Adrenal Medulla and Catecholamines Flashcards
What are some things that will trigger the hypothalamus to stimulate sympathetic neurons to act on the adrenal medulla to release epinephrine and norepinephrine?
Stress
Physical activity
Low blood glucose
The adrenal medulla is like a […]
Sympathetic ganglion
Preganglionic sympathetic nerves synapse on the adrenal medulla and release […] which binds to […] receptors on chromaffin cells casuing them to secrete […] or […] into the blood stream.
Ach
Nicotinic
Epi
NEpi
True/false: most of the chromaffin cells in the adrenal medulla secrete epinephrine.
True - 80% release Epi and 20% release NE
What are the embryological origins of the adrenal medulla and sympathetic ganglia?
Both derived from neural crest cells. During development, some of these neural crest cells commit to becoming sympathoadrenal lineage cells. Due to many transcription factors, some become sympathetic chain ganglia, others become adrenal medulla cells.

Discuss the short term and long term bodily responses to stress and how the adrenal gland is involved in these responses.

All pre-ganglionic neurons of the autonomic NS release […] onto […] receptors on post-ganglionic neurons.
Ach
Nicotinic
PSNS pre-ganglionic neuron releases […] onto […] receptor on post-ganglionic neuron. Post-ganglionic neuron releases […] onto […] receptor on target tissue.
Ach
Nicotinic
Ach
Muscarinic
SNS pre-ganglionic neuron releases […] onto […] receptor on post-ganglionic neuron. Post-ganglionic neuron releases […] onto […] receptor on target tissue. This is true for all tissues except […] and […] which instead have post-ganglionic neurons that release […] onto […] receptor.
Ach
Nicotinic
NE
Alpha and beta adrenergic
Sweat glands –> Ach onto muscarinic
Renal vascular smooth muscle –> dopamine onto D1 receptors
Review the synthesis of NE.
Tyrosine is brought into neuron terminal –> converted to LDOPA by tyrosine hydroxylase –> converted to dopamine –> dopamine loaded into vesicles by VMAT –> inside vesicle it is converted to NE –> NE released
- Bind to a1, b1, or b2 receptors on target tissue
- Bind to a2 autoreceptor that binds and inhibits NE synthesis
- Be reuptaken into neuron by NE transporter and oxidized by MAO or put back into vesicles
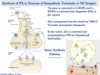
Describe the synthesis of Epi in chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla.
Tyrosine –> LDOPA – (tyrosine hydroxylase) –> Dopamine –> VMAT moves dopamine from cytosol into chromaffin granule –> DA – (dopamine beta hydroxylase) –> NE
- In chromaffin cells that make NE, the NE is put into a storage complex for storage until it needs to be released
- In chromaffin cells that make Epi, the NE is pumped back out into cytosol via VMAT where NE – (PMNT) –> Epi and Epi is pumped back into graunle via VMAT again and then put into storage complex

What are some of the ways that glucocorticoids and catacholamines work together to generate common effects?
Both mobilize fuel stores during stress
Both increase glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis and lipolysis
Complete the table.


Alpha 1 and beta 2 receptors bind […] with greater potency.
Alpha 2 receptors bind […] with greater potency
Epi
NE

Binding of Epi or NE to beta 1 receptor has what effect on heart?
Increased force and rate of contraction
Binding of NE and Epi to alpha 1 receptors on vascular smooth muscle causes […]
Vasoconstriction
Binding of Epi to Beta receptors in skeletal muscle and liver causes […]
If the sympathetic NS releases NE directly onto target tissues that need to be stimulated, why do we need an adrenal medulla to put NE and Epi into bloodstream?
Epi helps the SNS signaling function more efficiently and is helpful for reduction of orthostatic hypotension

- True/false: the adrenal medulla responds by secreting equal amounts of Epi and NE in response to challenges to homeostasis.
- True/false: the sympathetic and adrenal medulla response to the same stimulus are not always equivalent in magnitude.
- False
- True

- Epi and NE are metabolized by […] and […] enzymes in the […], […], and […].
- The breakdown product of NE is […] and the breakdown product of Epi is […].
- These breakdown products are converted to […] which is excreted by the […] and […].
- MAO; COMT; Liver, kidney, adrenal medulla
- Normetanephrine; metanephrine
- VMA; liver and kidney
Assays to check for circulating levels of NE and Epi tend to actually measure what?
Levels of their first breakdown product –> Normetanephrine and metanephrine
True/false: chromaffin cells only secrete Epi and NE.
False

How can the immune system affect the adrenal medulla?
Cytokines can cause chromaffin cells to release neuropeptides –> which then go to stimulate immune tissues

What is pheochromocytoma?

How can diabetes impact adrenal medulla?



