Paeds- MIH Flashcards
(11 cards)
What is Molar incisal Hypomineralisation?
Hypomineralisation of the molars and frequently the associated incisors.
Compare hypomineralised to hypoplastic
Hypomineralised- Disturbance of enamel formation resulting in reduced mineral content
(Amelogenesis- secretory stage was fine (tooth is correct shape) mineralisation stage = there are enamel defects )
Can affect bonding.
Hypoplastic- Reduced bulk or thickness of enamel (amorphus tooth)
(Amelogenesis- problem with secretory stage but mineralised correctly)
Should not affect bonding.
Compare the two types of hypoplastic teeth?
True hypoplastic- enamel did not form fully
Acquired hypoplastic- The tooth was hypomineralised but then lost enamel bulk after erruption.
What is the clinical presentation of MIH?
Brown/ white or yellow patches on MOLARS or INCISORS
The patches are demarkated (bumps)
Not symmetrical.
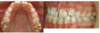
How does MIH affect the tooth?
- More sensitive (more nerve fibres in MIH= more innervation)
- Accumulation of immune cells
- Greater blood flow (trying to fix itself)
- Loss of tooth substance :
- enamel breakdown
- Tooth wear
- secondary caries.
What causes MIH?
It is unknown, but the developmental disturbance occurs within the babies first year of life (when the enamel matrix of the crown of the 1st permanent molar is laid down)
Can be related to nutritional disturbances (starting solid food or formula milk too late.
What questions do you ask a mother who’s child has MIH?
Pre-natal- did the mother have any problems within the 3rd trimester? (Pre-eclampsia/ gestational diabetes)
Natal? - Was the birth traumatic (emergency C section)
Did the baby need to go into an incubator?
Post natal- Has the baby had any diseases? (measles/ chicken pox/ rubella)
was the baby on any medications?
How do we treat MIH molars
- Composite restoration (remember bonding is difficult)
- GIC restoration (releases fluoride which would be good for oral health)
- Stainless steel crowns - if the tooth is too sensitive or lost too much to be restored.
- Extraction- if teeth are very poor, patient is better off without them.
What is important when extracting MIH teeth?
Wait until you can see the calcification of the bifurcation of the 7s before extracting the lower6s.
Wait until the Upper 7s have errupted before extracting the upper 6s- This prevents Crowding.
If you extract the lower 6s, you need to extract the upper 6s.
How do we treat MIH affected incisors
Acid pumice micro-abrasion- to get rid of the yellow or brown marks.
External bleaching- make the rest of the tooth white so colour difference with the white chalky patches isn’t as obvious.
Localised composite placement- put composite over the coloured patches.
Composite veneers (when patient is older)
What are the pain mechanism theories of MIH?
- Dentine hypersensistivty- Porous enamel or exposed dentine facilitates Fluid flow into the Dentinal tubules activated the A delta fibres (Hydrodynamic theory)
- Pulpal inflammation below the MIH Causes sensitisation of the C fibres.
- General sensitisation (Pain goes straight to the brain)


