The Brain Flashcards
General Features of the Brain


Features of the brain
Central suclus

Pre-central (motor cortex) and post-central (sensory cortex) either side of sulcus

Features of the brain
Longitudinal fissue

Contains anterior cerebral arteries

Features of the brain
Lateral fissue

Contains middle cerebral artery
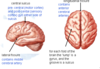
Features of the brain
Lumps and grooves of folds

Each lump is a Gyrus
Each groove is a Sulcus

Cerebral Hemispheres


Median Sagittal Section of the Brain


Corpus Callosum

White matter tract connecting the cerebral hemispheres

Association tracts
Between gyri of the same hemisphere
Commisural tracts/fibres
From one hemisphere to the corresponding region of the other
Projection fibres
From cerebrum to thalamus, brainstem etc
Coronal Section through Brain


Basal Ganglia
Regulate initiation and termination of body movements.
Thought to be involved with memory, planning and emotional response.
Diencephalon
Thalamus

Major sensory relay station
Spinal cord, brainstem, midbrain to the thalamus then to cerebral hemispheres
Involved in motor pathways

Diencephalon
Hypothalamus

Regulation of autonomic nervous system and homeostasis
Produces hormones

Diencephalon
Pineal gland

Epithalamus - Produces melatonin to regulate body clock
Epithalamus also contains habenular nucles for olfaction and emotional response

Midbrain
Connects

Connects pons and medulla to diencephalon

Midbrain
Superior Colliculi

Visiual tracking and scanning
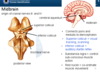
Midbrain
Inferior colliculi

Auditory startle reflex

Midbrain
Substatia niagra

Control sub-conscious muscle action

Midbrain
Red nuclei

Co-ordinate muscle movement

Pons

Pontine Nuclei - Coordinate and maximise voluntary motor output. Tracts which help with breathing.
Origin of Cranial Nerves V, VI, VII, and Vestibular Part of VIII

Medulla

Contains pyramids (motor tracts), cardiovascular centres, breathing centres, nuclei concerned with touch, pressure and vibration.
The olives - proprioception (joint and muscle position)
Origin of Cranial Nerves IX, X, XI, XII, and cochlear part of VIII

Cerebellum
Vermis

Between lobes











































