Anterior abdominal wall and peritoneum Flashcards




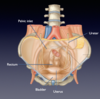
From superficial to deep, what structures are in the:
- Upper right abdominal quadrant
- Upper left abdominal quadrant
- Lower right abdominal quadrant
- Lower left abdominal quadrant
- S: liver, body/antrum of stomach, half of transverse colon, some of small intestine; D: Gallbladder, duodenum, part of pancreas
- S: Fundus and body of stomach, half transverse colon, part of small intestine; D: pancreas, spleen
- S: Small intestine; D: Ascending colon
- S: small intestine; D: descending colon
Which quadrant would you palate if concerned about appendicitis?
Lower right
Where are the kidneys located with respect to costal margin and upper quadrants?

The abdominal aorta bifurfaces at level of […]
Umbilicus




For each structure:
- Name
- Action
- Innervation


For each structure:
- Name
- Action
- Innervation


For each structure:
- Name
- Action
- Innervation


For each structure:
- Name
- Action
- Innervation






Where is the arcuate line?
Halfway between umbilicus and pubic bone




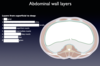
For each structure:
- What is the name
- What is it a branch of
- Where does it travel in abdomen


What vessel assists in providing blood to the anterior abdominal if a patient has had a CABG (coronary artery bypass graft) surgery?
Inferior epigastric




Inferior to the arcuate line, the anterior rectus sheath is made up which tissue layers?
EO aponeurosis + IO aponeurosis + transversus abdominis aponeurosis
Inferior to the arcuate line, the posterior rectus abdomins sheath is […]
Non existant - only the transversalis fascia is posterior to the RA inferior to arcuate line
Superior to arcuate line, the anterior rectus sheath is composed of what structures?
EO aponeurosis + anterior 1/2 of IO aponeurosis
Superior to arcuate line, the posterior rectus sheath is composed of what structures?
posterior 1/2 of IO aponeurosis + transversus abdominis aponeurosis
For each structure:
- What is the name
- What is contained in the fold


The medial umbilical fold contains the obliterated remains of what structure?
Umbilical artery
The median fold contains the obliterated remains of what structure?
Urachus
The lateral fold contains what structure?
Epigastric vessels


What provides the innervation to the skin of the anterior abdominal wall?
Ventral rami spinal nerves T7-T12


What is diastasis recti?

Label image. Also, what is the peritoneum?




What’s the difference between an intraperitoneal organ, primary retroperitoneal organ, and secondary retroperitoneal organ?
Intraperitoneal = organ that developed by growing into the peritoneum. As such, can be freely moved around in body during dissection/surgery.
Primary retro = developed behind peritoneum, cannot be moved around
Secondary retro = developed behind peritoneum but got pushed into peritoneum during development, in between level of movement from other 2
Label image.
Also, what is the mesentery?

Double fold of visceral peritoneum that attaches small bowel to abdominal wall

What is the greater omentum?
What does it connect?
- Double fold of double-layered peritoneum forming a 4-layered apron over the intestines
- Connects from stomach to transverse colon
What is the lesser omentum?
What does it connect?
- Double fold of peritoneum
- Connects liver to stomach; two parts: hepatogastric ligament + hepatoduodenal ligament


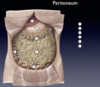

What is the predominant structure shown in this image?

Greater omentum


True/false: The entire small intestine is intraperitoneal.
False
True/false: the pancreas is intraperitoneal.
False - retro
True/false: the spleen is intraperitoneal.
True
True/false: the gallbladder is retroperitoneal
False - intraperitoneal
True/false: the liver is retroperitoneal.
False - intra


What is ascites?

Why can the peritoneal cavity be used in treatment of hydrocephaly?

What is peritonitis?
Innervation here is important

Which organs are retroperitoneal?

Within the abdomen, which organs are intraperitoneal?
- Stomach
- Small intestines (jejunum, ileum, some of duodenum)
- Spleen
- Liver
- Gallbladder
- Cecum
- Appendix
- Large intestine (transverse and sigmoid colons)


