Prenatal Diagnosis Screening Flashcards
What is the purpose of prenatal screening?
To identify fetuses affected with certain abnormalties so that the parents can make the most informed decision about how to proceed with the pregnancy.

What are some factors that clinicians can use to identify individuals who may be in need to prenatal screening?

Why is prenatal screening and diagnosis so important?
- What is the average risk for a couple with no risk factors?
- What is the burden of chromosomal aneuploidy?

What are the two approaches a clinician can take when talking about ways to check for prenatal genetic disorders?
Screening
Diagnostic



- What is CVS?
- When is it done?
- What are the risks?
- Chorionic villus sampling - transabdominal or transvaginal probe used to obtain samples of chorionic villi which are used for rapid chromosomal diagnosis within 5-7 days
- Done at weeks 10+
- Miscarriage (1/500, largely operator dependent), maternal infection, birth defects
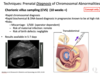
- What is amniocentesis?
- When is it done?
- What are the risks?
- Probe used to obtain sample of amniotic fluid for chromosomal diagnosis, cells must be cultured so it’s a little slower, 10-14 days lead tiem
- 15+ weeks
- Miscarriage, maternal infection, birth defects
Once a CVS or amniocentesis has been done, what is a newer test that is being used to evaluate the chromosomes obtained from these techniques?
Chromosomal microarray –> used to do karyotype, but that only tells you macroscopic changes, CMA has higher resolution, is automated and faster, uses DNA so eliminates need for cultured cells
Review how CMA is done.
Plate wells represent segments of one single chromosome. DNA from a healthy donor is affixed to the bottom of the well so it is known what segment of the chromosome is in each well. This DNA is radiolabeled red. Patient DNA is added and radiolabeled green. If the patient DNA has duplications in any segment, signal will read green. If patient DNA has deletions, signal will read red. If patient DNA is normal, signal will read yellow.

What does CMA detect?
- Compared to karyotype?
- In addition to karyotype?

If women don’t want to undergo invasive diagnostic tests, what is a new emerging screening tool they can use that is non invasive and no risk to the fetus but still has good sensitivity?
Cell Free DNA testing

What is cell free DNA testing?
- Where is the DNA derived from?
- When is it detectable?
- What is its half life?

True/false:
- Cell free DNA sequences only the DNA of the fetus.
- It determines chromosomal origins of millions of fragments and quantifies amounts of DNA.
- False - does not differentiate between mother and fetus DNA, sequences all DNA
- True

True/false: cfDNA is only helpful in screening for down syndrome.
False - useful in screening for other trisomies as well

True/false: cfDNA is not diagnostic.
True - it’s screening test
Despite being a good screening tool, cfDNA is subject to some false positive rates. Why?


Why is it important to screen for neural tube defects?
What are the available management options?

True/false: most women who have a child with an NTD have a family history of NTD.
False - 95% have no previously affected child or family history of NTD –> multifactorial etiology
What are 2 ways that you can screen for open NTDs during pregnancy?
- Serum AFP
- Done 15 - 20 weeks gestation
- Ultrasound
- Late first trimester to check for anencephaly
- 17 - 22 weeks to look for spina bifida
What is serum alpha-fetoprotein?
Where is it produced in 1st trimester?
Where is it produced in 2nd trimester?
What are its levels after birth?
When are increased levels seen in non-pregnant women, men and children?

When is the window for screening for AFP in maternal serum?
15 - 22 weeks
What is the purpose of recessive gene carrier screening of prospective parents?
When are the 2 times that this type of screening should be done?

Recessive Gene carrier screening
- Targeted at […] disorders that manifest primarily in […]
- Does not test for […]
- Allows high risk couples to have […]
- Appropriate for women who would consider […]

Why is it important to offer carrier testing?

What is the role of counseling in prenatal screening and diagnosis?



