HEART- cardiovascular diseases Flashcards
(37 cards)
What is hypertension?
Raised blood pressure.
What drugs are a risk factor for hypertension?
Non steroidal/ Corticosteroids and the oral contraceptive pill.
What is essential hypertension?
When we cannot find a cause for the hypertension.
What is renal artery stenosis?
A rarer cause of hypertension where the narrowing of an atery reduces the nutrients reaching the kidney. This makes the kindey smaller.
What is a phaeochromocytoma?
A tumour of the adrenal gland. This affects the hormone adrenaline.
What is Conn’s syndrome?
An increased production of aldosterone that can be due to a tumour of the adrenal gland
What is Cushing’s syndrome?
Excessive cortisol production by the adrenal gland that increases water retention. This causes hypertension.
How can we investigate hypertension?
- A urinalysis - to check the patient’s renal function
- Serum biochemistry- to check the patient’s plasma for electrolytes e.g. sodium. (too much salt absorption will be reflected in the plasma)
What drugs are used to reduce blood pressure?
The go to drugs are:
- Ace inhibitors for young patients or caucasians
- Calcium channel antagonists for older patients or coloured
We could also use
- Thiazide diuretic
- beta blocker
*
Compare the two types of heart arythmias?
Tachy arythmia- when the heart is beating too quickly which reduces coronary artery flow
Brady Arythmia- when the heart beat is too slow.
What are pacemakers used to treat?
Brady arythmias
What is shown in this ECG

This shows Asystole which is a lack of electrical activity (there is a wandering line)
What is shown in this ECG?
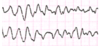
Ventricular fibrillation- where there is electrical activity but the heart isn’t beating.

What is shown in this ECG?

This is atrial fibrillation where there are irregular heart beats. Notice the different lengths between the firings.
Compare the two types of valve failure
Stenosis- When the valve doesn’t open so blood flow is restricted
Incompetence- When the valve doesn’t close (C for close)
What can cause valvular disease?
A congenital abnormality - when the valve doesn’t form properly
A myocardial Infarction- when the papillary muscles are damaged
Rhumatic fever- When an antibody targets the heart muscle.
How can we treat valvular disease?
We can treat valvular disease by replacing the valve with either a mechanical valve or a porcine valve.
Compare mechanical valves to pig valves.
Mechanical valves- These are metal valves and blood will clot to them in the body so the patient will have to take anti-coagulants.
Porcine valves- These are pig valves, they are natural valves so the blood will not stick. But they do not last as long as mechanical valves.
What is a septal defect?
These allow blood to move from one side of the heart to the other.
This increases the workload of the right side of the heart.
What is patent ductus arteriosis?
This is when the opening between the pulmonary artery and the aorta does not close after birth.
What is central cyanosis?
This is a congenital disease where there is more deoxygenated blood in your system. This means there is less oxygenated blood for your system.
What is heart failure?
When the heart’s CO is compromised
What are the main causes of heart failure?
Hypertension
Arythmias
Valvular disease
anaemia
How can heart failure cause a pulmonary edema?
The heart tries to compensate for heart failure by increasing the blood volume
The failing heart cannot cope with the increased fluid levels.
This increases heart failure.
The increased fluid builds up in the lungs.


