Anatomy-Trigeminal Nerve Flashcards
(49 cards)
Name the three divisions of the trigeminal nerve?
Opthalmic
Maxillary
Mandibular
Where does the opthalmic divison of the trigeminal exit the Skull?
Supra-orbital notch
Where does the maxillary division of the trigeminal nerve exit the skull?
Infra-orbital foramen
Where does the mandibular divison of the trigeminal nerve leave the skull?
Mental foramen
Label A, B,C

A- supra-orbital notch
B- infra-orbital foramen
C- Mental foramen

Label these parts of the palate:

A- palatine process of the maxilla
B- Horizontal plate of the palatine bone
C- Incisive Foramen
D- greater palatine foramen
E- Lesser palatine foramen

Label the parts of the mandible
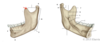
A- condylar process
B- Ramus
C- angle
E- mental foramen
F- Body
G- Head
H- Neck
J- coronoid process
K- mandibular foramen
L- lingula

What passes through the mandibular foramen?
Inferior alveolar nerve.
Where are teeth found in the jaw?
The alveolar process
Where does the trigeminal nerve originate from ?
Special visceral efferent nuclei
General somatic Afferent nuclei
Compare the motor and sensory nuclei of the trigeminal nerve.
There is 1 divison called the motor nucleus
There are 3 sensory divisons:
Mesencephalic nucleus
Chief sensory nucleus
Spinal nucleus.
Label this diagram:

A- motor
B- mesenchephalic
C- chief sensory
D- spinal nucleus.

WHat is the function & location of:
Motor nucleus?
LOCATION: pons
Function: muscles of mastication.
Compare the function and location of the Sensory nuclei?
Mesencephalic - midbrain - Proprioception
Chief sensory - Pons - discriminative touch
Spinal- medulla Oblongata - temperature and pain?
What is the terminal ganglion?
This is what the Sensory and motor nuceli exit the pons to become. This is before the trigeminal nerve divides into 3 divisons.
Where is the terminal ganglion found?
In meckle’s cave.
Explain the connection between the nuclei, the terminal ganglion and the Trigeminal nerve divisions.
the nuclei join together to become the terminal ganglion which then splits to become the divisions of the trigeminal nerve.
Where does CNV1 pass when it seperates from the trigeminal nerve?
Towards the superior orbital fissure.
Where does CNV2 pass when it seperates from the trigeminal nerve?
Through the foramen rotundum.
Where does CNV3 pass when it seperates from the trigeminal nerve?
Through the foramen ovale.
Label this image

A- trigeminal ganglion
B- CNV3 foramen ovale
C-CNV2 foramen rotundum
D- CNV1

Name the branches of the opthalmic division

A- nasociliary
B- lacrimal
C-Frontal
D- supraorbital
E- supratrochlear
F-anterior ethmoidal
G- infratrochlear
H- long ciliary
I- external nasal
Two of the branches of the opthalmic nerve are connected.
Which ones and discuss the connection?
The anterior ethmoidal continues to the tip of the nose as the external nasal nerve.
What is shingles ?
reactivation of the dormant chicken pox virus.



















