PROS- RPD Design Flashcards
Contains RPD design & Tooth modification (73 cards)
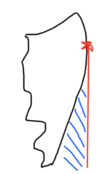
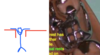
What is the part of the denture that the arrow is pointing to?
This is the denture flange and it is the replacement tissue which extends into the vestibular sulcus
Why can kennedy class IV not have a modification?
As the most posterior saddle defines the classification. Therefore, if the patient had another saddle it would be used for classification & the kennedy class IV would be reffered to as the modification.
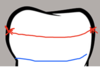
Compare denture support?
Using teeth for support directs the load through the PDL of the abutment teeth.
Using mucosa for support distributes the load over a wide area. This uses the hard palate and saddles.
Which tooth should we pick to provide support
Those teeth with the largest root area.
What is a denture rest?
This is the metal bit attached to the tooth that allows distribution of the load down the abutment teeth.
What are the functions of the rest?
- Preventing movement of the RPD towards the mucosa
- Distributing the occlusal load
- Supporting the placement of clasps
- Preventing the over-erruption of unopposed teeth
- Providing bracing on the anterior teeth
- Determining the axis of rotation for free end saddle RPDs.
What is important when designing an occlusal rest?
The rest should come down to the midline of the tooth. So it is large enough for the force goes down the long axis of the tooth .
It should not be placed on an occlusal contact point (as this would be very uncomfortable for the patient)
What is important for incisal rest design?
An incisal rest should only be used on the lower arch (it is unaesthetic on the upper)
What is an advantage of a cingulum rest?
The cingulum rest applies the stress at a lower level.
This means there is less rotational force, meaning the tooth is less likely to break.
Why is it rare to have a metal rest in an acrylic denture?
The metal rest is encorporated mechanically to the acrylic base which produces a pottential weak point in the denture (leading to denture failure)
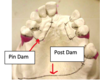
Where do we place rests on a bounded saddle?
On either side of the saddle area
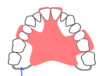
Where do we place rests on a free end saddle?
The opposite side of the tooth to the saddle.
This is to prevent torquing

Why is having a small surface area of mucosal support inadvisable?
As it will place pressure at the gingival margin and acclerate bone resorption causing denture failure.
Why are mucosa only dentures not recommended on the lower arch?
As the mucosal support on the lower arch is limited.
You can only use the buccal shelf.
What is an ‘every’ RPD design?
This is an open designed denture which spreads the load and keeps the gingival margins healthy.
The denture is kept in the mouth by the frictional contacts between the artificial teeth and the abutment teeth.
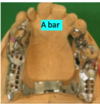
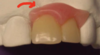
What is the arrow pointing to in this denture and what is the function?
The arrow is pointing to wire stops.
These prevent distal drift of the posterior teeth.
We want to prevent this drift as it would cause the loss of the frictional contacts resulting in the denture falling out.
What is Axial Torque?
When movement of the tooth one way causes the root to move the other. This causes breakdown of the Periodontal ligament.

What can we do if the chosen rest position is an occlusal contact point?
- We can move the rest onto the opposite side of the tooth
- Complete a preparation for the rest (requires drilling into a healthy tooth)
What is retention?
What prevents the denture from being dislodged.
Compare the two types of retention?
Direct retention- prevents vertical displacement of the denture.
Indirect retention- prevents rotational displacement of the denture.
How can we achieve retention?
- Mechanically- using clasps
- Muscular forces (over time lingual and buccal muscles will hold the denture in place)
- Physically- using
Adhesion- saliva on the denture
Cohesion- substances within saliva
- Through frictional contacts.
What are guideplanes
Guideplanes are paralell surfaces that provide frictional contacts.
What are clasps?
A metal arm that contacts the tooth in an undercut in order to prevent the removal of a denture base.
Compare guideplanes to clasps
Guideplanes don’t deform over time giving you long term retention.
Clasps deform.