachments

Lamina of thyroid cartilage and cricoid cartilage
To raphe and blend with middle constrictor and oesophagus

Inferior Constrictor
Functon

Propels food to oesophagus

Inferior Constrictor
Innervation

Pharyngeal plexus (vagus)

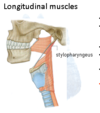
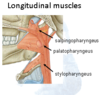
Inferior Constrictor


Longitudinal Muscles - Stylopharyngeus
Attachments

Base of styloid process of temporal bone to posterior border of thyroid cartilage, across the internal carotid artery.
Passes between superior and middle constrictors.