Dental disease- Periodontal disease Flashcards
(35 cards)
What do we expect to see in healthy gingvia?
Colour: pink
Texture: stipling
Margins: defined (knife edge and scalloped)

What is gingival crevicular fluid?
This is liquid that contains antibodies and so is used for host defence.
What do you see in the mouth of a patient with gingivitis?
Colour: red
Texture: no stipling
Margins: inflamed.
Plaque score: high
Bleeding score: high

Compare the immune response occuring in a healthy mouth compared to one that is suffering from gingivitis?
Healthy mouth:
- some gingival crevicular fluid
- Phagocytes/ Lymphocytes and complement.
Gingivitis:
- Increased flow of gingival crevicular fluid
- Increased lymphocytes and monocytes.
- Influx of neutrophils.
Why do the gingiva bleed on probing?
Because the Epithelium becomes uclerated
Why does cleaning teeth reverse gingivitis?
It removes the microbial challenge.
Compare gingivitis and periodontitis (definitions)
Gingivitis is inflamation of the soft tissues.
Periodontitis is inflamation of the soft and hard tissues.
At first sight- How does a patient presenting with periodontitis differ to a patient with gingivitis?
At first glance, they don’t.
You need to probe in order to see the difference.
On probing a patient with periodontitis will have pockets.
Compare true and false pockets
True pockets are when the pockets are due to LOSS of attachment and migration of the junctional epithelium.
False pockets are due to inflamation of the tissues.
Discuss the loss of attachment in a dental patient?
The rate of loss of attachment can be unpredictable so we have to monitor it.
What is the biofilm?
A layer of micro-organsisms found on the teeth- They interact in symbiosis.
Describe the biofilm in a patient suffering from periodontitis?
It is dysbiotic = unbalanced. Causing the inflammation
Discuss the mechansims that contribute to the mouth’s host immune response
Saliva- the immune response that protects the teeth (made of antiboides and enzymes e.g. S-Iga/ lyzozyme)
Gingival Crevicular fluid (will bathe the area)
Inflammatory and Immune response (neutrophils)
Epithelium (as a physical barrier which sheds cells and produces inflammatory mediators. The gingival tissues allow neutrophils to transvere through)
What determines bone resorption?
The inflamatory Mediators produced.
How do antibodies protect the immune system?
activating complement
marking bacteria (opzonisation) for phagocytosis
inhibiting adhesion and invasion
Neutralising toxins.
What are MMPs?
Matrix metalloproteinases which are enzymes that cause matrix degradation in periodontitis.
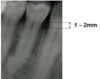
What is the normal level of bone?
1-2mm below the ADJ
Name and compare the different patterns of bone loss
Vertical bone loss- This occurs in thicker bone as the diameter will not reach the full bone.
Bone depth differs on either side
Horizontal bone loss- This occurs in thinner bone as the 2mm diameter of tissue destruction damages all of the bone.
Bone depth is the same.
Furcation bone loss- when bone is lost and the furcation regions are exposed.
Which type of bone loss has a greater chance at re-generation and why?
Vertical bone loss as there is a wall of bone where you can pack re-generative materials.

Why is smoking a risk factor of periodontal disease?
Smoking affects your immune system. This affects your immune response. So when the bacteria change, the patient is more likely to get Periodontal disease.
Smoking also makes the treatment less succesful
What are the local risk factors of periodontal disease?
- Anatomical :Enamel pearls, grooves, furcations, gingival recession.
- Tooth position- malalignment/ tooth crowding/ tiping/ migration and occlusal forces.
Iatrogenic- overhangs/ orthodontic appliances/defective margins and poorly designed RPDs.
What do you see in the mouth of a patient with periodontitis?
Bleeding = on probing
Radiographic bone loss (mobility of teeth)
Gingival recession
Probing depth of >4mm
Splaying of teeth.
What instrument do we use to measure peridontal pockets?
WHO CPITN BPE probe

What triggers Periodontal disease?
- Plaque and calculus accumulation
- Biofilm components
- Expression of Virulence factors


