Pain and Management Flashcards
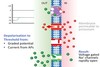
xwhat is the definition of Nociception
Nociception: the activation of neural pathways by stimuli that damage or threaten to damage tissues
what is the definition of Noxious Stimulus:
Noxious Stimulus: potentially damaging stimulus.
what is a Nociceptive stimulus:
Nociceptive stimulus: a stimulus that activates nociceptive pathways
what is the sensation for nociception
pain
what is the sensation for thermoreception
hot and cold
what is the sensation for mechanoreception
touch
what is the sensation for proprioception
position sense
what is the sensation for gustation
taste
what is the sensation for olfaction
smell
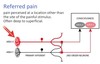
when you have pain radiated in healthy areas of the body. what is this called
referred pain
give an example when some pains, may not be painful
tumours
being born with a condition which, allows you to feel no pain can be dangerous. what is the name of this condition
congenital insensitivity
what is dentoalveolar pain
pain of the tooth and its surroundings
what is dentine sensitivity
when there is an increase sensitivity stimulus to the dentine, this is a result of erosion of the enamel.
what is reversible pulpitis
: occurs when there is inflammation of the pulp, however this inflammation can be reversed.

what is irreversible pulpitis
occurs when inflammation to the pulp causes vessel and nerve damage beyond repair.
what is periapical periodontitis
is an acute or chronic inflammatory lesion around the apex of a tooth root which is usually caused by bacterial invasion of the pulp of the tooth.

what is acute pericoronitis
is inflammation of the tissue surrounding a third molar. The condition most often occurs in molars that are partially impacted, or not fully visible. Most people with pericoronitis have a flap of gum tissue partially covering the crown of the erupting tooth.

what is a dry socket
: occurs when you have had a permanent tooth extracted and a blood clot fails to develop at the site of extraction. Or it dislodges or dissolves before the wound has healed. Causing allot of pain.

what is maxillary sinusitis
is the inflammation of the maxillary sinuses. The symptoms are usually a headache.

how are blocked salivary glands formed

salivary stones as a result of crystallized saliva block saliva ducts and direct the flow saliva back to the gland, causing it swell, resulting in pain.
which receptor is a a sense organ or cell that responds to mechanical stimuli such as touch or sound
mechanoreceptor

which receptor is a a sensory receptor for painful stimuli
nociceptors

where does perception of the stimuli occur
cerebral cortex