OPTEC- Amalgam Flashcards
(30 cards)
What is dental amalgam?
A dental material consisting of a mix of:
- powdered metals (silver/tin/copper & more)
- liquid non metal Mercury.
What are the amalgam components and what are their functions?
Powder components:
Silver and tin- form compound (Ag3Sn) that reacts with Hg to produce amalgam. -gamma phase
Copper- increases strength and hardness
Zinc- prevents oxidation of other metals
powdered Hg- to decrease reaction time.
Liquid components:
Mercury reacts with the metals.
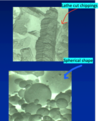
Compare the particle types used in amalgam?
Lathe cut- These are chippings produced by cutting a bar of metal (inglot) with a lathe
Spherical - Produced when droplets of metal are solidifed in an inert atmosphere.
Describe the setting reaction of traditional amalgam?
Ag3Sn reacts with mercury to form amalgam.
This produces the gamma phase:
gamma- provides good strength and corrosion resistance
gamma 1- provides good corrosion resistance.
gamma 2- makes amalagam weaker especially at the margins

Compare the two types of amalgam?
We have traditional amalgam - which produces gamma 2 in the setting reaction.
Copper enriched amalgam- This does not produce gamma 2 and has extra copper to improve amalgam setting.
Compare the two types of copper enriched alloy?
We have the dispersion modified amalgam which has two reactions before it sets.
Single composition amalgam which sets after one reaction
Why is zinc not included in some amalgam?
As zinc reacts with blood or saliva to produce H2 within the amalgam restoration.
This causes a build up of pressure.
& the restoration to expand downwards (pulpal pain) or Upwards (pushing up the restoration)
Discuss the properties of amalgam?
Compressive strength is not great initially but improves
It has a high abrasion resistance (this is good for posterior teeth but not deciduous teeth)
Creep occurs (the amalgam does not maintain good contact with the surrounding tissue) this causes ditched margins.
Biocompatability concerns of amlagam being toxic
Thermal expansion of x3 of tooth tissue. (Bad)
High thermal conductivity (bad)
Retention is mechanical
Amalgam shrinks when it sets.
Why is the gamma 2 removed in Copper enriched amalgam?
Gamma 2 phase is most likley to corrode. It weakens the amlagam material particularly at the margins.
What are some advantages of amalgam?
- It is durable
- It has good bulk strength and wear resistance.
- Has a shorter placement time
- Long term resistance to surface corrosion
- Cheap
What are the disadvantages of amalgam?
- Poor aesthetic qualities
- Does not bond easily to the dentinal surface
- Preparation of the retentive cavity requires damage to sound tissue.
- Galvanic response - acts like a battery in the mouth with other fillings
- marginal breakdown is common.
What is shown in this image?
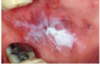
This is a lichenoid lesion which is a type 4 hypersensitivity reaction to the amalgam restoration in the mouth.
How do we treat a lichenoid lesion?
Replace the amalgam restoration with a composite one.
What is shown in this image?

This is tooth discolouring as a result of the corrosion products migrating into the porous material of the tooth.
What is shown in this image?

This is an amalgam tattoo,
When the fine amalgam particles migrate into the soft tissue.
Do not assume, it could be cancerous and nothing to do with the amalgam. case by case.
How do we design our amalgam cavity to prevent distortion or fracture?
- We have a cavity floor at 90° to the axial wall.
- a depth of 1.5mm to 2mm
Compare a self retentive box preparation to a proximo-occlusal preparation?
Self- retentive box preparation removes less tissue & places less amalgam.
A proximo-occlusal preparation destroys tooth tissue for retention.

What other ways are there of acheiving retention in an amalgam restoration?
- Adding grooves or dimples to the cavity design
- The placement of a pin in dentine around which amalgam is packed.
- Bonding amalgam into the booth.
What are the problems with a pin?
- Pins cause stress around the tooth.
- Dentine could crack
- The Pin conducts heat which can make the tooth more sensitive.
- If the filling leaks, we will not know as the pin will prevent the filling from falling out. (allowing secondary caries to develop)
What are the functions of the matrix?
Function of the matrix is:
- Allows close adaption at the cervical margin
- Allows good contact at the marginal ridge
- Allows adequate condensation of the amalgam.
- confines the amalgam to the cavity prep.
- Allows creation of the proximal form.
What are the functions of the wedge?
- Seperate the teeth
- prevent excess amalgam at the gingiva
- hold the matrix band in place
- Aid the contour of the proximal wall.
What is condensation?
How we adapt amalgam to the cavity walls.
This gets rid of excess mercury, bringing it to the surface so it can be scraped off.
What happens if we have inadequate condensation?
Inadequate condensation causes:
- lack of adaptation to the cavity- the spaces around the edges allow plaque build-up)
- poor bonding between amalgam increments.
- inferior mechanical properties as the amalgam is full of holes.
Why do we carve the amalgam restoration?
- In order to reproduce the occlusal anatomy
- To remove the amalgam at the surface which is the weakest amalgam.


